标签:扩展 技术 数字 表示 alt div func .com png
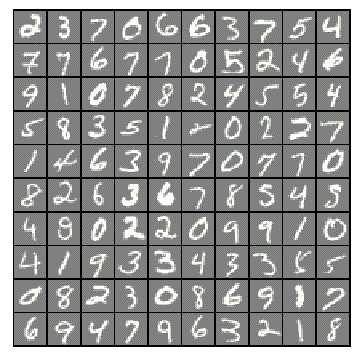
所需解决的问题是,训练一个Logistic Regression系统,使之能够识别手写体数字1-10,每张图片为20px*20px的灰度图。训练样例的输入X是5000行400列的一个矩阵,每一行存储一张图片(20^2=400),共5000个训练样例,而y则为手写体所表示的数字1-10。
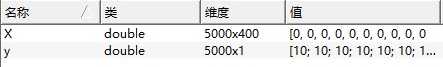
利用Logistic Regression进行多分类应用,其基础是将问题本身化解为z个二分类问题,其中z为类别的个数。第一步,将向量m*1维y扩展为矩阵m*z维矩阵Y,向量n+1维向量theta扩展为矩阵z*(n+1)维矩阵Theta。其意义是将一维数据转换至二维,以0,1表示,从而使我们能够利用二分类来解决问题。如下图:

第二步,利用内置函数fmincg来求解10组问题的最佳theta值,构建10*401维theta_all矩阵:
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2);
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1);
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% loop for every number, we train the theta of every number respectively.
initial_theta = zeros(n+1,1);
options = optimset(‘GradObj‘, ‘on‘, ‘MaxIter‘, 50);
for(i=1:num_labels)
y_b=(y==i);
all_theta(i,:) = fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X,y_b, lambda)), ...
initial_theta, options);
endfor
其中用到的lrCostFunction函数如下:
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda) %LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with %regularization % J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using % theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the % gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples J = 0; grad = zeros(size(theta)); tmp=ones(m,1); h = sigmoid(X*theta); h1=log(h); h2=log(tmp-h); y2=tmp-y; J=(y‘*h1+y2‘*h2)/(-m); theta(1)=0; J+=theta‘*theta*lambda/(2*m); grad=((X‘*(h-y))+lambda*theta)/m; grad = grad(:); end
第三步,合并该问题,构建“可能性矩阵”,然后选择可能性最大的项作为系统的输出:
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X) m = size(X, 1); num_labels = size(all_theta, 1); p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); X = [ones(m, 1) X]; probMatrix = X*all_theta‘; [pVector,p] = max(probMatrix,[],2); end
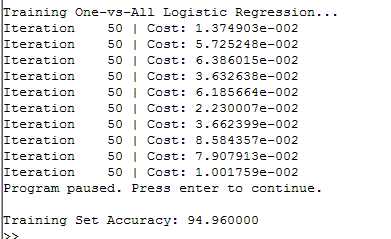
使用Logistic Regression Algorithm进行多分类数字识别的Octave仿真
标签:扩展 技术 数字 表示 alt div func .com png
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/rhyswang/p/6868865.html