标签:logs 服务器同步 置配 运行 rc.local 命令 服务 nobody auth
环境:Centos 6.9
两台服务器,A(192.168.223.129) 和 B(192.168.223.130)。A 作为服务端,B作为客户端从A服务器同步目录。把A的/usr/src 目录下的内容同步到B的/rsync/ 目录。
首先配置下epel 源:
rpm -ivh https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/epel/epel-release-latest-6.noarch.rpm
全都先安装下rsync:
yum install rsync
然后,A 先创建/etc/rsyncd.conf 配置文件(默认没有),内容如下:
uid = nobody gid = nobody #hosts allow = * hosts allow = 192.168.223.130 use chroot = no pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log [tools] path = /usr/src comment = Rsync share test auth users = haha secrets file = /etc/rsync_users read only = yes
echo "haha:1234567" >/etc/rsync_users #配置同步需要的用户和秘密
chmod 600 /etc/rsync_users #必须要修改权限,不然会报错
开启服务端:
rsync --daemon --config=/etc/rsyncd.conf
会已守护进程的方式后台运行。
可以把这句写到/etc/rc.local 中,开机启动。
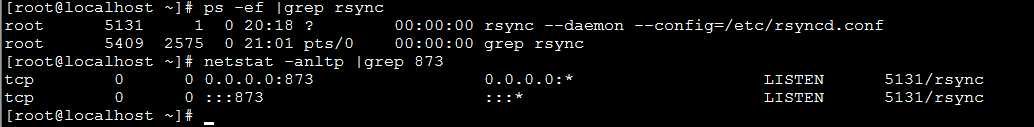
rsync 监听端口是873,说明服务端已经配置好了。
接下来是B服务器客户端:
客户端不用配置配置文件,直接可以从服务端同步目录,命令如下:
/usr/bin/rsync -avzP --delete --password-file=/etc/rsync.pass haha@192.168.223.129::tools /rsync/
注意:客户端要生成/etc/rsync.pass 这个密码文件(路径随意),内容是同步账号的密码,即:echo "1234567" >/etc/rsync.pass, 并且权限要是600,不然会报错。
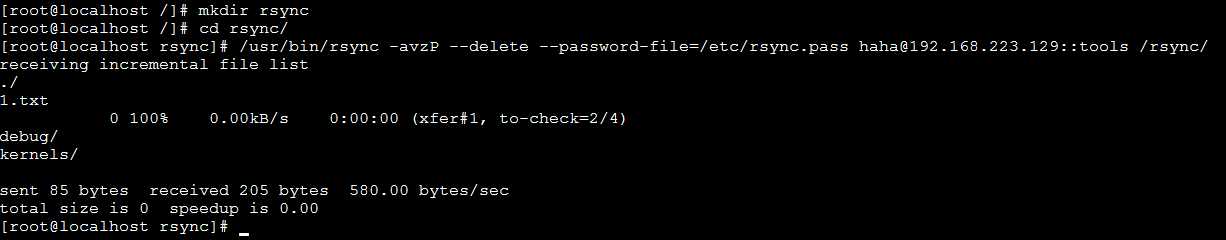
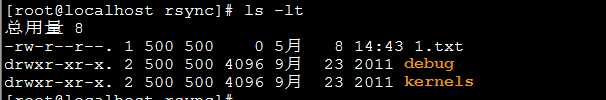
如图,从A 服务器同步过来两个文件夹和一个文件。
标签:logs 服务器同步 置配 运行 rc.local 命令 服务 nobody auth
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangss/p/6827881.html