标签:pen 类设计 开始 表的操作 删除元素 strlen val ide clear
1. LinkList类的设计要点
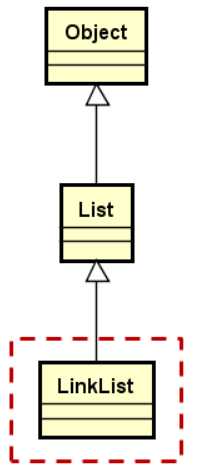

(1)用类模板实现,通过头结点访问后继结点
(2)定义内部结点类型Node(注意继承于自定义的Object顶层父类),用于描述数据域和指针域.
(3)实现线性表的关键操作(增、删、查等)
2. 单链表的内部结构
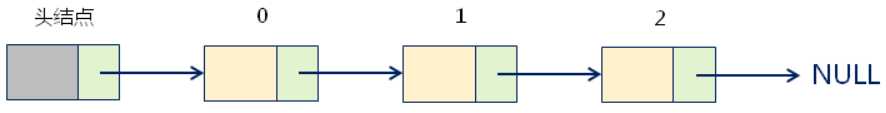
(1)头结点在单链表中的意义:辅助数据元素的定位,方便插入和删除操作;
(2)头结点不存储实际的数据元素
3. 单链表的操作
(1)插入元素
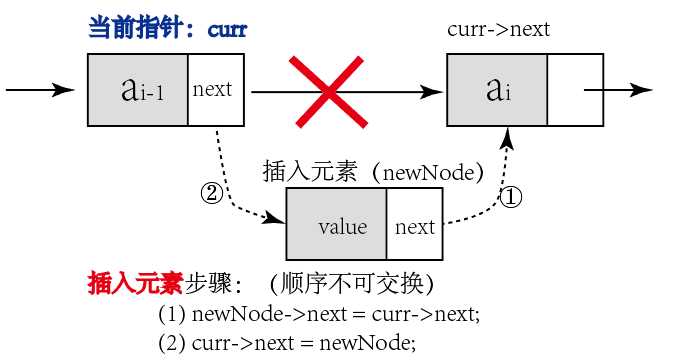
①从头结点开始,通过current指针定位到目标位置(注意:current->next保留着目标元素的地址)
②从堆空间中申请新的Node结点
③执行插入操作
node->value = e; node->next = current->next; current->next = node;
(2)删除元素
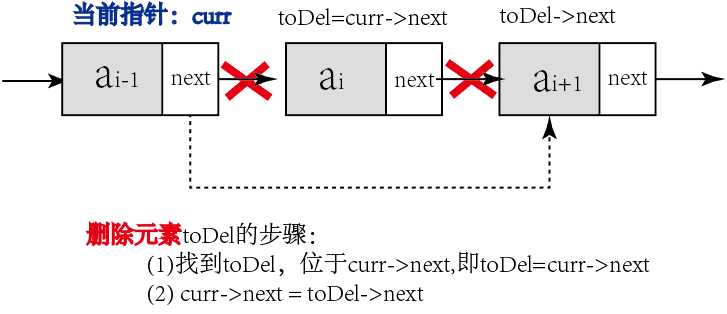
①从头结点开始,通过current指针定位到目标位置(toDel地址保存在curr->next中)
②使用toDel指针指向需要删除的结点
③执行删除操作
toDel = current->next; current->next = toDel->next; delete toDel;
【编程实验】单链表的实现
//Object.h

#ifndef _OBJECT_H_ #define _OBJECT_H_ namespace DTLib { class Object { public: //以下四个重载函数用于统一不同编译器new失败时的结果不同的问题。 //throw()表示不抛出异常,即如果申请内请失败时,统一返回NULL而不抛异常 void* operator new(unsigned int size) throw(); void operator delete(void* p); void* operator new[](unsigned int size) throw(); void operator delete[](void* p); virtual ~Object() = 0; }; } #endif // _OBJECT_H_
//Object.cpp

#include "Object.h" #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; namespace DTLib { void * Object::operator new(unsigned int size) throw() { return malloc(size); } void Object::operator delete(void *p) { free(p); } void *Object::operator new[](unsigned int size) throw() { //当用new Test[5]时,只须传入数组元素的个数,编译器会向operator new[](...)函数的参数 //传入5*sizeof(Test) + sizeof(unsigned int),其中的sizeof(unsigned int)为额外 //空间,用于保存元素的个数。 return malloc(size); } void Object::operator delete[](void *p) { free(p); } Object::~Object() { } }
//Exception.h

