标签:style blog http color os 使用 io ar for
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/accry/article/details/6676009
题意:
原子弹爆炸,一些互不相交的线段,求能辐射到的线段个数(可以将原子弹爆炸点视为泛光源)
分析:
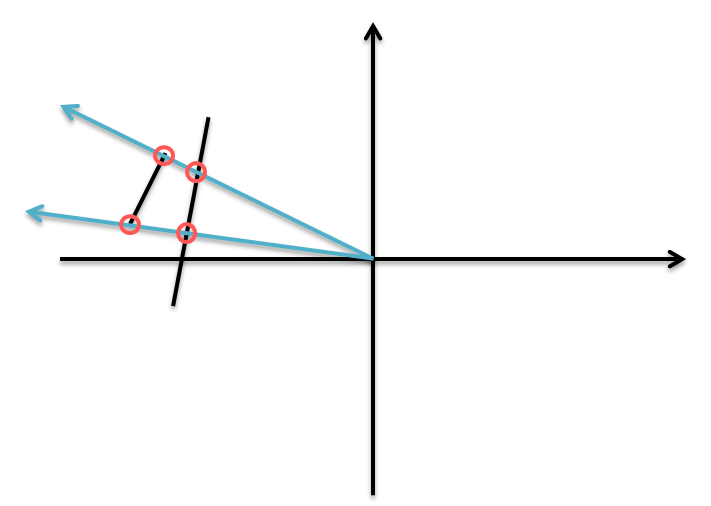
以辐射源为中心对周围的点按照极坐标角度进行排序,然后在极坐标上使用扫描线方法。
维护一个集合,集合内的元素是与扫描线相交的线段,排序依据是线段与扫描线的交点到辐射源的距离。该集合中的最小元素就是被照射到的线段。
有关容器(set)排序依据的说明:
在扫描线运动前后,如果有两个线段存在于容器中,这两个线段与扫描线的交点到辐射源的距离远近关系不会发生变化。若发生变化,表示扫描线运动范围内两个线段有交点,与题目提供的已知条件不符。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <set> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 #define EPS 1e-8 8 #define LS0(a) (a << 1) 9 #define LS1(a) ((a << 1) | 1) 10 11 const int MAXN = 20010; 12 struct Point { 13 double x, y; 14 Point(double _x = 0.0, double _y = 0.0): x(_x), y(_y) {} 15 Point operator + (const Point &b) const { 16 return Point(x + b.x, y + b.y); 17 } 18 Point operator - (const Point &b) const { 19 return Point(x - b.x, y - b.y); 20 } 21 double operator ^ (const Point &b) const { 22 return x * b.y - y * b.x; 23 } 24 bool operator < (const Point &b) const { //逆时针 25 return x * b.y < y * b.x; 26 } 27 void input() { 28 scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y); 29 } 30 double diso() { 31 return sqrt(x * x + y * y); 32 } 33 34 }cur,ps[MAXN]; 35 36 Point lnlncross_pt(Point aa, Point ad, Point ba, Point bd) { // 求直线交点 37 ad = ad - aa; 38 bd = bd - ba; 39 double tmp = bd ^ ad; 40 return Point( 41 (ad.x * bd.x * (ba.y - aa.y) + aa.x * bd.x * ad.y - ba.x * ad.x * bd.y) / tmp, 42 (ad.y * bd.y * (aa.x - ba.x) + ba.y * ad.y * bd.x - aa.y * bd.y * ad.x) / tmp); 43 } 44 45 struct Item { // 扫描线的点类型 46 Point *u, *v; 47 int type; // 1: 线段起点; 0: 线段终点; 48 int sgid; // 线段序号 49 Item(Point *_u = NULL, Point *_v = NULL, int _ty = 0, int _id = 0) 50 : u(_u), v(_v), type(_ty), sgid(_id) {} 51 bool operator < (const Item &b) const { 52 if(u == b.u && v == b.v) 53 return false; 54 Point au = lnlncross_pt(Point(0.0, 0.0), cur, *u, *v); 55 Point bu = lnlncross_pt(Point(0.0, 0.0), cur, *b.u, *b.v); 56 return au.diso() < bu.diso(); 57 } 58 59 }item[MAXN]; 60 61 bool flag[MAXN]; 62 set<Item> Scan; 63 64 65 bool cmp(const Item &a, const Item &b) { //极角排序 从-PI到-PI内 66 return atan2(a.u->y, a.u->x) < atan2(b.u->y, b.u->x); 67 68 } 69 70 void inputps(int n) { 71 Point src, a, b; 72 src.input(); 73 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 74 // 读取线段并求得相对于光源的坐标 75 a.input(); a = a - src; 76 b.input(); b = b - src; 77 // 保证线段的极角序 78 if(b < a) swap(a, b); 79 ps[LS0(i)] = a; 80 ps[LS1(i)] = b; 81 item[LS0(i)] = Item(&ps[LS0(i)], &ps[LS1(i)], 0, i); 82 item[LS1(i)] = Item(&ps[LS1(i)], &ps[LS0(i)], 1, i); 83 } 84 sort(item, item + 2 * n, cmp); 85 } 86 87 88 89 