标签:就会 函数 jpg 精确 blog 冲突 img 决定 table
Hash函数
非哈希表的特点:关键字在表中的位置和它之间不存在一个确定的关系,查找的过程为给定值一次和各个关键字进行比较,查找的效率取决于和给定值进行比较的次数。
哈希表的特点:关键字在表中位置和它之间存在一种确定的关系。
哈希函数:一般情况下,需要在关键字与它在表中的存储位置之间建立一个函数关系,以f(key)作为关键字为key的记录在表中的位置,通常称这个函数f(key)为哈希函数。
hash : 翻译为“散列”,就是把任意长度的输入,通过散列算法,变成固定长度的输出,该输出就是散列值。
这种转换是一种压缩映射,散列值的空间通常远小于输入的空间,不同的输入可能会散列成相同的输出,所以不可能从散列值来唯一的确定输入值。
简单的说就是一种将任意长度的消息压缩到莫伊固定长度的消息摘要的函数。
hash冲突:就是根据key即经过一个函数f(key)得到的结果的作为地址去存放当前的key value键值对(这个是hashmap的存值方式),但是却发现算出来的地址上已经有人先来了。就是说这个地方被抢了啦。这就是所谓的hash冲突啦。
哈希函数处理冲突的方法
1.开放定址法:

其中 m 为表的长度
对增量di有三种取法:
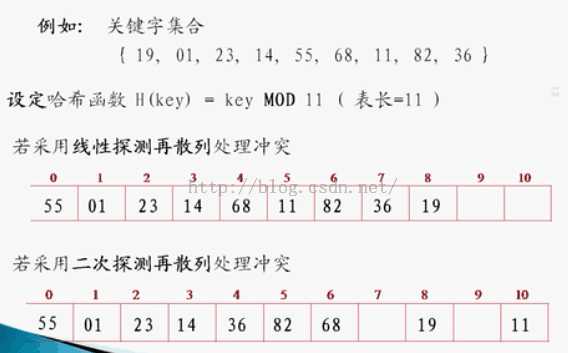
线性探测再散列 di = 1 , 2 , 3 , ... , m-1
平方探测再散列 di = 1 2 , -2 , 4 , -4 , 8 , -8 , ... , k的平方 , -k平方
随机探测再散列 di 是一组伪随机数列
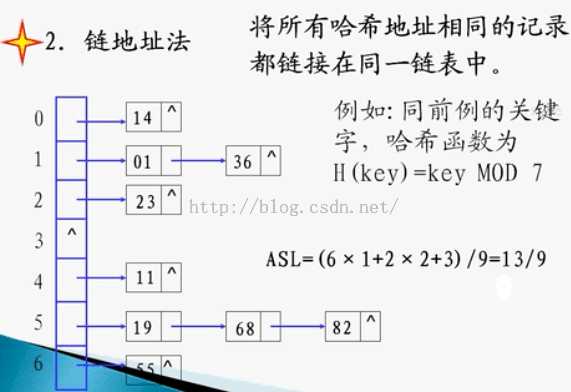
2.链地址法
这种方法的基本思想是将所有哈希地址为i的元素构成一个称为同义词链的单链表,并将单链表的头指针存在哈希表的第i个单元中,因而查找、插入和删除主要在同义词链中进行。链地址法适用于经常进行插入和删除的情况。
3.再哈希
这种方法是同时构造多个不同的哈希函数:
Hi=RH1(key) i=1,2,…,k
当哈希地址Hi=RH1(key)发生冲突时,再计算Hi=RH2(key)……,直到冲突不再产生。这种方法不易产生聚集,但增加了计算时间。
4.建立公共溢出区
这种方法的基本思想是:将哈希表分为基本表和溢出表两部分,凡是和基本表发生冲突的元素,一律填入溢出表
HashMap的Hash冲突处理办法
hashmap出现了Hash冲突的时候采用第二种办法:链地址法。
代码示例:
有一个”国家”(Country)类,我们将要用Country对象作为key,它的首都的名字(String类型)作为value。下面的例子有助于我们理解key-value对在HashMap中是如何存储的。
public class Country { String name; long population; public Country(String name, long population) { super(); this.name = name; this.population = population; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public long getPopulation() { return population; } public void setPopulation(long population) { this.population = population; } // If length of name in country object is even then return 31(any random // number) and if odd then return 95(any random number). // This is not a good practice to generate hashcode as below method but I am // doing so to give better and easy understanding of hashmap. @Override public int hashCode() { if (this.name.length() % 2 == 0) return 31; else return 95; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { Country other = (Country) obj; if (name.equalsIgnoreCase((other.name))) return true; return false; } }