#ifndef _EXCEPTION_H_ #define _EXCEPTION_H_ #include "Object.h" namespace DTLib { #define THROW_EXCEPTION(e, m) (throw e(m, __FILE__, __LINE__)) class Exception : public Object { protected: char* m_message; char* m_location; void init(const char* message, const char* file, int line); public: //构造函数 Exception(const char* message); Exception(const char* file, int line); Exception(const char *message, const char *file, int line); //拷贝构造函数 Exception(const Exception& e); //重载赋值操作符 Exception& operator=(const Exception& e); virtual const char* message() const; virtual const char* location() const; //注意: //(1)析构函数是较为特殊的函数,一旦定义了析构函数,不管这个函数是不是纯虚函数,就 //必须提供实现。因为,对象在销毁时,最后都会调用父类的析构函数。如果父类不提供实现, //当对象销毁过程中调用到父类析构函数时,就找不到析构函数,也就不知该如何析构下去。 //因此,尽管这里将析构函数声明为纯虚函数,但Exception类仍提供析构函数的实现。以便 //最后正确释放掉m_message和m_location所指的堆空间. //(2)此外,声明为纯虚函数,可以让该类只能作为接口使用,而且也强迫子类必须 //提供析构函数的实现。 virtual ~Exception() = 0; //纯虚函数 }; //计算异常类 class ArithmeticException: public Exception { public: ArithmeticException():Exception(0){} ArithmeticException(const char* message):Exception(message){} ArithmeticException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} ArithmeticException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} ArithmeticException(const ArithmeticException& e): Exception(e){} ArithmeticException& operator=(const ArithmeticException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //空指针异常类 class NullPointerException: public Exception { public: NullPointerException():Exception(0){} NullPointerException(const char* message):Exception(message){} NullPointerException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} NullPointerException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} NullPointerException(const NullPointerException& e): Exception(e){} NullPointerException& operator=(const NullPointerException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //越界异常类 class IndexOutOfBoundsException: public Exception { public: IndexOutOfBoundsException():Exception(0){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message):Exception(message){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} IndexOutOfBoundsException(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e): Exception(e){} IndexOutOfBoundsException& operator=(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //内存不足异常类 class NotEnoughMemoryException: public Exception { public: NotEnoughMemoryException():Exception(0){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const char* message):Exception(message){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} NotEnoughMemoryException(const NotEnoughMemoryException& e): Exception(e){} NotEnoughMemoryException& operator=(const NotEnoughMemoryException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //参数错误异常类 class InvalidParameterException: public Exception { public: InvalidParameterException():Exception(0){} InvalidParameterException(const char* message):Exception(message){} InvalidParameterException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} InvalidParameterException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} InvalidParameterException(const InvalidParameterException& e): Exception(e){} InvalidParameterException& operator=(const InvalidParameterException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; //无效操作异常类(成员函数调用时,如果状态不正确则抛出异常) class InvalidOperationException: public Exception { public: InvalidOperationException():Exception(0){} InvalidOperationException(const char* message):Exception(message){} InvalidOperationException(const char*file, int line):Exception(file, line){} InvalidOperationException(const char *message, const char* file, int line):Exception(message, file, line){} InvalidOperationException(const InvalidOperationException& e): Exception(e){} InvalidOperationException& operator=(const InvalidOperationException& e) { Exception::operator =(e); return *this; } }; } #endif // _EXCEPTION_H_
//Exception.cpp

#include "Exception.h" #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; namespace DTLib { void Exception::init(const char *message, const char *file, int line) { m_message = strdup(message); //复制message的内容 m_location = NULL; if(file != NULL){ char sl[16]={0}; itoa(line, sl, 10);//将整数line转为字符串,其中的10表示转换为十进制格式 //m_location的格式为:file:line\0; m_location = static_cast<char*>(malloc(strlen(file) + strlen(sl) + 2)); //注意:申请内存失败时无须再抛NotEnoughMemoryException异常,从宏观上看,父类 //是无法抛出子类型的异常的。从逻辑上看也不能抛出这个异常,因为当父类构造时出现异常时, //如果去抛出子类异常,则必然需要构造子类,但这又得先调用父类构造函数(会再一次产 //生异常,从而造成Exception构造函数的递归调用,从而造成死循环!) if(m_location != NULL){ //内存申请成功 m_location = strcpy(m_location, file); m_location = strcat(m_location, ":"); m_location = strcat(m_location, sl); } } } //构造函数 Exception::Exception(const char* message) { init(message, NULL, 0); } Exception::Exception(const char* file, int line) { init(NULL, file, line); } Exception::Exception(const char *message, const char *file, int line) { init(message, file, line); } //拷贝构造函数 Exception::Exception(const Exception& e) { //深拷贝 m_message = strdup(e.m_message); m_location = strdup(e.m_location); } //重载赋值操作符 Exception& Exception::operator=(const Exception& e) { if(this != &e){ //防止自赋值 free(m_message); free(m_location); //深拷贝 m_message = strdup(e.m_message); m_location = strdup(e.m_location); } return *this; } const char* Exception::message() const { return m_message; } const char* Exception::location() const { return m_location; } Exception::~Exception() { free(m_message); free(m_location); } }
//List.h