bool sgcross_with_ax(Item &a) { //与射线相交判断 good 以前不知道的东西 90 Point tmp(-1.0, 0.0); 91 return (*a.u ^ *a.v) * (*a.u ^ tmp) > 0.0 92 && (*a.u ^ tmp) * (tmp ^ *a.v) > 0.0; 93 } 94 95 96 97 int main() { 98 int n; 99 while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { 100 inputps(n); 101 memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag)); 102 // 初始化极角扫描器 初始射线向量为(-1.0,0) 103 Scan.clear(); 104 for(int i = 0; i < 2 * n; ++i) { 105 cur = *item[i].u; 106 if(item[i].type == 1 && sgcross_with_ax(item[i])) 107 Scan.insert(item[i]); 108 } 109 // 极角扫描 110 for(int i = 0; i < 2 * n; ++i) { 111 cur = *item[i].u; 112 if(item[i].type == 1) 113 Scan.insert(item[i]); 114 else 115 Scan.erase(Item(item[i].v, item[i].u, 1, item[i].sgid)); 116 if(!Scan.empty()) 117 flag[Scan.begin()->sgid] = true; 118 } 119 int ans = 0; 120 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 121 if(flag[i])ans ++; 122 printf("%d\n", ans); 123 } 124 return 0; 125 126 }
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_64675f540100o02x.html
题目描述:
给你n(50000)个不相交的圆,告诉你各个圆的xy坐标和半径,问你最近的两个圆之间的距离(两圆心之间的距离减去各自的半径)
解题报告:
暴力的做法扫描任意两圆之间的最近距离,取最小值,n^2复杂度,超时。
正解为:
二分枚举每个圆半径的增量mid。
那么此时的每个圆i的半径为R[i] + mid(R[i]为这个圆原来的半径),对于这组新的半径,如果在n个圆中存在两个圆相交,那么就说明mid偏大,反之,如果不存在,则mid偏小。这样就可以达到二分的目的。
二分的复杂度可以在此近似为logn,那么问题转化为:怎样在O(n)或者O(nlogn)的时间内检测出n个圆内是否存在相交的情况,答案是“扫描线”。
常见的扫描线通常利用在正方形的各种检测和求和:在x方向从左到右扫描,y方向用set或者线段树维护当前的线段位置即可,如果覆盖相同的线段即相交。
如下:
从左到右依次扫描竖直的四条线段ABCD,
A:插入1~3的线段
B:插入0~2的线段,和现存的1~3线段冲突,所以存在相交情况。
C:删除1~3线段
D:删除0~2线段
但是现在是圆形,从左到右扫描,一个圆的开始位置和结束位置之间,这个圆的纵向线段长度是在不断变化的,需要另外的一种方法。
这里采用两条扫描线,均是从左向右,每次检测的是这两条扫描线之间的圆的碰撞情况。
如图:
第一条扫描线从左往右依次是每个圆的左边界,即竖直线L1,L2,L3。
第二条扫描线从左往右依次是每个圆的右边界,即竖直线R1,R2,R3。
两条扫描线均是从最左边的L1和R1开始,保证L扫描线的x坐标永远小于R扫描线的x坐标即可。扫描流程如下,假设有n个圆,i为Li,j为Rj:
i = j = 1
while(i <= n or j <= n)
{
if(i == n + 1) 删除圆j,j++;
else if (j == n + 1) 插入圆i,检测圆i的圆心和y方向相邻两圆的碰撞情况。i++。
else if (i <= n and Li 在Ri的左边)
插入圆i,检测圆i的圆心和y方向相邻两圆的碰撞情况。i++。
else 删除圆j,j++;
}
简要解释如下:
While中有4个分支
前两个是边界情况,很容易理解。
第三个是L扫描线的推进,即插入圆。
第四个条件:由于只需检测Li 和 Rj两条扫描线之间的圆的相交情况,所以,Li之前的圆都需要删除
当扫描线为Li和Rj时,已经插入的圆都是x方向起点小于等于Li,x方向终点大于等于Rj,即在Li和Rj之间是连续不间断的,所以只需检测插入圆的圆心的上下相邻的两个即可,不可能跳跃。即假设圆心位置从下到上一次编号1~m,那么插入圆x后,不可能出现x和x+2相交而不和x+1相交的情况(应为在Li和Rj之间是连续的)。
至于检测的方法就是线段树或者set了。
上图的扫描线过程是:
初始为L1,R1
L1 < R1, 插入圆A,检测无碰撞,变为L2,R1
L2 < R1, 插入圆B,检测无碰撞,变为L3, R1
L3 > R1, 删除圆B,变为L3,R2
L3 < R2,插入圆C,检测到碰撞,结束
