标签:方法 void util package int 情况 else 类对象 data
this:(this表示当前对象)
--在类的方法定义中使用this关键字代表使用该方法的对象的引用
--当必须指出当前使用方法的对象是谁时要使用this
--有时this可以处理方法中成员变量和参数重名的情况
--this可以看作是一个变量, 它的值是当前对象的引用
static 静态的(不在堆里面也不在栈里面, 在数据区(data seg)):
--类名直接 . 出来的变量是静态变量, 每个类里面的静态变量只有一份, 是公用的(赋值后每个实例化的类都可使用)
--静态方法中不可访问非静态成员
--静态变量和静态方法不需要实例化
被声明为static的变量、常量和方法被称为静态成员。静态成员是属于类所有的,区别于个别对象,可以在本类或其他类使用类名和 " . " 运算符调用静态成员。
语法格式为: 类名.静态类成员
在Java语句中对静态方法有以下两点规定:
1.在静态方法中,不可以使用this关键字
2.在静态方法中,不可以直接调用非静态方法
package com.hanqi.maya.model; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //System.out.println(Person.currentNum); Person p1 = new Person(); Person p2 = new Person(); Person p3 = new Person(); // static 静态变量, 不管你实例化多少个, 都共享一份 p1.currentNum = 2; System.out.println(p2.currentNum++); //输出值为:2 System.out.println(p3.currentNum); //输出值为:3 } }
package:
便于管理大型软件系统中数目众多的类, 解决类名重名的现象
puclic class 类名 {
private 类型 属性1;
private 类型 属性2;
set, get
}
package com.hanqi.maya.model; public class Person { private String name; private String sex; public Person(String name, String sex) { super(); this.name = name; this.sex = sex; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; }
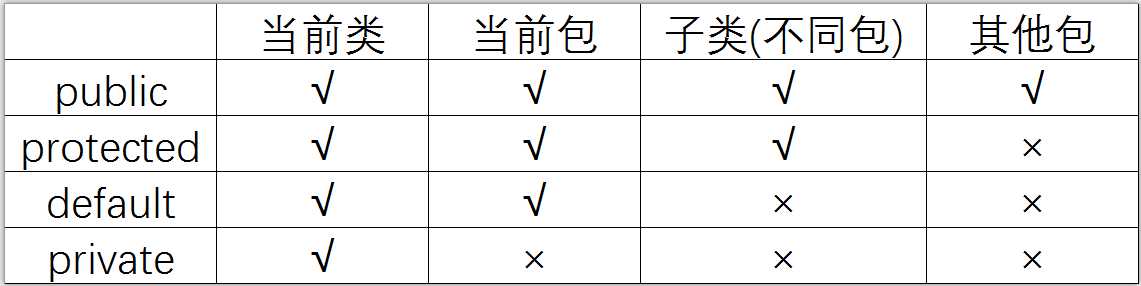
super: 指向父类的引用
this: 指向当前类的引用
final的变量值不能改变
final的方法不能被重写
final的类不能被继承
1.简单一点的案例:
package com.hanqi.maya.model; public class Pet { //父类,宠物 protected String name; protected int sex; protected int age; protected int happy; protected int healthy; protected int hungry; public Pet(){ //空的构造方法 } public Pet(String name, int sex){ //有参数的构造方法 this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = 1; this.happy = 80; this.healthy = 100; this.hungry = 80; } public void playGame(){ } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(int sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getHappy() { return happy; } public void setHappy(int happy) { this.happy = happy; } public int getHealthy() { return healthy; } public void setHealthy(int healthy) { this.healthy = healthy; } public int getHungry() { return hungry; } public void setHungry(int hungry) { this.hungry = hungry; } }
package com.hanqi.maya.model; //子类,猫(也可以为狗啊、猪啊之类的) public class Cat extends Pet { //extends 表示继承 public Cat(){ } public Cat(String catNmane, int catSex){ super(catNmane, catSex); //super,关键字,父类对象的引用 } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("宠物名称" + this.name); System.out.println("宠物性别" + this.sex); System.out.println("宠物年龄" + this.age); System.out.println("开心值" + this.happy); System.out.println("健康值" + this.healthy); System.out.println("饥饿度" + this.hungry); } }
package com.hanqi.maya.text; import com.hanqi.maya.model.Cat; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat cat = new Cat("花花", 1); //实例化 cat.showInfo(); //调用子类(猫)方法,执行 } }
控制台输出:

2.添加一些玩法或者其他操作
package com.hanqi.maya.model; public class Pet { //父类,宠物 protected String name; protected int sex; protected int age; protected int happy; protected int healthy; protected int hungry; public Pet(){ //空的构造方法 } public Pet(String name, int sex){ //有参数的构造方法 this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = 1; this.happy = 80; this.healthy = 100; this.hungry = 80; } public void playGame(){ //添加一个情况,玩游戏,改变值 if(!check()){ System.out.println("各项属性值不能为负数!"); return; } System.out.println("与"+this.name+"一起玩"); this.happy += 10; this.healthy -= 5; this.hungry += 12; } public void eat(){ //添加一个情况,吃东西,改变值 if(!check()){ System.out.println("各项属性值不能为负数!"); return; } System.out.println("与"+this.name+"一起吃"); this.healthy += 5; this.hungry -= 20; } public boolean check(){ //总的一个判断条件,确保各项属性值不为负数 if(this.happy>0 && this.healthy>0 && this.hungry>0){ return true; } if(happy<0){ happy = 0; }if(healthy<0){ healthy = 0; }if(hungry<0){ hungry = 0; } return false; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(int sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getHappy() { return happy; } public void setHappy(int happy) { this.happy = happy; } public int getHealthy() { return healthy; } public void setHealthy(int healthy) { this.healthy = healthy; } public int getHungry() { return hungry; } public void setHungry(int hungry) { this.hungry = hungry; } }
package com.hanqi.maya.model; //子类,猫(也可以为狗啊、猪啊之类的) public class Cat extends Pet { //extends 表示继承 public Cat(){ } public Cat(String catNmane, int catSex){ super(catNmane, catSex); //super,关键字,父类对象的引用 } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("宠物名称" + this.name); System.out.println("宠物性别" + this.sex); System.out.println("宠物年龄" + this.age); System.out.println("开心值" + this.happy); System.out.println("健康值" + this.healthy); System.out.println("饥饿度" + this.hungry); } }
package com.hanqi.maya.text; import com.hanqi.maya.model.Cat; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat cat = new Cat("花花", 1); //实例化 cat.playGame(); cat.eat(); cat.eat(); cat.eat(); cat.eat(); cat.eat(); cat.eat(); cat.showInfo(); } }

3.最后一种情况
package com.hanqi.maya.model; public class Pet { //父类,宠物 protected String name; protected int sex; protected int age; protected int happy; protected int healthy; protected int hungry; public Pet(){ //空的构造方法 } public Pet(String name, int sex){ //有参数的构造方法 this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = 1; this.happy = 80; this.healthy = 100; this.hungry = 80; } public void playGame(){ //添加一个情况,玩游戏,改变值 if(!check()){ System.out.println("各项属性值不能为负数!"); return; } System.out.println("与"+this.name+"一起玩"); this.happy += 10; this.healthy -= 5; this.hungry += 12; } public void eat(){ //添加一个情况,吃东西,改变值 if(!check()){ System.out.println("各项属性值不能为负数!"); return; } System.out.println("与"+this.name+"一起吃"); this.healthy += 5; this.hungry -= 20; } public boolean check(){ //总的一个判断条件,确保各项属性值不为负数 if(this.happy>0 && this.healthy>0 && this.hungry>0){ return true; } if(happy<0){ happy = 0; }if(healthy<0){ healthy = 0; }if(hungry<0){ hungry = 0; } return false; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(int sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getHappy() { return happy; } public void setHappy(int happy) { this.happy = happy; } public int getHealthy() { return healthy; } public void setHealthy(int healthy) { this.healthy = healthy; } public int getHungry() { return hungry; } public void setHungry(int hungry) { this.hungry = hungry; } }
package com.hanqi.maya.model; //子类,猫(也可以为狗啊、猪啊之类的) public class Cat extends Pet { //extends 表示继承 public Cat(){ } public Cat(String catNmane, int catSex){ super(catNmane, catSex); //super,关键字,父类对象的引用 } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("宠物名称" + this.name); System.out.println("宠物性别" + this.sex); System.out.println("宠物年龄" + this.age); System.out.println("开心值" + this.happy); System.out.println("健康值" + this.healthy); System.out.println("饥饿度" + this.hungry); } }
package com.hanqi.maya.text; import java.util.Scanner; import com.hanqi.maya.model.Cat; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat cat = new Cat("花花", 1); //实例化 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); boolean flag = true; while(flag){ printControl(); String s = scanner.nextLine(); if("1".equals(s)){ cat.showInfo(); } else if("2".equals(s)){ cat.eat(); } else if("3".equals(s)){ cat.playGame(); } else if("bye".equals(s)){ flag = false; } else{ System.out.println("尚未开发!"); } } scanner.close(); //scanner 最后一定要关闭 } public static void printControl(){ System.out.println("1--显示信息"); System.out.println("2--吃饭"); System.out.println("3--玩游戏"); } }

标签:方法 void util package int 情况 else 类对象 data
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sutao/p/7201322.html