public class HashMapStructure { public static void main(String[] args) { Country india = new Country("India", 1000); Country japan = new Country("Japan", 10000); Country france = new Country("France", 2000); Country russia = new Country("Russia", 20000); HashMap<Country, String> countryCapitalMap = new HashMap<Country, String>(); countryCapitalMap.put(india, "Delhi"); countryCapitalMap.put(japan, "Tokyo"); countryCapitalMap.put(france, "Paris"); countryCapitalMap.put(russia, "Moscow"); Iterator<Country> countryCapitalIter = countryCapitalMap.keySet().iterator();// put debug point at this line while (countryCapitalIter.hasNext()) { Country countryObj = countryCapitalIter.next(); String capital = countryCapitalMap.get(countryObj); System.out.println(countryObj.getName() + "----" + capital); } }
}
在注释处加入debug,可以通过watch查看countryCapitalMap的结构:
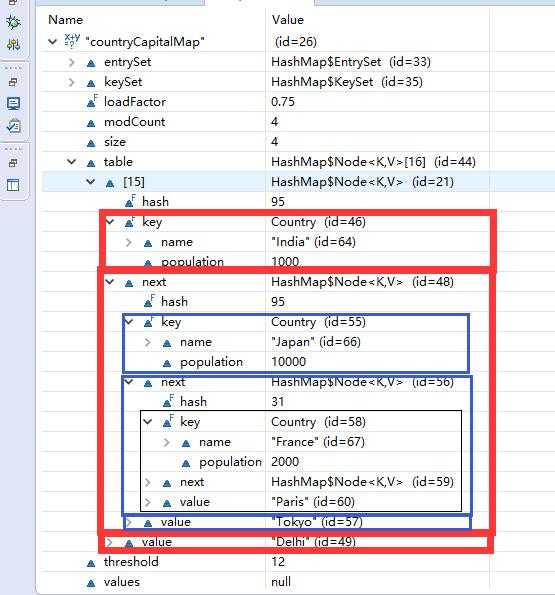
从上图可以观察到以下几点:
有一个叫做table大小是16的Entry数组。
这个table数组存储了Entry类的对象。HashMap类有一个叫做Entry的内部类。这个Entry类包含了key-value作为实例变量。我们来看下Entry类的结构。Entry类的结构:
static class Entry implements Map.Entry{ final K key; V value; Entry next; final int hash; ...//More code goes here }
1).每当往hashmap里面存放key-value对的时候,都会为它们实例化一个Entry对象,这个Entry对象就会存储在前面提到的Entry数 组table中。现在你一定很想知道,上面创建的Entry对象将会存放在具体哪个位置(在table中的精确位置)。答案就是,根据key的 hashcode()方法计算出来的hash值(来决定)。hash值用来计算key在Entry数组的索引。
2).现在,如果你看下上图中数组的索引15,它有一个叫做HashMap$Entry的Entry对象。
3).我们往hashmap放了4个key-value对,但是看上去好像只有1个元素!!!这是因为,如果两个元素有相同的hashcode,它们会 被放在同一个索引上。问题出现了,该怎么放呢?原来它是以链表(LinkedList)的形式来存储的(逻辑上)。因此他们都在hash值为15的位置 上存着了,然后把多个Entry,用next进行链接。
标签:就会 函数 jpg 精确 blog 冲突 img 决定 table
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jing99/p/6985618.html