#ifndef _LIST_H_ #define _LIST_H_ #include "Object.h" namespace DTLib { template <typename T> class List : public Object { protected: //禁用拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符 //List(const List&); //List& operator=(const List&); public: //由于以上添加了拷贝构造函数,编译将不再提供 //默认的一些构造函数。这里需要手工加上无参构造函数 List(){} virtual bool insert(const T& e) = 0;//往线性表尾部插入元素 virtual bool insert(int index, const T& elem) = 0; virtual bool remove(int index) = 0; virtual bool get(int index, T& elem) const = 0; virtual int length() const = 0; virtual void clear() = 0; }; } #endif // _LIST_H_
//LinkList.h
#ifndef _LINKLIST_H_ #define _LINKLIST_H_ #include "list.h" #include "Exception.h" namespace DTLib { template <typename T> class LinkList : public List<T> { protected: //结点类型(内部类) struct Node : public Object { T value; //数据域 Node* next; //指针域s }; //由于m_header在定义时会调用T的构造函数。如果T的设计者在构造函数中抛出异常,当LinkList<T> list时会产生异常。这时调用者可能会怀疑是 //LinkList设计出了问题,而不会认为是T的问题,因为他根本就没有手工定义T的对象(如:T t),为了防止这种现象的出现,可“借尸还魂”,防止在定义 //m_header时调用T的构造函数。
//mutable Node m_header; //头结点 //“借尸还魂”:定义一个与Node内存模型完全一样的结构体 mutable struct : public Object{ char reserved[sizeof(T)]; Node* next; } m_header; int m_length; //链表长度 //获取指定下标的元素 Node* position(int index) const { Node* ret = (Node*)&m_header; //由于const对象不能修改成员变量的值 //对m_header取地址就可能会修改m_header //的值,可将m_header声明为mutable for(int pos=0; pos<index; ++pos){ ret = ret->next; } return ret; //注意要查找的元素地址保存在该节点的next指针域中 } public: LinkList() { m_header.next = NULL; m_length = 0; } bool insert(const T &elem) { return insert(m_length, elem); } bool insert(int index, const T& elem) { bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index <= m_length)); if (ret){ Node* node = new Node(); Node* current = position(index); node->value = elem; node->next = current->next; current->next = node; ++m_length; }else{ THROW_EXCEPTION(NotEnoughMemoryException, "Not enougth memory to insert new element ..."); } return ret; } bool remove(int index) { bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length)); if(ret){ Node* current = position(index); //要删除的元素地址保存在curr->next中 Node* toDel = current->next; current->next = toDel->next; delete toDel; --m_length; } return ret; } bool set(int index, const T& elem) { bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length); if(ret){ Node* current = position(index); (current->next)->value = elem; } return ret; } T get(int index) const { T ret; if(get(index, ret)){ return ret; }else{ THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid paramter index to get element ..."); } } bool get(int index, T& elem) const { bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length); if(ret){ Node* current = position(index); elem = (current->next)->value; } return ret; } int length() const { return m_length; } void clear() { while(m_header.next){ Node* toDel = m_header.next; m_header.next = toDel->next; delete toDel; } m_length = 0; } ~LinkList() { clear(); } }; } #endif // _LINKLIST_H_
//main.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "LinkList.h" using namespace std; using namespace DTLib; class Test { public: Test() { throw 0; //在构造函数中抛异常,故意制造出来的! } }; int main() { //测试1 LinkList<int> list; for(int i=0; i<5; i++){ list.insert(0, i); list.set(0, i*i); } for(int i=0; i<list.length(); i++){ cout << list.get(i) << " "; } cout << endl; list.remove(2); for(int i=0; i<list.length(); i++){ cout << list.get(i) << " "; } cout << endl; list.clear(); for(int i=0; i<list.length(); i++){ cout << list.get(i) << endl; } //测试2 LinkList<Test> lt; //如果LinkList类不采用借尸还魂来解决Test抛异常的话, //LinkList的使用者会以为这个异常是LinkList类设计 //的问题,因为他们认为自己并没有调用Test的构造函数, //所以不会怀疑是Test类设计的问题,而是LinkList类的问题。 return 0; } /*输出结果: 16 9 4 1 0 16 9 1 0 */
4. 小结
(1)通过类模板实现链表,包括头结点成员和长度成员。
(2)定义结点类型,并通过堆中的结点对象构成链式存储
(3)为了避免构造错误的隐患,头结点类型需要重定义
(4)插入和删除操作需要保证链表的完整性
标签:pen 类设计 开始 表的操作 删除元素 strlen val ide clear
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/5iedu/p/6914139.html