标签:style blog http color os 使用 strong ar for
傅里叶变换在信息处理应用中具有很实用的价值,而快速傅里叶变换,即FFT,是实用的计算算法。
本文介绍FFT和2维FFT的C#实现方法。
1. FFT编程依据
FFT是按照如图结构(也称蝶形结构)进行运算(图片来源于网络)。
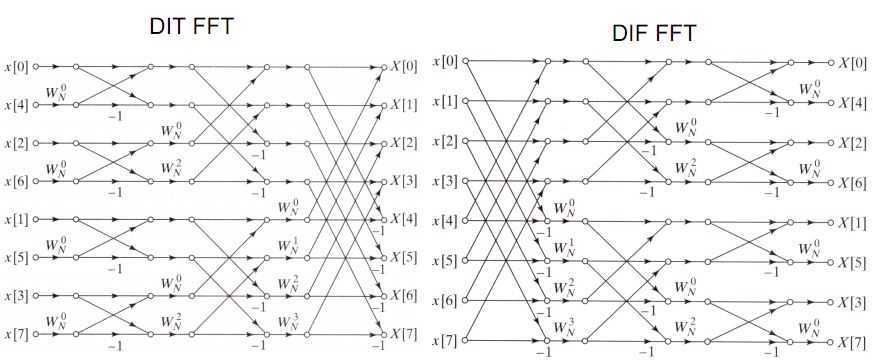
图中,箭头代表数据流向,箭头与箭头的合并点代表相加,箭头下面的常数代表相乘,WN(注:N为下标) = exp(-j * 2 * PI / N),j为虚数单位,DIT的输入(或DIF的输出)序列重排点y[m]与初始输入点x[n]的关系为:m与n互为倒位序(例:001 -- 100,011 -- 110)。
该图给出的是8点FFT例程,其余2^N点FFT可按照这个图进行类推,类推后可以发现,2^N点FFT只需用三个循环套嵌即可实现。
对于idft的算法,根据公式X[k] = 对n求和{x[n] * (WN) ^ kn}以及x[n] = 对k求和{X[k] * (WN) ^ (-kn)} /N可知,只需将FFT算法中的WN换为(1 / WN)并将最后结果除以N即可得到idft。
2. FFT算法实现
由于作者并不擅长面向对象编程,仅仅是在功能上实现了本文需求,代码在阅读、效率上有很多缺陷。
下面是FFT算法的实现,完整的实现在文章后面。
// 快速傅里叶变换 // 作者:死猫 // ComplexList src:数据输入 // ref int lenght:欲变换数据的长度,函数调用后此值更改为实际变换长度 // int flag:区分fft或dtft,为1为fft,为-1为idft private static ComplexList fft_core(ComplexList src, ref int lenght, int flag) { //按时间抽取FFT方法(DIT) //补零后长度 int relog2N = ReLog2N(lenght); int bitlenghth = relog2N; int N = 0x01 << bitlenghth; //重新复制数据,同时进行 // 逆序排放,并补零 int index; ComplexList Register = new ComplexList(N); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { index = ReArrange(i, bitlenghth); Register[i] = (index < src.Lenght) ? src[index] : new Complex(0); } //生成WN表,以免运行时进行重复计算 ComplexList WN = new ComplexList(N / 2); for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++) { WN[i] = new Complex(Math.Cos(2 * Math.PI / N * i), -flag * Math.Sin(2 * Math.PI / N * i)); } //蝶形运算 int Index0, Index1; Complex temp; for (int steplenght = 2; steplenght <= N; steplenght *= 2) { for (int step = 0; step < N / steplenght; step++) { for (int i = 0; i < steplenght / 2; i++) { Index0 = steplenght * step + i; Index1 = steplenght * step + i + steplenght / 2; temp = Register[Index1] * WN[N / steplenght * i]; Register[Index1] = Register[Index0] - temp; Register[Index0] = Register[Index0] + temp; } } } //若为idft if (-1 == flag) { for (int i = 0; i < Register.Lenght; i++) { Register[i] /= N; } } //赋值 lenght = N; /* //清理内存 WN = null; temp = null; GC.Collect(); */ //返回 return Register; }
3. 二维FFT变换
2维傅里叶变换是在1维傅里叶变换基础上实现的,实现方法为:
1. 对2维输入数据的每一行进行FFT变换,变换结果仍然按行存入一个二维数组中;
2. 对按行FFT变换后的结果,对每一列进行FFT变换,变换结果仍然按列存入一个二维数组中,该数组即为2维FFT变换结果。
代码实现如下:
// 2维快速傅里叶变换 // 作者:死猫 // int width, int height:欲变换数据的长度和宽度,函数调用后此值更改为实际变换长度 // int flag:区分fft或dtft,为1为fft,为-1为idft private static Complex2D fft_2D_core(Complex2D src, ref int width, ref int height, int flag) { //补零后长度 int width_Log2N = ReLog2N(width); int height_Log2N = ReLog2N(height); int Relog2N = Math.Max(width_Log2N, height_Log2N); int ReWidth = 0x01 << Relog2N; int ReHeight = 0x01 << Relog2N; //重新复制数据,清零 Complex2D ReList2D = new