标签:排名 strong 个数 import extends 适用于 取整 list hit
符号表是一种存储键值对的数据结构并且支持两种操作:将新的键值对插入符号表中(insert);根据给定的键值查找对应的值(search)。

几个设计决策:
在设计方法时没有指定处理对象,而是使用了泛型。
并且将键(Key)和值(Value)区分开来。
规则:
每个值(Value)都只对应一个键(Key)(即不允许存在重复的键)。
当用例代码向表中存入的键值对和表中的已有的键(以及关联的值)冲突时,新的值替代旧的值。
键不能为空,否则会抛出空指针异常。
同样规定值不能为Null,因为API中get函数,如果键不存在会返回null,如果在表中的值可以为null的话,就会产生混淆。
这个规定产生两个结果:
可以用get()方法是否返回null来判断给定的key是否存在表中。
可以用put(key, null)来实现删除。
可以由其他函数来实现,如:
//shorthand methods public boolean contains(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function contains"); return get(key) != null; } //shorthand methods public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; }
对象的equals方法。
最好用不可变的数据类型作为键,否则表的一致性是不可保证的。
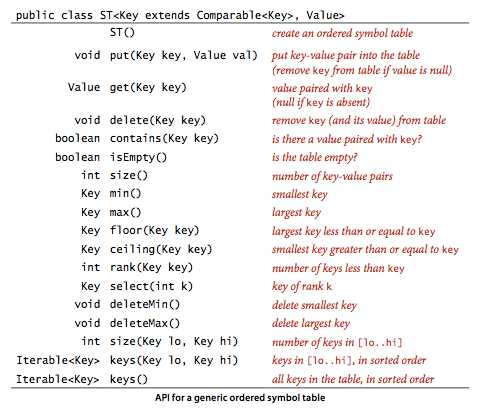
对于实现了Comparable的键,符号表可利用这一特性来保持键的有序性。
这就大大拓展了API,根据键的相对位置定义更多使用的操作。这种表就叫有序符号表。
只要符号表出现了泛型变量Key extends Comparable<Key>,那么这个符号表就实现了有序性。
在有序符号表中有获取最大(最小)键操作和删除最大(最小)键操作。
之前的Priority Queue也有类似的操作,主要区别在优先队列中可以存在重复的键而符号表不行。
向下取整:floor, find the largest key that is less than or equal to the given key.
向上取整:ceiling, find the smallest key that is greater than or equal to the given key.
rank(key), 小于key的键的个数。
select(k), 返回第k大的键,即符号表中有k个键小于返回的键(k的取值范围为0到st.size)。
i == rank(select(i)),key = select(rank(key))
上述两个等式可以更好的理解这两个操作。
对于给定的范围有多少个键在这个范围,或者哪些键在这些范围?
public int size(Key lo, Key hi)
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi)
这两个函数实现了上述操作。
当方法需要返回一个键,但符号表没有符合的键时,抛出一个异常。
或者返回null。
可以由其他函数来实现,如:
//shorthand methods public void deleteMin() { if(isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("underflow error"); delete(min()); } //shorthand methods public void deleteMax() { if(isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("underflow error"); delete(max()); } //shorthand methods public int size(Key lo, Key hi) { if (lo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to size() is null"); if (hi == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("second argument to size() is null"); if(hi.compareTo(lo) < 0) return 0; else if(contains(hi)) return rank(hi) - rank(lo) + 1; else return rank(hi) - rank(lo); } //shorthand methods public Iterable<Key> keys() { if(isEmpty()) return new LinkedList<>(); return keys(min(), max()); }
任何一个Comparable类型的两个值a和b都要保证(a.compareTo(b) == 0)和a.equals(b)的返回值相等。
为了避免二义性,在有序符号表中只使用compareTo()方法来比较两个键,即a.compareTo(b) == 0来表示a和b是否相等。
无论是用a.compareTo(b) == 0还是用a.equals(b),都用比较来表示一个符号表条目和一个被查找的键的比较操作。
如果比较操作不在内循环,则统计数组的访问次数。
两个用例:一个用来跟踪在小规模输入下的行为测试用例,一个用来寻找更高效实现的性能测试用例。
public static void main(String[] args) { ST<String, Integer> st = new ST<String, Integer>(); for(int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) { String key = StdIn.readString(); if(key.equals("-")) { key = StdIn.readString(); st.delete(key); StdOut.println("delete " + key); } else { st.put(key, i); StdOut.println("put" + " " + key + " " + i); } StdOut.print(st.size() + " key-value pairs:"); for(String s : st.keys()) StdOut.print(" " + s + " " + st.get(s)); StdOut.println(); } }
跟课本的有所不同,加上了delete操作,更好的观测行为。
public static void main(String[] args) { int minlen = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); SequentialSearchST<String, Integer> st = new SequentialSearchST<>(); //build symbol table and count frequencies while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String word = StdIn.readString(); if(word.length() < minlen) continue;//ignore short keys Integer freq = st.get(word); if(freq == null) st.put(word, 1); else st.put(word, freq + 1); } //find a key with the highest frequency count String max = ""; st.put(max, 0); for(String word : st.keys()) if(st.get(word) > st.get(max)) max = word; StdOut.println(max + " " + st.get(max)); }
这个是对课本的用例进行改进后的,消除对contains的调用。
本章一直用这个用例来进行性能测试。用例特点:
查找(search)和插入(insert)操作交叉进行。
大量不同的键。
查找(search)比插入(insert)操作多的多。
虽然不可预测,查找和插入的模式并非随机。
顺序查找用的是数据结构是链表,每个节点存储一个键值对。
get()的实现为遍历链表,用equals函数比较寻找的键和节点中的键。如果有匹配的键,则返回相应的值。
否则,返回null。
//search for key, return associated value public Value get(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function get"); for(Node current = first; current != null; current = current.next) { if(key.equals(current.key)) return current.val;//search hit } return null;//search miss }
put()的实现也是遍历链表,如果有匹配的键,则更新相应的值,否则,在链表头插入新的节点。
