标签:border space ati message hand 查找 控制 ble 循环
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息 sys.maxint 最大的Int值 sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
import logging logging.debug(‘debug message‘) logging.info(‘info message‘) logging.warning(‘warning message‘) logging.error(‘error message‘) logging.critical(‘critical message‘)
默认情况下Python的logging模块将日志打印到了标准输出中,且只显示了大于等于WARNING级别的日志,这说明默认的日志级别设置为WARNING(日志级别等级CRITICAL > ERROR > WARNING > INFO > DEBUG),默认的日志格式为日志级别:Logger名称:用户输出消息。
灵活配置日志级别,日志格式,输出位置:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,
format=‘%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s‘,
datefmt=‘%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S‘,
filename=‘/tmp/test.log‘,
filemode=‘w‘)
logging.debug(‘debug message‘)
logging.info(‘info message‘)
logging.warning(‘warning message‘)
logging.error(‘error message‘)
logging.critical(‘critical message‘)
配置参数:
 View Code
View Codeimport logging logger = logging.getLogger() # 创建一个handler,用于写入日志文件 fh = logging.FileHandler(‘test.log‘) # 再创建一个handler,用于输出到控制台 ch = logging.StreamHandler() formatter = logging.Formatter(‘%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s‘) fh.setFormatter(formatter) ch.setFormatter(formatter) logger.addHandler(fh) #logger对象可以添加多个fh和ch对象 logger.addHandler(ch) logger.debug(‘logger debug message‘) logger.info(‘logger info message‘) logger.warning(‘logger warning message‘) logger.error(‘logger error message‘) logger.critical(‘logger critical message‘)
logging库提供了多个组件:Logger、Handler、Filter、Formatter。Logger对象提供应用程序可直接使用的接口,Handler发送日志到适当的目的地,Filter提供了过滤日志信息的方法,Formatter指定日志显示格式。另外,可以通过:logger.setLevel(logging.Debug)设置级别。
之前我们学习过用eval内置方法可以将一个字符串转成python对象,不过,eval方法是有局限性的,对于普通的数据类型,json.loads和eval都能用,但遇到特殊类型的时候,eval就不管用了,所以eval的重点还是通常用来执行一个字符串表达式,并返回表达式的值。
 View Code
View Code我们把对象(变量)从内存中变成可存储或传输的过程称之为序列化,在Python中叫pickling,在其他语言中也被称之为serialization,marshalling,flattening等等,都是一个意思。序列化之后,就可以把序列化后的内容写入磁盘,或者通过网络传输到别的机器上。反过来,把变量内容从序列化的对象重新读到内存里称之为反序列化,即unpickling。
如果我们要在不同的编程语言之间传递对象,就必须把对象序列化为标准格式,比如XML,但更好的方法是序列化为JSON,因为JSON表示出来就是一个字符串,可以被所有语言读取,也可以方便地存储到磁盘或者通过网络传输。JSON不仅是标准格式,并且比XML更快,而且可以直接在Web页面中读取,非常方便。
JSON表示的对象就是标准的JavaScript语言的对象一个子集,JSON和Python内置的数据类型对应如下:
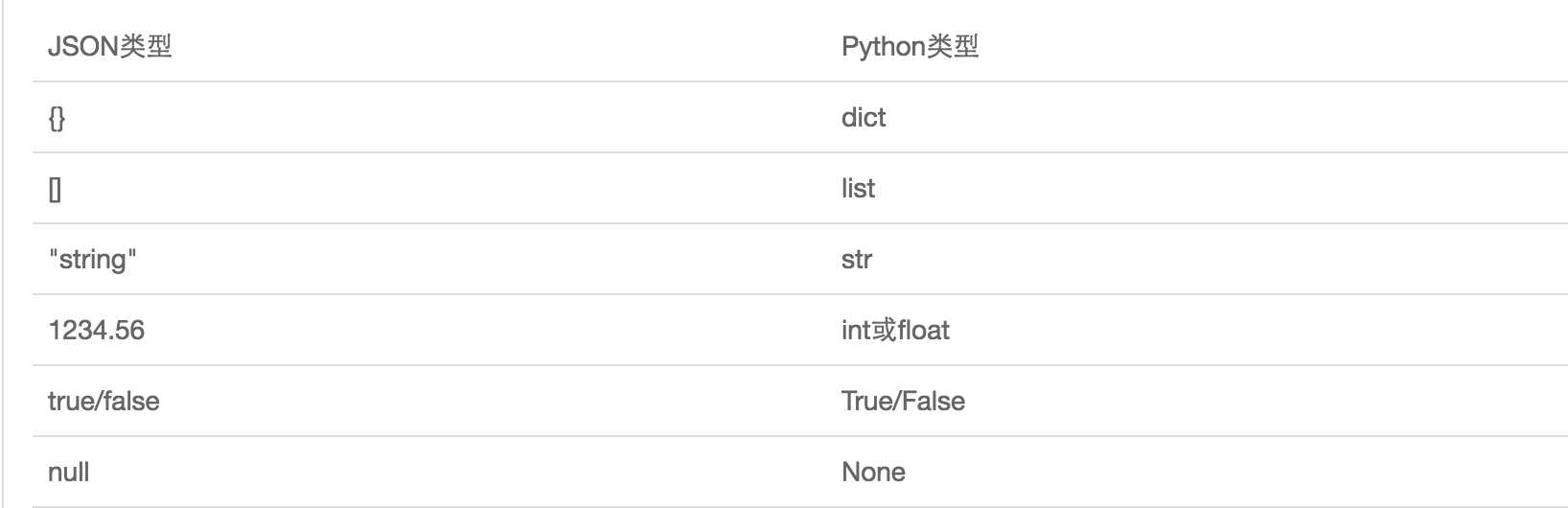
 View Code
View Codepython在文本中的使用:
#----------------------------序列化
import json
dic={‘name‘:‘alvin‘,‘age‘:23,‘sex‘:‘male‘}
print(type(dic))#<class ‘dict‘>
data=json.dumps(dic)
print("type",type(data))#<class ‘str‘>
print("data",data)
f=open(‘序列化对象‘,‘w‘)
f.write(data) #-------------------等价于json.dump(dic,f)
f.close()
#-----------------------------反序列化<br>
import json
f=open(‘序列化对象‘)
new_data=json.loads(f.read())# 等价于data=json.load(f)
