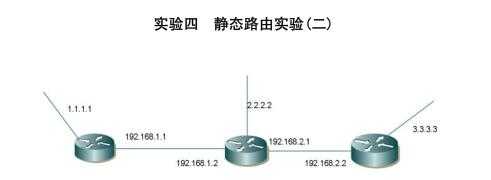
一、实验目的
通过此实验,了解静态路由和默认路由的区别所在。
二、实验步骤
rack01#show running-config
!
interface Loopback0
ip address
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.1
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.1
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay0
!
rack02#show running-config
!
interface Loopback0
ip address
![技术分享]()
2.2.2.2
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.2
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay0
!
interface Serial1/1
ip address
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.1
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay0
!
rack03#show running-config
!
interface Loopback0
ip address
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.3
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/1
ip address
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.2
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay0
!
在 rack01 及 rack03 上配置一条默认静态路由
rack01(config)#ip route0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.2
rack03(config)#ip route0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.1
rack01#show ip route
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0]via
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.2
![技术分享]()
1.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
L
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.0/30 is directly connected, Serial1/0
L
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, Serial1/0
可以看到一条 S*路由,代表的为默认静态路由。
Rack02 我们配置标准的静态路由
rack02(config)#ip route
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.0
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.0
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.1
rack02(config)#ip route
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.0
![技术分享]()
255.255.255.0
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.2
rack02#show ip route
![技术分享]()
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
S
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.0 [1/0]via
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.1
![技术分享]()
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C
![技术分享]()
2.2.2.2 is directly connected, Loopback0
![技术分享]()
3.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
S
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.0 [1/0]via
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.2
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.0/30 is directly connected, Serial1/0
L
![技术分享]()
192.168.1.2/32 is directly connected, Serial1/0
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.0/30 is directly connected, Serial1/1
L
![技术分享]()
192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, Serial1/1
我们可以看到刚才写的两条静态路由。
我们在 rack01 上进行测试,并且是以源地址为
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.1,来 ping
![技术分享]()
2.2.2.2 来
看看结果。
rack01#ping
Protocol [ip]:
T arget IP address:
![技术分享]()
2.2.2.2
Repeat count [5]:
Datagram size [100]:
T imeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]: y
Source address or interface:
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.1
T ype of service [0]:
Set DFbit in IP header? [no]:
V alidate reply data? [no]:
Data pattern [0xABCD]:
Loose, Strict, Record, T imestamp, V erbose[none]:
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
T ype escape sequence to abort.
Sending5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.3, timeout is2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max =16/86/156 ms
我们看到可以通信,然后我们在来看看 ping
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.3 试一试。
rack01#ping
Protocol [ip]:
T arget IP address:
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.3
Repeat count [5]:
Datagram size [100]:
T imeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]: y
Source address or interface:
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.1
T ype of service [0]:
Set DFbit in IP header? [no]:
V alidate reply data? [no]:
Data pattern [0xABCD]:
Loose, Strict, Record, T imestamp, V erbose[none]:
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
T ype escape sequence to abort.
Sending5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.3, timeout is2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of
![技术分享]()
1.1.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max =16/86/156 ms
也没有问题。
通过这个验我们可以学习到:默认路由和静态路由的区别,默认路由是当目
标地址在路由表中找不到具体的路由条目时,则使用这条默认路由(上面的例子
中,rack01 是没有
![技术分享]()
2.2.2.2和
![技术分享]()
3.3.3.3 的,所以当查找这两个地址时路由表没有
找到,则匹配这个默认路由)。而静态路由没有这个特点,他只是根据路由表中
配置的具体路由条目去查找。
请同学们思考一个问题,如果在 R2上也配置两条默认路由,不配置普通静
态可不可以通信,这样配置之后有什么缺点?