标签:and 层次遍历 amp efi lin 注意 左右 each 这一
Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node".
What if the given tree could be any binary tree? Would your previous solution still work?
Note:
For example,
Given the following binary tree,
1
/ 2 3
/ \ 4 5 7
After calling your function, the tree should look like:
1 -> NULL
/ 2 -> 3 -> NULL
/ \ 4-> 5 -> 7 -> NULL
这一题和上一题Populating next right pointer in each node的区别在于二叉树不是完美二叉树,所以每次的第一个结点不一定是沿着左子树的最左端一直向下。这样层与层转变,就不一样。
方法一:
代码原出处没有解释,这里给出个人理解。上一题是这题的特殊情况,所以这题的代码也能通过上一题。
核心思想是:层次遍历。最外层的while循环是,负责层层之间的转化。 先将同层中的前结点和下一层的首结点标记为nullptr。内层while循环是负责某一层的遍历。对某一层,先确定下一层的首结点,这里是用firNode来实现的。
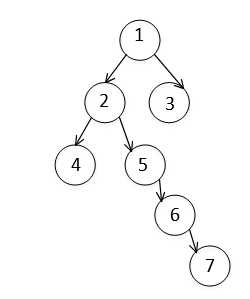
特别值得注意: 当cur=4时,重新进入内层while循环,因,4为叶节点,故,循环内的第二、三个if条件都不满足,firNode依旧为nullptr,此时cur=cur->next;再次循环,firNode=6,完成层层之间的转换。说明,firNode不是没有条件的在左右孩子中选择。
/** * Definition for binary tree with next pointer. * struct TreeLinkNode { * int val; * TreeLinkNode *left, *right, *next; * TreeLinkNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void connect(TreeLinkNode *root) { TreeLinkNode *cur=root; while(cur) { TreeLinkNode *firNext=nullptr; //下一层的第一个结点 TreeLinkNode *prev=nullptr; //同一层中的前结点 while(cur) { if(firNext==nullptr) firNext=cur->left?cur->left:cur->right; if(cur->left) { if(prev) prev->next=cur->left; prev=cur->left; } if(cur->right) { if(prev) prev->next=cur->right; prev=cur->right; } cur=cur->next; } cur=firNext; } } };
方法二:
递归,虽然不满题意,但有利于熟悉递归算法,依旧写在这。代码来源Grandyang博友。
// Recursion, more than constant space class Solution { public: void connect(TreeLinkNode *root) { if (!root) return; TreeLinkNode *p = root->next; while (p) { if (p->left) { p = p->left; break; } if (p->right) { p = p->right; break; } p = p->next; } if (root->right) root->right->next = p; if (root->left) root->left->next = root->right ? root->right : p; connect(root->right); connect(root->left); } };
[Leetcode] Populating next right pointer in each node ii 填充每个节点的右指针
标签:and 层次遍历 amp efi lin 注意 左右 each 这一
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/love-yh/p/6985403.html