Complex2D(ReWidth, ReHeight); ReList2D.Clear(); int width_temp = Math.Min(src.Width, width); int height_temp = Math.Min(src.Height, height); for (int i = 0; i < height_temp; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < width_temp; j++) { ReList2D[i, j] = new Complex(src[i, j].Re, src[i, j].Im); } } ComplexList Xn; ComplexList Xk; int Lenght_temp; //第1遍fft for (int i = 0; i < ReHeight; i++) { Xn = ReList2D.GetRow(i); Lenght_temp = Xn.Lenght; Xk = fft_core(Xn, ref Lenght_temp, flag); ReList2D.SetRow(i, Xk); } //第2遍fft for (int i = 0; i < ReWidth; i++) { Xn = ReList2D.GetColumn(i); Lenght_temp = Xn.Lenght; Xk = fft_core(Xn, ref Lenght_temp, flag); ReList2D.SetColumn(i, Xk); } //赋值 width = ReWidth; height = ReHeight; //清理内存 Xn = null; Xk = null; GC.Collect(); //返回 return ReList2D; }
3. 二维FFT测试结果
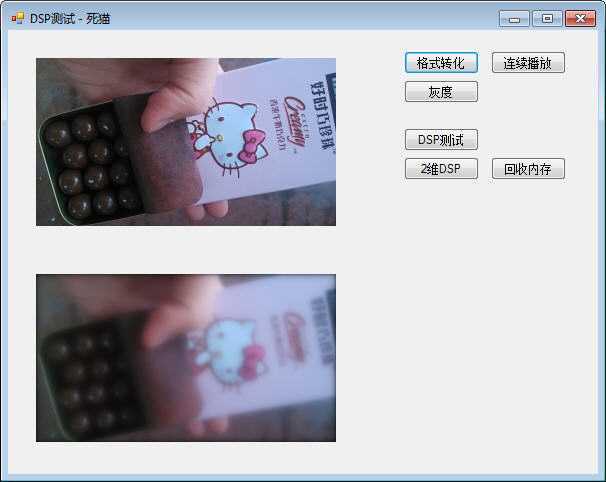
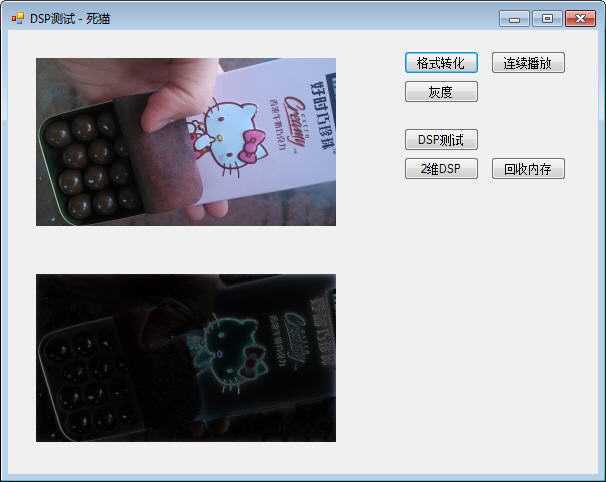
我对一张图片进行低通、高通滤波,其传输函数分别为:
低通:Hlp(z) = (1 - a) / 2 * (1 + 1 / z) / (1 - a * 1 / z),a = 0.8;
高通:Hhp(z) = (1 + a) / 2 * (1 - 1 / z) / (1 - a * 1 / z),a = 0.7。
低通、高通滤波测试结果分别如下:
4. 其余相关代码实现
由于作者并不擅长面向对象编程,仅仅是在功能上实现了本文需求,代码在阅读、效率上有很多缺陷。
代码1:
// 快速傅里叶变换 // ComplexList src:数据输入,若长度非2的n次幂, // 则函数对末尾补零后的数据进行运算 public static ComplexList fft(ComplexList src) { int lenght = src.Lenght; return fft_core(src, ref lenght, 1); } // 快速傅里叶变换 // ComplexList src:数据输入 // ref int lenght:欲变换的长度,函数调用后此值更改为实际变换长度 public static ComplexList fft(ComplexList src, ref int lenght) { return fft_core(src, ref lenght, 1); } // 快速傅里叶变换的逆变换 // ComplexList src:数据输入 public static ComplexList idft(ComplexList src) { int lenght = src.Lenght; return idft(src, ref lenght); } // 快速傅里叶变换的逆变换 // ComplexList src:数据输入 // ref int lenght:欲变换数据的长度,函数调用后此值更改为实际变换长度 public static ComplexList idft(ComplexList src, ref int lenght) { return fft_core(src, ref lenght, -1); } public static Complex2D fft_2D(Complex2D src) { int width = src.Width; int height = src.Height; return fft_2D_core(src, ref width, ref height, 1); } public static Complex2D idft_2D(Complex2D src) { int width = src.Width; int height = src.Height; return fft_2D_core(src, ref width, ref height, -1); }
代码2:
// 获取按位逆序,bitlenght为数据长度 // fft函数内使用 private static int ReArrange(int dat, int bitlenght) { int ret = 0; for (int i = 0; i < bitlenght; i++) { if (0 != (dat & (0x01 << i))) ret |= ((0x01 << (bitlenght - 1)) >> i); } return ret; } // 获取扩展长度后的幂次 // 由于fft要求长度为2^n,所以用此函数来获取所需长度 public static int ReLog2N(int count) { int log2N = 0; uint mask = 0x80000000; for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if (0 != ((mask >> i) & count)) { if ((mask >> i) == count) log2N = 31 - i; else log2N = 31 - i + 1; break; } } return log2N; }