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<set> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<cmath> 7 using namespace std; 8 #define size 50000 9 #define eps 1e-8 10 #define sqr(x) ((double)(x) * (x)) 11 int Left[size], Right[size], Up[size], up_rank[size]; 12 int X[size], Y[size], R[size]; 13 int t, n; 14 double mid; 15 set<int> mytree; 16 typedef set<int>::iterator it; 17 bool cmp_left(const int &a, const int &b){return (X[a] - R[a] < X[b] - R[b]);} 18 bool cmp_right(const int &a, const int &b){return (X[a] + R[a] < X[b] + R[b]);} 19 bool cmp_up(const int &a, const int &b){if (Y[a] == Y[b]) return X[a] < X[b]; else return Y[a] < Y[b];} 20 bool collid(int a, int b) 21 { 22 a = Up[a]; 23 b = Up[b]; 24 return (sqr(X[a] - X[b]) + sqr(Y[a] - Y[b]) - sqr(R[a] + R[b] + mid + mid) <= 0); 25 } 26 bool insert(int &id) 27 { 28 it i = mytree.insert(id).first; 29 if (i != mytree.begin()) 30 { 31 if (collid(id, *--i)) 32 return false; 33 ++i; 34 } 35 if (++i != mytree.end()) 36 { 37 if (collid(id, *i)) 38 return false; 39 } 40 return true; 41 } 42 bool remove(int v) { 43 it i = mytree.find(v); 44 if (i != mytree.begin() && i != --mytree.end()) { 45 int a = *--i; 46 ++i; 47 int b = *++i; 48 if (collid(a, b)) { 49 return false; 50 } 51 } 52 mytree.erase(v); 53 return true; 54 } 55 56 bool judge() 57 { 58 mytree.clear(); 59 int l = 0, r = 0; 60 while(l < n || r < n) 61 { 62 if (r == n 63 ||l != n && (X[Right[r]] + R[Right[r]] + mid) - (X[Left[l]] - R[Left[l]] - mid) >= 0) 64 { 65 if (!insert(up_rank[Left[l++]])) return true; 66 } 67 else if (!remove(up_rank[Right[r++]])) 68 return true; 69 } 70 return false; 71 } 72 double jeogia() 73 { 74 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 75 Left[i] = Right[i] = Up[i] = i; 76 sort(Left, Left + n, cmp_left); 77 sort(Right, Right + n, cmp_right); 78 sort(Up, Up + n, cmp_up); 79 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 80 up_rank[Up[i]] = i; 81 double s = 0, t = sqrt(sqr(X[0] - X[1]) + sqr(Y[0] - Y[1])) - R[0] - R[1]; 82 while(t - s >= eps) 83 { 84 mid = (s + t) * 0.5; //mid 为各个圆需要加上的半径长度 85 if (judge()) t = mid;//是否有圆相交 86 else s = mid; 87 } 88 return t + s; 89 } 90 int main() 91 { 92 scanf("%d", &t); 93 while(t-- && scanf("%d", &n)) 94 { 95 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 96 scanf("%d%d%d", &X[i], &Y[i], &R[i]); 97 printf("%.6f\n", jeogia()); 98 } 99 return 0; 100 }
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Rlemon/archive/2013/07/31/3227729.html
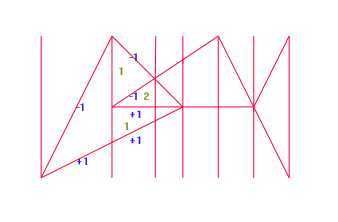
求平面的n个三角形的不同覆盖次数(1 - n)的面积 。
题意:给你n个三角形,问覆盖1~n次的面积各是多少,n < 50;
分析:取出所有端点和交点的x坐标,排序,然后对于每一段xi~xi+1的范围的线段都是不相交的,所以组成的
面积要么是三角形,要么是梯形,可以直接用公式算面积,然后对于每一个三角形的线段都标记该段对于
从下往上的扫描线来说是入边还是出边,然后就可以直接计算出这块面积被覆盖了几次;如入边加1,出边减一
下图,黄色表示覆盖次数;
