标签:文件名 lan 特殊字符 框架 encoding schema res 规范 let
1、描述数据
2、作为配置文件存在
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
中间不要加空格,后面加?号
当我们写好的一个xml文件写入内存的时候会转换为二进制保存,这个时候会查码表,记事本保存的时候是gbk,而保存的时候默认查码表时用的是utf-8,
根节点 Root节点
元素节点 Element节点
属性节点 Attribute节点
文本节点 Text节点
注释节点 Comment节点
CDATA节点。
文档节点: document节点

案例一:(自定义一个xml文档)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <root> <!-- 有且仅有一个根节点 --> <student id="stu_1"> <name>张三</name> <age>15</age> </student> <student id="stu_2"> <name>李四</name> <age>25</age> </student> <student id="stu_3"> <name>王五</name> <age>35</age> </student> </root>
结果:

XML Schema 是基于 XML 的 DTD 替代者。
XML Schema 可描述 XML 文档的结构。
XML Schema 语言也可作为 XSD(XML Schema Definition)来引用。
XML Schema 的作用是定义 XML 文档的合法构建模块,类似 DTD。
案例:建立一个xsd规则文件,并在xml文档中引入,起约束作用。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/student" xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/student" elementFormDefault="qualified"> <!-- xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" 字段表示引用w3c --> <xsd:element name="root" > <!-- 创建xml文档的根节点 --> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="student" maxOccurs="5"> <!-- 创建student节点,且这个节点在xml文档中最多出现5次 --> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string"></xsd:element> <xsd:element name="age" type="xsd:int"></xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:string"></xsd:attribute> <!-- 属性 的定义一定要放在最后面定义--> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema>
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"此字段表示该schema文件中使用的元素和数据类型来自于http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema这个名称空间
,同样指出来自于"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"名称空间的元素和数据类型必须使用带"xsd: "前缀,一般在这里我们可以省略前缀。
其URI应该是targetNamespace的属性值。例如在a.xml中要用到student.xsd定义的扩展数据类型,必须引用xmlns="http://www.example.org/student"。
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/student" 此字段表示该schema文件中使用的元素和数据类型来自于“http://www.example.org/student”这个命名空间,而这个命名空间就是该student.xsd
文件(targetNamespace定义的),也就是引入本文件。前缀为“tns”
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <root xmlns="http://www.example.org/student" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example.org/student student.xsd "> <student> <name>张三</name> <age>15</age> </student> </root>
xmlns="http://www.example.org/student" 此字段表示引入命名空间为“http://www.example.org/student”的类型和元素,
xmlns:xsi是指web.xml遵守xml规范
xsi:schemaLocation是指具体用到的schema资源 ,格式为:“需引入的命名空间 文件名 ” //注意空格,文件名后也要有一个空格,文件名和明明空间也要有一个空格。
结果:
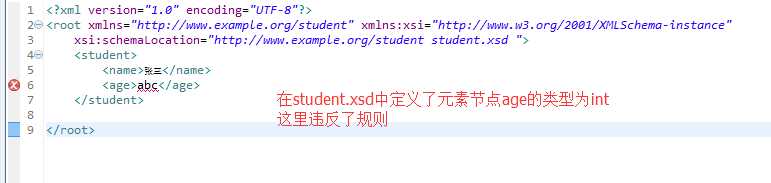
案例二:
student.xsd:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/student" xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/student" elementFormDefault="qualified"> <!-- xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" 字段表示引用w3c --> <xsd:element name="other" ></xsd:element> <xsd:element name="root" > <!-- 创建xml文档的根节点 --> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence > <xsd:element name="student" maxOccurs="5" > <!-- 创建student节点,且这个节点在xml文档中最多出现5次 --> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string"></xsd:element> <xsd:element name="age" > <xsd:simpleType> <!-- 设置元素节点的值为10~50之间,且为整型 --> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:integer"> <xsd:maxInclusive value="50"></xsd:maxInclusive> <xsd:minInclusive value="10"></xsd:minInclusive> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="sex" type="tns:sex"></xsd:element> <!-- 引用本文件自定义的类型,用用tns前缀 --> <xsd:element name="content" type="xsd:string"></xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> <xsd:attribute name="id" type="xsd:string" ></xsd:attribute> <!-- 属性 的定义一定要放在最后面定义--> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <xsd:simpleType name="sex"> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:enumeration value="男"></xsd:enumeration> <xsd:enumeration value="女"></xsd:enumeration> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:schema>
jdbc.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/jdbc" xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/jdbc" elementFormDefault="qualified"> <element name="jdbcInfo"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="jdbcDriver" type="string"></element> <element name="url" type="string"></element> <element name="user" type="string"></element> <element name="password" type="string"></element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema>
b.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <other xmlns="http://www.example.org/student" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xmlns:jdbc="http://www.example.org/jdbc" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example.org/student student.xsd 5 http://www.example.org/jdbc jdbc.xsd "> 6 <student> 7 <name>张三</name> 8 <age>25</age> 9 <sex>男</sex> 10 <content> 11 张三备注<![CDATA[</hello>]]></content> 12 13 </student> 14 <jdbc:jdbcInfo> 15 <jdbc:jdbcDriver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</jdbc:jdbcDriver> 16 <jdbc:url>jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test</jdbc:url> 17 <jdbc:user>root</jdbc:user> 18 <jdbc:password></jdbc:password> 19 </jdbc:jdbcInfo> 20 </other>
特殊字符 替代符号
& &
< <
> >
" "
‘ &apos
JDK:
DOM
SAX
JAXB java and xml Binding
开源(一般都是用开源的)
JDOM
DOM4J:hibernate框架就是使用dom4j来解析映射文件。
X-Stream:java跟XML之间转换的工具(java转成xml文件/字符串,
xml文件/字符串转为java对象)
DOM/JDom:将XML文件中的内容一次性的读取到内存中。读取数据量比较少的数据有优势。
SAX: 基于事件的驱动。读取数据量比较大的XML文件。
标签:文件名 lan 特殊字符 框架 encoding schema res 规范 let
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shyroke/p/6803246.html