标签:入参 reduce 训练 ict ice sum step nim 准备
i
mport tensorflow as tf import numpy as np # 添加层 def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None): # add one more layer and return the output of this layer Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size])) biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1) Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs # 1.训练的数据 # Make up some real data x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:, np.newaxis] noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise # 2.定义节点准备接收数据 # define placeholder for inputs to network xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) # 3.定义神经层:隐藏层和预测层 # add hidden layer 输入值是 xs,在隐藏层有 10 个神经元 l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) # add output layer 输入值是隐藏层 l1,在预测层输出 1 个结果 prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None) # 4.定义 loss 表达式 # the error between prediciton and real data loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) # 5.选择 optimizer 使 loss 达到最小 # 这一行定义了用什么方式去减少 loss,学习率是 0.1 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) # important step 对所有变量进行初始化 init = tf.initialize_all_variables() sess = tf.Session() # 上面定义的都没有运算,直到 sess.run 才会开始运算 sess.run(init) # 迭代 1000 次学习,sess.run optimizer for i in range(1000): # training train_step 和 loss 都是由 placeholder 定义的运算,所以这里要用 feed 传入参数 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) if i % 50 == 0: # to see the step improvement print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))
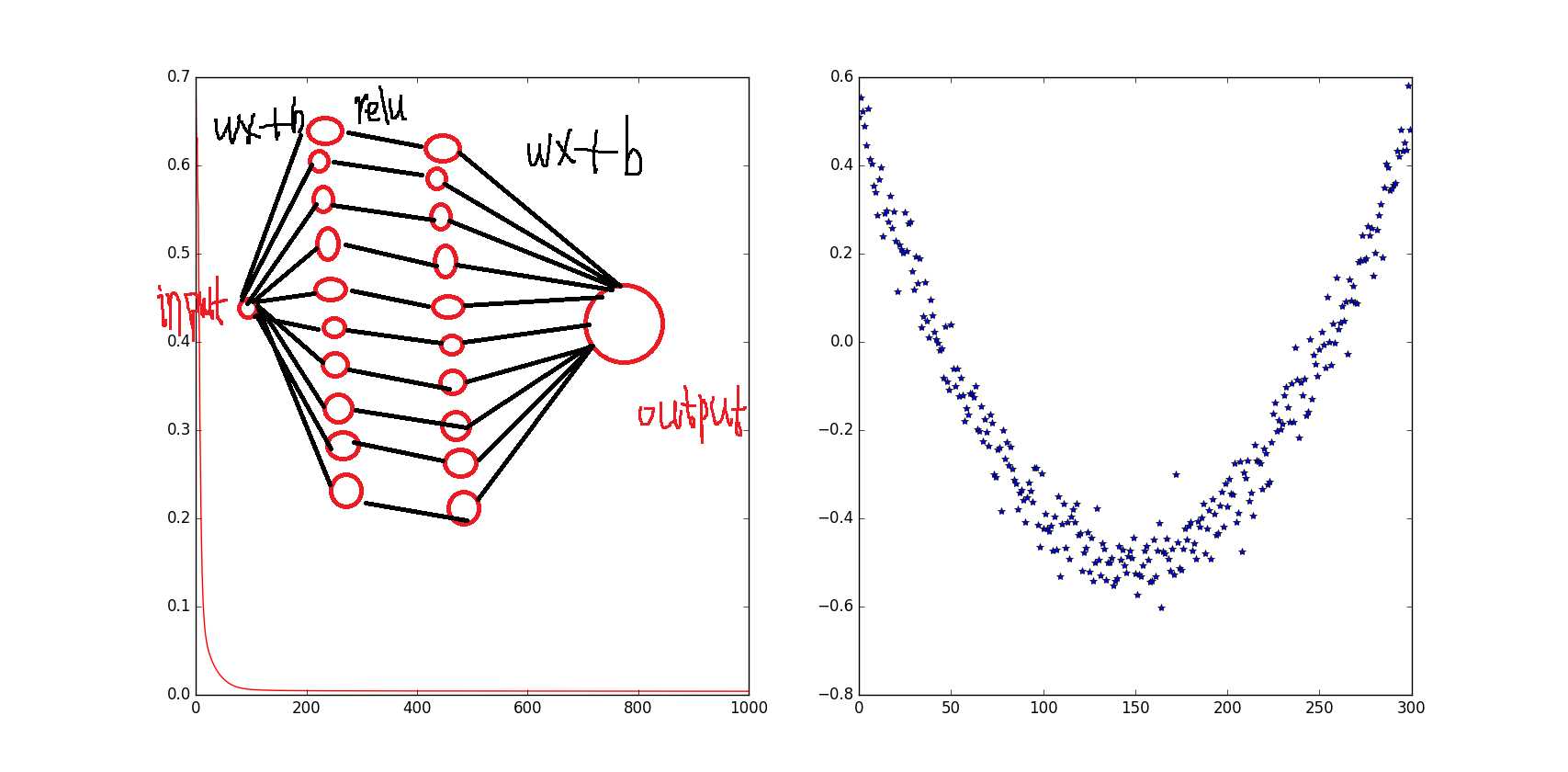
参考:http://www.jianshu.com/p/e112012a4b2d
标签:入参 reduce 训练 ict ice sum step nim 准备
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lovephysics/p/7221605.html