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<cmath> 6 #include<vector> 7 #include<cstdlib> 8 #define pbk push_back 9 using namespace std; 10 const int N = 25050+10; 11 const double eps = 1e-10; 12 inline double sqr(double x){ 13 return x * x; 14 } 15 inline int dcmp(double x){ 16 return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; 17 } 18 struct Point{ 19 double x,y; 20 int kind; 21 Point(){} 22 Point(double x,double y,int kind = 0):x(x),y(y),kind(kind){} 23 bool operator < (const Point &p)const{ 24 return dcmp(x - p.x) < 0 || ( dcmp(x - p.x) == 0 && dcmp(y - p.y) < 0 ); 25 } 26 Point operator - (const Point &p)const{ 27 return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y); 28 } 29 Point operator + (const Point &p)const{ 30 return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y); 31 } 32 Point operator * (const double &k)const{ 33 return Point (x*k , y*k); 34 } 35 Point operator / (const double &k)const{ 36 return Point (x/k, y/k); 37 } 38 double operator * (const Point &p)const{ 39 return x * p.y - y * p.x; 40 } 41 double operator / (const Point &p)const{ 42 return x * p.x + y * p.y; 43 } 44 void input(){ 45 scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y); 46 } 47 void ot(){ 48 printf("%lf %lf\n",x,y); 49 } 50 }; 51 struct Line{ 52 Point a,b; 53 int kind; 54 Line (){} 55 Line (Point a,Point b,int kind = 0):a(a),b(b),kind(kind){} 56 double operator * (const Point &p)const{ 57 return ( b - a ) * ( p - a ); 58 } 59 double operator / (const Point &p)const{ 60 return ( p - a) / ( p - b); 61 } 62 bool parallel(const Line &v){ 63 return !dcmp( ( b - a ) * ( v.b - v.a ) ); 64 } 65 int LineCrossLine(const Line &v){ 66 if ( (*this).parallel(v) ){ 67 return ( dcmp( v * a ) == 0); 68 }return 2; 69 } 70 int SegCrossSeg(const Line &v){ 71 int d1 = dcmp( (*this) * v.a); 72 int d2 = dcmp( (*this) * v.b); 73 int d3 = dcmp( v * a); 74 int d4 = dcmp( v * b); 75 if ( ( d1 ^ d2 ) == -2 && ( d3 ^ d4 ) == -2 ) return 2; 76 return ( ( d1 == 0 && dcmp( (*this) / v.a ) <= 0 ) 77 || ( d2 == 0 && dcmp( (*this) / v.b ) <= 0 ) 78 || ( d3 == 0 && dcmp( v / a ) <= 0 ) 79 || ( d4 == 0 && dcmp( v / b ) <= 0 ) 80 ); 81 } 82 Point CrossPoint(const Line &v){ 83 double s1 = v * a, s2 = v * b; 84 return ( a * s2 - b * s1) / (s2 - s1); 85 } 86 void input(){ 87 a.input(); b.input(); 88 } 89 void ot(){ 90 a.ot(); b.ot(); 91 } 92 93 }; 94 95 int n,poly_n,xn; 96 vector<double> lx; 97 vector<Line> line; 98 double ans[N]; 99 void init(){ 100 int sz = line.size(); 101 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++){ 102 for (int j = i+1; j < sz; j++){ 103 if (line[i].SegCrossSeg(line[j]) == 2){ 104 Point p = line[i].CrossPoint(line[j]); 105 lx.pbk(p.x); 106 } 107 } 108 } 109 110 sort(lx.begin(),lx.end()); 111 xn = unique(lx.begin(),lx.end()) - lx.begin(); 112 } 113 vector<Point> qu[N]; 114 void work(){ 115 