public void put(Key key, Value val) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function put"); if(val == null) { delete(key); return; } for(Node current = first; current != null; current = current.next) { if(key.equals(current.key)) { current.val = val;//search hit: update val return; } } first = new Node(key, val, first);//search miss: add new node. n++; }
delete()实现:
public void delete(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function delete"); Node fakehead = new Node(null, null, first); for(Node prev = fakehead; prev.next != null; prev = prev.next) { if(key.equals(prev.next.key)) { prev.next = prev.next.next; n--; break; } } first = fakehead.next; }
整个代码:
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class SequentialSearchST<Key, Value> { private Node first; private int n; public SequentialSearchST() { first = null; n = 0; } public void put(Key key, Value val) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function put"); if(val == null) { delete(key); return; } for(Node current = first; current != null; current = current.next) { if(key.equals(current.key)) { current.val = val;//search hit: update val return; } } first = new Node(key, val, first);//search miss: add new node. n++; } //search for key, return associated value public Value get(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function get"); for(Node current = first; current != null; current = current.next) { if(key.equals(current.key)) return current.val;//search hit } return null;//search miss } public void delete(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function delete"); Node fakehead = new Node(null, null, first); for(Node prev = fakehead; prev.next != null; prev = prev.next) { if(key.equals(prev.next.key)) { prev.next = prev.next.next; n--; break; } } first = fakehead.next; } public Iterable<Key> keys() { Queue<Key> queue = new LinkedList<>(); for(Node cur = first; cur != null; cur = cur.next) { queue.add(cur.key); } return queue; } //shorthand methods public boolean contains(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function contains"); return get(key) != null; } //shorthand methods public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; } public int size() { return n; } //inner class private class Node { Key key; Value val; Node next; public Node(Key key, Value val, Node next) { this.key = key; this.val = val; this.next = next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SequentialSearchST<String, Integer> st = new SequentialSearchST<String, Integer>(); for(int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) { String key = StdIn.readString(); if(key.equals("-")) { key = StdIn.readString(); st.delete(key); StdOut.println("delete " + key); } else { st.put(key, i); StdOut.println("put" + " " + key + " " + i); } StdOut.print(st.size() + " key-value pairs:"); for(String s : st.keys()) StdOut.print(" " + s + " " + st.get(s)); StdOut.println(); } } }
测试数据:
A B C D - B C E F - A B - B - F - D
Test Client的输出结果:
put A 0 1 key-value pairs: A 0 put B 1 2 key-value pairs: B 1 A 0 put C 2 3 key-value pairs: C 2 B 1 A 0 put D 3 4 key-value pairs: D 3 C 2 B 1 A 0 delete B 3 key-value pairs: D 3 C 2 A 0 put C 5 3 key-value pairs: D 3 C 5 A 0 put E 6 4 key-value pairs: E 6 D 3 C 5 A 0 put F 7 5 key-value pairs: F 7 E 6 D 3 C 5 A 0 delete A 4 key-value pairs: F 7 E 6 D 3 C 5 put B 9 5 key-value pairs: B 9 F 7 E 6 D 3 C 5 delete B 4 key-value pairs: F 7 E 6 D 3 C 5 delete F 3 key-value pairs: E 6 D 3 C 5 delete D 2 key-value pairs: E 6 C 5
结论1:在含有N个键值对的基于无序链表的符号表中,未命中的查找(search miss)和插入(insert)操作都需要N次比较。命中的查找(search hit)在最坏的情况下需要N次比较。
推论:向一个空表中插入N个不同的键需要~N2/2次比较。
随机查找命中,即在符号表中查找每个键的可能性是相同的,所以平均比较次数是(1+2+……+N)/N = (N+1)/2 ~ N/2
采用的数据结构是一对平行的数组,一个用于存储键,一个用于存储值。
算法需要保持数组中的Comparable类型的键有序,然后使用数组的索引来高效的实现其他操作。
这份实现的核心是rank方法:
//return the number of keys in the table that are smaller than key //the heart method public int rank(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function rank"); int lo = 0, hi = n - 1; while(lo <= hi) { int mid = lo + (hi - lo)/2; int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[mid]); if(cmp < 0) { hi = mid - 1; } else if(cmp > 0) { lo = mid + 1; } else { return mid; } } return lo; }
