标签:each arch 处理 code second etc pid hashset ram
前言
最近工作中是做日志分析的平台,采用了sparkstreaming+kafka,采用kafka主要是看中了它对大数据量处理的高性能,处理日志类应用再好不过了,采用了sparkstreaming的流处理框架 主要是考虑到它本身是基于spark核心的,以后的批处理可以一站式服务,并且可以提供准实时服务到elasticsearch中,可以实现准实时定位系统日志。
实现
Spark-Streaming获取kafka数据的两种方式-Receiver与Direct的方式。
一. 基于Receiver方式
这种方式使用Receiver来获取数据。Receiver是使用Kafka的高层次Consumer API来实现的。receiver从Kafka中获取的数据都是存储在Spark Executor的内存中的,然后Spark Streaming启动的job会去处理那些数据。代码如下:
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("log-etl").setMaster("local[4]"); JavaStreamingContext jssc = new JavaStreamingContext(sparkConf, new Duration(2000)); int numThreads = Integer.parseInt("4"); Map<String, Integer> topicMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); topicMap.put("group-45", numThreads); //接收的参数分别是JavaStreamingConetxt,zookeeper连接地址,groupId,kafak的topic JavaPairReceiverInputDStream<String, String> messages = KafkaUtils.createStream(jssc, "172.16.206.27:2181,172.16.206.28:2181,172.16.206.29:2181", "1", topicMap);
刚开始的时候系统正常运行,没有发现问题,但是如果系统异常重新启动sparkstreaming程序后,发现程序会重复处理已经处理过的数据,这种基于receiver的方式,是使用Kafka的高阶API来在ZooKeeper中保存消费过的offset的。这是消费Kafka数据的传统方式。这种方式配合着WAL机制可以保证数据零丢失的高可靠性,但是却无法保证数据被处理一次且仅一次,可能会处理两次。因为Spark和ZooKeeper之间可能是不同步的。官方现在也已经不推荐这种整合方式,官网相关地址 http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-kafka-integration.html ,下面我们使用官网推荐的第二种方式kafkaUtils的createDirectStream()方式。
二.基于Direct的方式
这种新的不基于Receiver的直接方式,是在Spark 1.3中引入的,从而能够确保更加健壮的机制。替代掉使用Receiver来接收数据后,这种方式会周期性地查询Kafka,来获得每个topic+partition的最新的offset,从而定义每个batch的offset的范围。当处理数据的job启动时,就会使用Kafka的简单consumer api来获取Kafka指定offset范围的数据。
代码如下:
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("log-etl"); JavaStreamingContext jssc = new JavaStreamingContext(sparkConf, Durations.seconds(2)); HashSet<String> topicsSet = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(topics.split(","))); HashMap<String, String> kafkaParams = new HashMap<String, String>(); kafkaParams.put("metadata.broker.list", brokers); // Create direct kafka stream with brokers and topics JavaPairInputDStream<String, String> messages = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream( jssc, String.class, String.class, StringDecoder.class, StringDecoder.class, kafkaParams, topicsSet );
这种direct方式的优点如下:
1.简化并行读取:如果要读取多个partition,不需要创建多个输入DStream然后对它们进行union操作。Spark会创建跟Kafka partition一样多的RDD partition,并且会并行从Kafka中读取数据。所以在Kafka partition和RDD partition之间,有一个一对一的映射关系。
2.一次且仅一次的事务机制:基于receiver的方式,在spark和zk中通信,很有可能导致数据的不一致。
3.高效率:在receiver的情况下,如果要保证数据的不丢失,需要开启wal机制,这种方式下,为、数据实际上被复制了两份,一份在kafka自身的副本中,另外一份要复制到wal中, direct方式下是不需要副本的。
三.基于Direct方式丢失消息的问题