print(type(new_data))
##----------------------------序列化
import pickle
dic={‘name‘:‘alvin‘,‘age‘:23,‘sex‘:‘male‘}
print(type(dic))#<class ‘dict‘>
j=pickle.dumps(dic)
print(type(j))#<class ‘bytes‘>
f=open(‘序列化对象_pickle‘,‘wb‘)#注意是w是写入str,wb是写入bytes,j是‘bytes‘
f.write(j) #-------------------等价于pickle.dump(dic,f)
f.close()
#-------------------------反序列化
import pickle
f=open(‘序列化对象_pickle‘,‘rb‘)
data=pickle.loads(f.read())# 等价于data=pickle.load(f)
print(data[‘age‘])
shelve模块比pickle模块简单,只有一个open函数,返回类似字典的对象,可读可写;key必须为字符串,而值可以是python所支持的数据类型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import shelve f = shelve.open(r‘shelve.txt‘) # f[‘stu1_info‘]={‘name‘:‘alex‘,‘age‘:‘18‘}# f[‘stu2_info‘]={‘name‘:‘alvin‘,‘age‘:‘20‘}# f[‘school_info‘]={‘website‘:‘oldboyedu.com‘,‘city‘:‘beijing‘}### f.close() print(f.get(‘stu_info‘)[‘age‘]) |
该模块适用于配置文件的格式与windows ini文件类似,可以包含一个或多个节(section),每个节可以有多个参数(键=值)。
来看一个好多软件的常见文档格式如下:
[DEFAULT] ServerAliveInterval = 45 Compression = yes CompressionLevel = 9 ForwardX11 = yes [bitbucket.org] User = hg [topsecret.server.com] Port = 50022 ForwardX11 = no
如果想用python生成一个这样的文档怎么做呢?
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config["DEFAULT"] = {‘ServerAliveInterval‘: ‘45‘,
‘Compression‘: ‘yes‘,
‘CompressionLevel‘: ‘9‘,
‘ForwardX11‘:‘yes‘
}
config[‘bitbucket.org‘] = {‘User‘:‘hg‘}
config[‘topsecret.server.com‘] = {‘Host Port‘:‘50022‘,‘ForwardX11‘:‘no‘}
with open(‘example.ini‘, ‘w‘) as configfile:
config.write(configfile)
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
#---------------------------查找文件内容,基于字典的形式
print(config.sections()) # []
config.read(‘example.ini‘)
print(config.sections()) # [‘bitbucket.org‘, ‘topsecret.server.com‘]
print(‘bytebong.com‘ in config) # False
print(‘bitbucket.org‘ in config) # True
print(config[‘bitbucket.org‘]["user"]) # hg
print(config[‘DEFAULT‘][‘Compression‘]) #yes
print(config[‘topsecret.server.com‘][‘ForwardX11‘]) #no
print(config[‘bitbucket.org‘]) #<Section: bitbucket.org>
for key in config[‘bitbucket.org‘]: # 注意,有default会默认default的键
print(key)
print(config.options(‘bitbucket.org‘)) # 同for循环,找到‘bitbucket.org‘下所有键
print(config.items(‘bitbucket.org‘)) #找到‘bitbucket.org‘下所有键值对
print(config.get(‘bitbucket.org‘,‘compression‘)) # yes get方法取深层嵌套的值
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read(‘example.ini‘) config.add_section(‘yuan‘) config.remove_section(‘bitbucket.org‘) config.remove_option(‘topsecret.server.com‘,"forwardx11") config.set(‘topsecret.server.com‘,‘k1‘,‘11111‘) config.set(‘yuan‘,‘k2‘,‘22222‘) config.write(open(‘new2.ini‘, "w"))
标签:border space ati message hand 查找 控制 ble 循环
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/heysn21/p/7066966.html