对于get方法,如果键在数组中,调用rank方法即可知道键在数组中的位置。否则不存在,返回null。
public Value get(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function get"); if(isEmpty()) return null; int k = rank(key); if(k < n && keys[k].compareTo(key) == 0) return vals[k]; else return null; }
对于put方法,如果键在数组中,调用rank方法即可知道更新该键值的位置,或者插入的位置。
插入的时候,需要将后边的键都往后移动一个位置(对于大数组,移动的开销将会非常大)。
public void put(Key key, Value val) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function put"); if(val == null) { delete(key); return; } //it works when ST is empty(n = 0) int k = rank(key); if(k < n && keys[k].compareTo(key) == 0) { vals[k] = val;//key is already in symbol table return; } //move for(int j = n; j > k; j--) { keys[j] = keys[j-1]; vals[j] = vals[j-1]; } keys[k] = key; vals[k] = val; n++; }
delete操作:其中对于大数组,移动的开销也会非常大。
public void delete(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function delete"); if(isEmpty()) return; int k = rank(key); if(k < n && keys[k].compareTo(key) == 0) {//key is in symbol table //move for(int j = k; j < n - 1; j++) { keys[j] = keys[j+1]; vals[j] = vals[j+1]; } n--; keys[n] = null;// to avoid loitering vals[n] = null; } }
其余操作:
public Key min() { if(isEmpty()) return null; return keys[0]; } public Key max() { if(isEmpty()) return null; return keys[n -1]; } public Key select(int k) { if(k < 0 || k >= n) return null; return keys[k]; } public Key ceiling(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function ceiling"); if(isEmpty()) return null; int k = rank(key); if(k == n) return null; else return keys[k]; } public Key floor(Key key) { if(key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key is null in function floor"); if(isEmpty()) return null; int k = rank(key); if(k < n && keys[k].compareTo(key) == 0) return keys[k]; else if(k == 0) return null; else return keys[k-1]; } public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) { if(lo == null || hi == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("one of the arguements is null in function keys"); Queue <Key> queue = new LinkedList<>(); if(lo.compareTo(hi) > 0 || isEmpty()) return queue;//special case for(int i = rank(lo); i < rank(hi); i++) { queue.add(keys[i]); } if(contains(hi)) queue.add(keys[rank(hi)]); return queue; } //shorthand methods public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; } //shorthand methods public boolean contains(Key key) { return get(key) != null; } public int size() { return n; } //shorthand methods public void deleteMin() { if(isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("underflow error"); delete(min()); } //shorthand methods public void deleteMax() { if(isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("underflow error"); delete(max()); } //shorthand methods public int size(Key lo, Key hi) { if (lo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to size() is null"); if (hi == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("second argument to size() is null"); if(hi.compareTo(lo) < 0) return 0; else if(contains(hi)) return rank(hi) - rank(lo) + 1; else return rank(hi) - rank(lo); } //shorthand methods public Iterable<Key> keys() { if(isEmpty()) return new LinkedList<>(); return keys(min(), max()); }
Test Client测试结果(数据同上):
put A 0 1 key-value pairs: A 0 put B 1 2 key-value pairs: A 0 B 1 put C 2 3 key-value pairs: A 0 B 1 C 2 put D 3 4 key-value pairs: A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3 delete B 3 key-value pairs: A 0 C 2 D 3 put C 5 3 key-value pairs: A 0 C 5 D 3 put E 6 4 key-value pairs: A 0 C 5 D 3 E 6 put F 7 5 key-value pairs: A 0 C 5 D 3 E 6 F 7 delete A 4 key-value pairs: C 5 D 3 E 6 F 7 put B 9 5 key-value pairs: B 9 C 5 D 3 E 6 F 7 delete B 4 key-value pairs: C 5 D 3 E 6 F 7 delete F 3 key-value pairs: C 5 D 3 E 6 delete D 2 key-value pairs: C 5 E 6
结论1:在N个键的有序数组中进行二分查找最多需要logN + 1次比较(无论是否成功)。
但是put和delete这两个方法太慢了。
结论2:向大小为N的数组中插入一个新元素,在最坏的情况下需要访问~2N次数组。因此向一个空的符号表中插入N个元素,在最坏的情况下需要访问~N2次数组。
二分查找法适用于静态表(不允许插入),在初始化的时候就进行排序。
但是二分查找法不适用于查找和插入操作是混合进行的,而且符号表非常大的情况。
目前很多应用都需要同时支持高效的查找和插入两种操作。
如何保证查找和插入操作都是对数级别的算法和数据结构?
首先,要支持高效的插入操作,需要一种链式结构;但是单链接的链表是不能支持二分查找法的。
为了将二分查找法的效率和链表的灵活性结合起来,需要更加复杂的数据结构,二叉查找树。
标签:排名 strong 个数 import extends 适用于 取整 list hit
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/songdechiu/p/6819003.html