for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) ans[i] = 0; 116 for (int i = 0; i < xn-1; i++){ 117 int k = 0; 118 for (int j = 0; j+1 < qu[i].size(); j++){ 119 k += qu[i][j].kind; 120 ans[ k ] += (lx[i+1] - lx[i]) * (qu[i][j+1].x+qu[i][j+1].y - qu[i][j].x - qu[i][j].y) / 2; 121 } 122 } 123 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%.10lf\n",ans[i]); 124 } 125 void check(){ 126 for (int i = 0; i < xn - 1; i++){ 127 cout<<qu[i].size()<<" >.<"<<endl; 128 for (int j = 0; j < qu[i].size(); j++){ 129 qu[i][j].ot(); cout<<qu[i][j].kind<<endl; 130 } 131 } 132 } 133 void solve(){ 134 for (int i = 0; i < xn; i++) qu[i].clear(); 135 for (int i = 0; i < line.size(); i++){ 136 int j = lower_bound(lx.begin(),lx.begin()+xn,line[i].a.x) - lx.begin(); 137 for (; j+1 < xn; j++ ){ 138 double l = lx[j], r = lx[j+1]; 139 if (dcmp(r - line[i].b.x) > 0) break; 140 Point p1 = line[i].CrossPoint(Line(Point(l,0), Point(l,1))); 141 Point p2 = line[i].CrossPoint(Line(Point(r,0), Point(r,1))); 142 qu[j].pbk(Point(p1.y, p2.y,line[i].kind)); 143 } 144 } 145 for (int i = 0; i < xn - 1; i++) sort(qu[i].begin(), qu[i].end()); 146 // check(); 147 work(); 148 } 149 int main(){ 150 int T; scanf("%d",&T); 151 while (T--){ 152 scanf("%d",&n); 153 lx.clear(); line.clear();; 154 for (int i = 0; i < n ;i++){ 155 Point t[4]; 156 for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++ ){ 157 t[j].input(); 158 } 159 t[3] = t[0]; 160 int flag = 1; 161 if (dcmp( (t[1] - t[0])*(t[2] - t[0]) ) == 0) flag = 0; 162 163 for (int i = 0; i < 3 && flag; i++ ){ 164 lx.pbk(t[i].x); 165 for (int j = i+1; j < 3; j++){ 166 Line tmp; tmp.a = t[i]; tmp.b = t[j]; 167 if (dcmp( tmp.a.x - tmp.b.x ) > 0) swap(tmp.a, tmp.b); 168 169 Line tmp2 = Line(t[3-i-j], Point(t[3-i-j].x, t[3-i-j].y - 1)); 170 if (tmp.LineCrossLine(tmp2) != 2) continue; 171 Point tp = tmp.CrossPoint(tmp2); 172 if (dcmp(tp.y - t[3-i-j].y) < 0) tmp.kind = 1; 173 else tmp.kind = -1; 174 line.pbk(tmp); 175 } 176 } 177 } 178 init(); 179 solve(); 180 } 181 return 0; 182 }
hdu 3255 Farming (矩形体积并)
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/ivan_zjj/article/details/7741133
题意:
有N块农田,每块农田中种一种作物,每种作物都有一个价格,当在同一区域内种植了两种不同的作物时,作物价格大的生存下来,生命值小的死亡。求最后的所有作物的能买的总钱数。
思路:
扫描线求体积并,和前面的一个求体积交差不多。 我们可以将作物的价格看作是立体的高,这样就可以直接枚举Z轴求二维矩形面积并了。本题关键是转化,思路很好。
先将蔬菜价值(即高度)从小到大排序,然后一层一层地开始扫描,计算每层中的面积并,这个就同二维扫描一样。
然后再用面积乘以这层的高度,即得到该层的体积并。然后所有层的体积加起来,即为所求。
把价值等价成高,从价格高的开始枚举
假如i的价格>j的价格,先把价格为i的矩形更新到线段树中,然后价格为i的总价值就是面积(S1)*价格i
然后对于价格j,把i和j价格的矩形都更新到线段树中,然后此时属于j的总价值就是现在的(总面积(S2)-S1)*j;
想象一下长方体,交错在一次,有高有低,怎么求出整个立体形的体积)
