标签:过程 prot containe == string -- 内存区域 required 不包含
Objective-C语言是一门动态语言,它将很多静态语言在编译和链接时期做的事放到了运行时来处理。这种动态语言的优势在于:我们写代码时更具灵活性,如我们可以把消息转发给我们想要的对象,或者随意交换一个方法的实现等。
这种特性意味着Objective-C不仅需要一个编译器,还需要一个运行时系统来执行编译的代码。对于Objective-C来说,这个运行时系统就像一个操作系统一样:它让所有的工作可以正常的运行。这个运行时系统即Objc Runtime。Objc Runtime其实是一个Runtime库,它基本上是用C和汇编写的,这个库使得C语言有了面向对象的能力。
Runtime库主要做下面几件事:
Objective-C runtime目前有两个版本:Modern runtime和Legacy runtime。Modern Runtime 覆盖了64位的Mac OS X Apps,还有 iOS Apps,Legacy Runtime 是早期用来给32位 Mac OS X Apps 用的,也就是可以不用管就是了。
在这一系列文章中,我们将介绍runtime的基本工作原理,以及如何利用它让我们的程序变得更加灵活。在本文中,我们先来介绍一下类与对象,这是面向对象的基础,我们看看在Runtime中,类是如何实现的。
Objective-C类是由Class类型来表示的,它实际上是一个指向objc_class结构体的指针。它的定义如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
/// An opaque type that represents an Objective-C class.typedef struct objc_class *Class; /// Represents an instance of a class.struct objc_object { Class isa;}; /// A pointer to an instance of a class.typedef struct objc_object *id; |
由此可见,Class是一个指向objc_class结构体的指针,而id是一个指向objc_object结构体的指针,其成员isa是一个指向objec_class结构体的指针。
查看objc/runtime.h中objc_class结构体的定义如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
struct objc_class { Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;#if !__OBJC2__ Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 父类 const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 类名 long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 类的版本信息,默认为0 long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 类信息,供运行期使用的一些位标识 long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 该类的实例变量大小 struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 该类的成员变量链表 struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法定义的链表 struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法缓存 struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 协议链表#endif} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; |
在这个定义中,下面几个字段是我们感兴趣的
针对cache,我们用下面例子来说明其执行过程:
|
1
|
NSArray *array = [[NSArray alloc] init]; |
其流程是:
objc_object是表示一个类的实例的结构体,它的定义如下(objc/objc.h):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
struct objc_object { Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;};typedef struct objc_object *id; |
可以看到,这个结构体只有一个字体,即指向其类的isa指针。这样,当我们向一个Objective-C对象发送消息时,运行时库会根据实例对象的isa指针找到这个实例对象所属的类。Runtime库会在类的方法列表及父类的方法列表中去寻找与消息对应的selector指向的方法。找到后即运行这个方法。
当创建一个特定类的实例对象时,分配的内存包含一个objc_object数据结构,然后是类的实例变量的数据。NSObject类的alloc和allocWithZone:方法使用函数class_createInstance来创建objc_object数据结构。
另外还有我们常见的id,它是一个objc_object结构类型的指针。它的存在可以让我们实现类似于C++中泛型的一些操作。该类型的对象可以转换为任何一种对象,有点类似于C语言中void *指针类型的作用。
上面提到了objc_class结构体中的cache字段,它用于缓存调用过的方法。这个字段是一个指向objc_cache结构体的指针,其定义如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
struct objc_cache { unsigned int mask /* total = mask + 1 */ OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; unsigned int occupied OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; Method buckets[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;}; |
该结构体的字段描述如下:
在上面我们提到,所有的类自身也是一个对象,我们可以向这个对象发送消息(即调用类方法)。如:
|
1
|
NSArray *array = [NSArray array]; |
这个例子中,+array消息发送给了NSArray类,而这个NSArray也是一个对象。既然是对象,那么它也是一个objc_object指针,它包含一个指向其类的一个isa指针。那么这些就有一个问题了,这个isa指针指向什么呢?为了调用+array方法,这个类的isa指针必须指向一个包含这些类方法的一个objc_class结构体。这就引出了meta-class的概念
|
1
|
meta-class是一个类对象的类。 |
当我们向一个对象发送消息时,runtime会在这个对象所属的这个类的方法列表中查找方法;而向一个类发送消息时,会在这个类的meta-class的方法列表中查找。
meta-class之所以重要,是因为它存储着一个类的所有类方法。每个类都会有一个单独的meta-class,因为每个类的类方法基本不可能完全相同。
再深入一下,meta-class也是一个类,也可以向它发送一个消息,那么它的isa又是指向什么呢?为了不让这种结构无限延伸下去,Objective-C的设计者让所有的meta-class的isa指向基类的meta-class,以此作为它们的所属类。即,任何NSObject继承体系下的meta-class都使用NSObject的meta-class作为自己的所属类,而基类的meta-class的isa指针是指向它自己。这样就形成了一个完美的闭环。