代码3:
public class Complex2D { double[] _Complex2D_Re; double[] _Complex2D_Im; public int Width { get; private set; } public int Height { get; private set; } public Complex this[int Row, int Column] { get { return new Complex(_Complex2D_Re[Row * Width + Column], _Complex2D_Im[Row * Width + Column]); } set { _Complex2D_Re[Row * Width + Column] = ((Complex)value).Re; _Complex2D_Im[Row * Width + Column] = ((Complex)value).Im; } } public Complex2D(int width, int height) { Width = width; Height = height; int lenght = Width * Height; _Complex2D_Re = new double[lenght]; _Complex2D_Im = new double[lenght]; } public void Clear() { Array.Clear(_Complex2D_Re, 0, _Complex2D_Re.Length); Array.Clear(_Complex2D_Im, 0, _Complex2D_Im.Length); } public ComplexList GetColumn(int index) { ComplexList ret = new ComplexList(Height); for(int i = 0; i < Height; i++) { ret[i] = this[i, index]; } return ret; } public int SetColumn(int index, ComplexList src) { for (int i = 0; i < Height; i++) { this[i, index] = (i < src.Lenght) ? src[i] : new Complex(0); } return 0; } public ComplexList GetRow(int index) { ComplexList ret = new ComplexList(Width); for(int i = 0; i < Width; i++) { ret[i] = this[index, i]; } return ret; } public int SetRow(int index, ComplexList src) { for (int i = 0; i < Width; i++) { this[index, i] = (i < src.Lenght) ? src[i] : new Complex(0); } return 0; } public Complex2D GetAmplitude() { Complex2D ret = new Complex2D(Width, Height); for (int i = 0; i < Height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < Width; j++) { ret[i, j] = new Complex(this[i, j].Modulus()); } } return ret; } } public class ComplexList { double[] _ComplexList_Re; double[] _ComplexList_Im; public int Lenght { get; private set; } public Complex this[int Index] { get { return new Complex(_ComplexList_Re[Index], _ComplexList_Im[Index]); } set { _ComplexList_Re[Index] = ((Complex)value).Re; _ComplexList_Im[Index] = ((Complex)value).Im; } } public ComplexList(int lenght) { Lenght = lenght; _ComplexList_Re = new double[Lenght]; _ComplexList_Im = new double[Lenght]; } public ComplexList(double[] re) { Lenght = re.Length; _ComplexList_Re = re; _ComplexList_Im = new double[Lenght]; } public ComplexList(double[] re, double[] im) { Lenght = Math.Max(re.Length, im.Length); if (re.Length == im.Length) { _ComplexList_Re = re; _ComplexList_Im = im; } else { _ComplexList_Re = new double[Lenght]; _ComplexList_Im = new double[Lenght]; for (int i = 0; i < re.Length; i++) _ComplexList_Re[i] = re[i]; for (int i = 0; i < im.Length; i++) _ComplexList_Im[i] = im[i]; } } public void Clear() { Array.Clear(_ComplexList_Re, 0, _ComplexList_Re.Length); Array.Clear(_ComplexList_Im, 0, _ComplexList_Im.Length); } public double[] GetRePtr() { return _ComplexList_Re; } public double[] GetImPtr() { return _ComplexList_Im; } public ComplexList Clone() { return new ComplexList((double[])(_ComplexList_Re.Clone()), (double[])(_ComplexList_Im.Clone())); } public ComplexList GetAmplitude() { double[] amp = new double[Lenght]; for (int i = 0; i < Lenght; i++) { amp[i] = this[i].Modulus(); } return new ComplexList(amp); } } public class Complex { public double Re; public double Im; public Complex() { Re = 0; Im = 0; } public Complex(double re) { Re = re; Im = 0; } public Complex(double re, double im) { Re = re; Im = im; } public double Modulus() { return Math.Sqrt(Re * Re + Im * Im); } public override string ToString() { string retStr; if (Math.Abs(Im) < 0.0001) retStr = Re.ToString("f4"); else if (Math.Abs(Re) < 0.0001) { if (Im > 0) retStr = "j" + Im.ToString("f4"); else retStr = "- j" + (0 - Im).ToString("f4"); } else { if (Im > 0) retStr = Re.ToString("f4") + "+ j" + Im.ToString("f4"); else retStr = Re.ToString("f4") + "- j" + (0 - Im).ToString("f4"); } retStr += " "; return retStr; } //操作符重载 public static Complex operator +(Complex c1, Complex c2) { return new Complex(c1.Re + c2.Re, c1.Im + c2.Im); } public static Complex operator +(double d, Complex c) { return new Complex(d + c.Re, c.Im); } public static Complex operator -(Complex c1, Complex c2) { return new Complex(c1.Re - c2.Re, c1.Im - c2.Im); } public static Complex operator -(double d, Complex c) { return new Complex(d - c.Re, -c.Im); } public static Complex operator *(Complex c1, Complex c2) { return new Complex(c1.Re * c2.Re - c1.Im * c2.Im, c1.Re * c2.Im + c2.Re * c1.Im); } public static Complex operator *(Complex c, double d) { return new Complex(c.Re * d, c.Im * d); } public static Complex operator *(double d, Complex c) { return new Complex(c.Re * d, c.Im * d); } public static Complex operator /(Complex c, double d) { return new Complex(c.Re / d, c.Im / d); } public static Complex operator /(double d, Complex c) { double temp = d / (c.Re * c.Re + c.Im * c.Im); return new Complex(c.Re * temp, -c.Im * temp); } public static Complex operator /(Complex c1, Complex c2) { double temp = 1 / (c2.Re * c2.Re + c2.Im * c2.Im); return new Complex((c1.Re * c2.Re + c1.Im * c2.Im) * temp, (-c1.Re * c2.Im + c2.Re * c1.Im) * temp); } }
标签:style blog http color os 使用 strong ar for
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Si-Mao/p/3950023.html