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 int N , M ; 5 int h[5] ; 6 const int MAXN = 30010 ; 7 struct point{ 8 int x, y ; 9 void get(){ 10 scanf("%d %d",&x,&y) ; 11 } 12 }; 13 struct Node{ 14 point p1 , p2 ; 15 int h; 16 }p[MAXN] ; 17 18 struct Seg{ 19 int l ,r , h , s ; 20 Seg(){} 21 Seg(int a, int b ,int c, int d) 22 :l(a) , r(b) , h(c) , s(d){} 23 bool operator<(const Seg& cmp) const{ 24 return h < cmp.h ; 25 } 26 }pp[MAXN<<1] ; 27 28 int x[MAXN<<1] ; 29 30 int find(int val , int l, int r){ 31 while( l<r ) { 32 int mid = (l + r)>> 1; 33 if( x[mid] < val ) l = mid + 1 ; 34 else r = mid ; 35 } 36 return l ; 37 } 38 39 int col[MAXN<<3] , sum[MAXN<<3] ; 40 41 void pushup(int l, int r, int idx){ 42 if( col[idx] ) sum[idx] = x[r+1] - x[l] ; 43 else if( l == r ) sum[idx] = 0 ; 44 else{ 45 sum[idx] = sum[idx<<1] + sum[idx<<1|1] ; 46 } 47 } 48 49 void update(int l, int r, int idx, int a , int b , int v){ 50 if(l==a && b==r){ 51 col[idx] += v ; 52 pushup(l , r , idx); 53 return ; 54 } 55 int mid = (l + r)>> 1; 56 int ls = idx<<1 , rs = idx<<1|1 ; 57 if( b<=mid ) update(l , mid ,ls , a , b, v); 58 else if( mid<a ) update(mid+1, r, rs ,a ,b , v ); 59 else{ 60 update( l ,mid , ls , a, mid, v ); 61 update( mid+1, r, rs, mid+1, b , v ); 62 } 63 pushup(l ,r, idx); 64 } 65 66 void solve(){ 67 std::sort(h+1, h+M+1) ; 68 h[0] = 0 ; 69 __int64 res = 0 ; 70 for(int i=1;i<=M;i++){ 71 int hh = h[i] ; 72 int m = 0 ; 73 for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){ 74 if( p[j].h >= hh ){ 75 pp[m] = Seg( p[j].p1.x , p[j].p2.x ,p[j].p1.y , 1 ) ; 76 x[m++] = p[j].p1.x ; 77 pp[m] = Seg( p[j].p1.x , p[j].p2.x ,p[j].p2.y , -1 ); 78 x[m++] = p[j].p2.x ; 79 } 80 } 81 std::sort( x , x+m ); 82 std::sort(pp ,pp+m ); 83 int n = 1 ; 84 for(int j=1;j<m;j++){ 85 if( x[j-1] != x[j] ) x[n++] = x[j] ; 86 } 87 n-- ; 88 memset(col, 0, sizeof(col) ); 89 memset(sum, 0 ,sizeof(sum) ); 90 __int64 ans = 0 ; 91 92 for(int j=0;j<m-1;j++){ 93 int s = find( pp[j].l, 0 ,n ); 94 int e = find( pp[j].r , 0 , n ) - 1 ; 95 if(s <= e) update(0, MAXN<<1 ,1 , s, e ,pp[j].s ); 96 ans += (__int64)(sum[1])*(__int64)( pp[j+1].h - pp[j].h ); 97 } 98 res += ans*(__int64)( h[i] - h[i-1] ) ; 99 } 100 printf("%I64d\n",res); 101 } 102 103 int main(){ 104 int ncas , cas ; 105 scanf("%d",&ncas); 106 for(cas=1 ;cas<=ncas ; cas++){ 107 scanf("%d %d",&N, &M ); 108 for(int i=1;i<=M;i++){ 109 scanf("%d",&h[i]); 110 } 111 for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){ 112 p[i].p1.get() ; 113 p[i].p2.get() ; 114 int a ; 115 scanf("%d",&a); 116 p[i].h = h[a] ; 117 } 118 printf("Case %d: ",cas); 119 solve() ; 120 } 121 return 0 ; 122 }
标签:style blog http color os 使用 io ar for
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bfshm/p/3946370.html