貌似这种方式很完美,但是还是有问题的,当业务需要重启sparkstreaming程序的时候,业务日志依然会打入到kafka中,当job重启后只能从最新的offset开始消费消息,造成重启过程中的消息丢失。kafka中的offset如下图(使用kafkaManager实时监控队列中的消息):
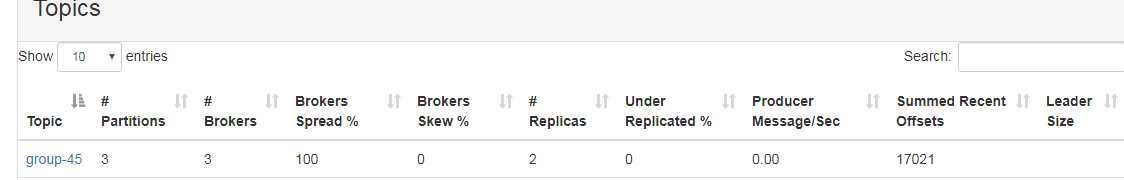
当停止业务日志的接受后,先重启spark程序,但是发现job并没有将先前打入到kafka中的数据消费掉。这是因为消息没有经过zk,topic的offset也就没有保存
四.解决消息丢失的处理方案
一般有两种方式处理这种问题,可以先spark streaming 保存offset,使用spark checkpoint机制,第二种是程序中自己实现保存offset逻辑,我比较喜欢第二种方式,以为这种方式可控,所有主动权都在自己手中。
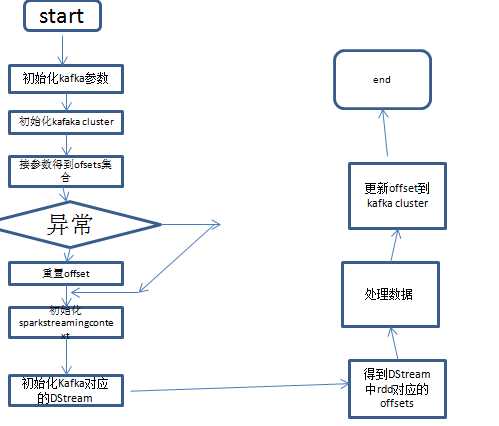
先看下大体流程图,
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]").setAppName("log-etl"); Set<String> topicSet = new HashSet<String>(); topicSet.add("group-45"); kafkaParam.put("metadata.broker.list", "172.16.206.17:9092,172.16.206.31:9092,172.16.206.32:9092"); kafkaParam.put("group.id", "simple1"); // transform java Map to scala immutable.map scala.collection.mutable.Map<String, String> testMap = JavaConversions.mapAsScalaMap(kafkaParam); scala.collection.immutable.Map<String, String> scalaKafkaParam = testMap.toMap(new Predef.$less$colon$less<Tuple2<String, String>, Tuple2<String, String>>() { public Tuple2<String, String> apply(Tuple2<String, String> v1) { return v1; } }); // init KafkaCluster kafkaCluster = new KafkaCluster(scalaKafkaParam); scala.collection.mutable.Set<String> mutableTopics = JavaConversions.asScalaSet(topicSet); immutableTopics = mutableTopics.toSet(); scala.collection.immutable.Set<TopicAndPartition> topicAndPartitionSet2 = kafkaCluster.getPartitions(immutableTopics).right().get(); // kafka direct stream 初始化时使用的offset数据 Map<TopicAndPartition, Long> consumerOffsetsLong = new HashMap<TopicAndPartition, Long>(); // 没有保存offset时(该group首次消费时), 各个partition offset 默认为0 if (kafkaCluster.getConsumerOffsets(kafkaParam.get("group.id"), topicAndPartitionSet2).isLeft()) { System.out.println(kafkaCluster.getConsumerOffsets(kafkaParam.get("group.id"), topicAndPartitionSet2).left().get()); Set<TopicAndPartition> topicAndPartitionSet1 = JavaConversions.setAsJavaSet((scala.collection.immutable.Set)topicAndPartitionSet2); for (TopicAndPartition topicAndPartition : topicAndPartitionSet1) { consumerOffsetsLong.put(topicAndPartition, 0L); } } // offset已存在, 使用保存的offset else { scala.collection.immutable.Map<TopicAndPartition, Object> consumerOffsetsTemp = kafkaCluster.getConsumerOffsets("simple1", topicAndPartitionSet2).right().get(); Map<TopicAndPartition, Object> consumerOffsets = JavaConversions.mapAsJavaMap((scala.collection.immutable.Map)consumerOffsetsTemp); Set<TopicAndPartition> topicAndPartitionSet1 = JavaConversions.setAsJavaSet((scala.collection.immutable.Set)topicAndPartitionSet2); for (TopicAndPartition topicAndPartition : topicAndPartitionSet1) { Long offset = (Long)consumerOffsets.get(topicAndPartition); consumerOffsetsLong.put(topicAndPartition, offset); } } JavaStreamingContext jssc = new JavaStreamingContext(sparkConf, new Duration(5000)); kafkaParamBroadcast = jssc.sparkContext().broadcast(kafkaParam); // create direct stream JavaInputDStream<String> message = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream( jssc, String.class, String.class, StringDecoder.class, StringDecoder.class, String.class, kafkaParam, consumerOffsetsLong, new Function<MessageAndMetadata<String, String>, String>() { public String call(MessageAndMetadata<String, String> v1) throws Exception { System.out.println("接收到的数据《《==="+v1.message()); return v1.message(); } } ); // 得到rdd各个分区对应的offset, 并保存在offsetRanges中 final AtomicReference<OffsetRange[]> offsetRanges = new AtomicReference<OffsetRange[]>(); JavaDStream<String> javaDStream = message.transform(new Function<JavaRDD<String>, JavaRDD<String>>() { public JavaRDD<String> call(JavaRDD<String> rdd) throws Exception { OffsetRange[] offsets = ((HasOffsetRanges) rdd.rdd()).offsetRanges(); offsetRanges.set(offsets); return rdd; } }); // output javaDStream.foreachRDD(new Function<JavaRDD<String>, Void>() { public Void call(JavaRDD<String> v1) throws Exception { if (v1.isEmpty()) return null; List<String> list = v1.collect(); for(String s:list){ System.out.println("数据==="+s); } for (OffsetRange o : offsetRanges.get()) { // 封装topic.partition 与 offset对应关系 java Map TopicAndPartition topicAndPartition = new TopicAndPartition(o.topic(), o.partition()); Map<TopicAndPartition, Object> topicAndPartitionObjectMap = new HashMap<TopicAndPartition, Object>(); topicAndPartitionObjectMap.put(topicAndPartition, o.untilOffset()); // 转换java map to scala immutable.map scala.collection.mutable.Map<TopicAndPartition, Object> testMap = JavaConversions.mapAsScalaMap(topicAndPartitionObjectMap); scala.collection.immutable.Map<TopicAndPartition, Object> scalatopicAndPartitionObjectMap = testMap.toMap(new Predef.$less$colon$less<Tuple2<TopicAndPartition, Object>, Tuple2<TopicAndPartition, Object>>() { public Tuple2<TopicAndPartition, Object> apply(Tuple2<TopicAndPartition, Object> v1) { return v1; } }); // 更新offset到kafkaCluster kafkaCluster.setConsumerOffsets(kafkaParamBroadcast.getValue().get("group.id"), scalatopicAndPartitionObjectMap); System.out.println("原数据====》"+o.topic() + " " + o.partition() + " " + o.fromOffset() + " " + o.untilOffset() ); } return null; } }); jssc.start(); jssc.awaitTermination(); }
基本使用这种方式就可以解决数据丢失的问题。
文章来源:https://my.oschina.net/u/1792341/blog/1341327
SparkStreaming与Kafka整合遇到的问题及解决方案
标签:each arch 处理 code second etc pid hashset ram
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wyfjk/p/7162131.html