通过上面的描述,再加上对objc_class结构体中super_class指针的分析,我们就可以描绘出类及相应meta-class类的一个继承体系了,如下图所示:
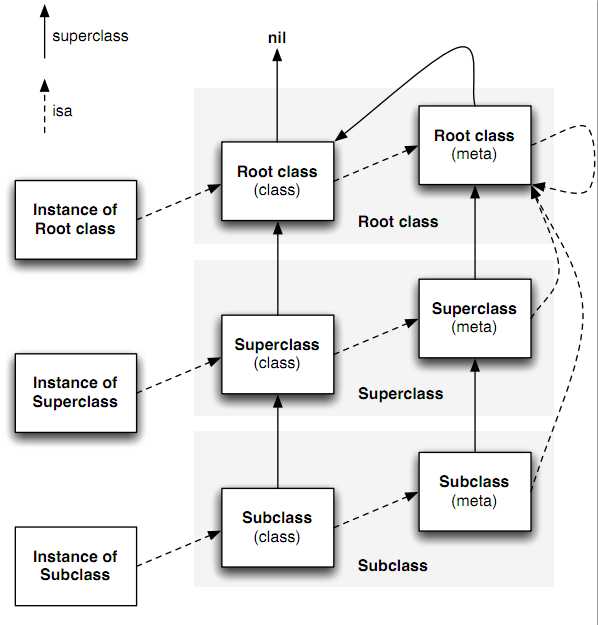
对于NSObject继承体系来说,其实例方法对体系中的所有实例、类和meta-class都是有效的;而类方法对于体系内的所有类和meta-class都是有效的。
讲了这么多,我们还是来写个例子吧:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
#import "ViewController.h"#import <objc/runtime.h>@interface ViewController ()@endvoid TextMetaCLass(id self,SEL _cmd);@implementation ViewControllervoid TextMetaCLass(id self,SEL _cmd){ NSLog(@"This Object is %p",self); NSLog(@"Class is %@, super class is %@",[self class],[self superclass]); Class currentClass = [self class]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { NSLog(@"Following the isa pointer %d times gives %p", i ,currentClass); /** * 获取类对象 * * @param object 想要获取的类 * * @return 类对象或nil */ currentClass = objc_getClass((__bridge void *)currentClass); } NSLog(@"NSObject‘s class is %p", [NSError class]); NSLog(@"NSObject‘s meta class is %p", objc_getClass((__bridge void *)[NSError class]));}- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; /** * 创建一个新的类 * * @param superclass 作为新类的父类,若为空,则为根类 * @param name 新类的名字 * @param extraBytes 为类或元类对象分配字节数,通常都是为0 * * @return 新类或为空nil(如果创建不成功:新的类名已经存在) */ Class newClass = objc_allocateClassPair([NSError class], "TestClass", 0); /** * 为新类添加新方法(注意:不可同名) * * @param newClass 要添加方法的类 * @param testMetaClass 将要添加的方法名字 * @param imp 函数方法的声明 ,且该函数至少有两个参数对象,分别为self 和 _cmd. * @param types 字符数组用于描述方法中的参数类型,因为方法中必须有self 和 _cmd 这两个参数,所以第二个跟第三个字符必须是“@:” * @return YES 添加方法成功 NO 添加方法失败 */ class_addMethod(newClass, @selector(testMetaClass), (IMP)TextMetaCLass, "v@:"); /** * 为类添加新的实例变量(注意:不支持为现有的类、元类添加实例变量) * * @param cls 要添加实例变量的类对象 * @param name 变量名字 * @param size 为变量分配内存空间 * @param alignment * @param types 变量的类型 * * @return YES 添加实例变量成功 NO 添加实例变量失败 */ //class_addIvar(<#__unsafe_unretained Class cls#>, <#const char *name#>, <#size_t size#>, <#uint8_t alignment#>, <#const char *types#>) /** * 注册通过方法objc_allocateClassPair创建的类 * * @param cls 即开发者创建的类 */ objc_registerClassPair(newClass); id instance = [[newClass alloc] initWithDomain:@"some domain" code:0 userInfo:nil]; [instance performSelector:@selector(testMetaClass)]; } |
这个例子是在运行时创建了一个NSError的子类TestClass,然后为这个子类添加一个方法testMetaClass,这个方法的实现是TestMetaClass函数。
运行后,打印结果是
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
2016-08-11 14:47:55.559 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] This Object is 0x7fcbd8d4dc202016-08-11 14:47:55.560 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] Class is TestClass, super class is NSError2016-08-11 14:47:55.560 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] Following the isa pointer 0 times gives 0x7fcbd8d276d02016-08-11 14:47:55.560 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] Following the isa pointer 1 times gives 0x02016-08-11 14:47:55.560 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] Following the isa pointer 2 times gives 0x02016-08-11 14:47:55.560 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] Following the isa pointer 3 times gives 0x02016-08-11 14:47:55.560 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] NSObject‘s class is 0x106854a882016-08-11 14:47:55.560 Runtime1-类与对象[27720:1858642] NSObject‘s meta class is 0x0 |
我们在for循环中,我们通过objc_getClass来获取对象的isa,并将其打印出来,依此一直回溯到NSObject的meta-class。分析打印结果,可以看到最后指针指向的地址是0x0,即NSObject的meta-class的类地址。
这里需要注意的是:我们在一个类对象调用class方法是无法获取meta-class,它只是返回类而已。
runtime提供了大量的函数来操作类与对象。类的操作方法大部分是以class为前缀的,而对象的操作方法大部分是以objc或object_为前缀。下面我们将根据这些方法的用途来分类讨论这些方法的使用。
我们可以回过头去看看objc_class的定义,runtime提供的操作类的方法主要就是针对这个结构体中的各个字段的。下面我们分别介绍这一些的函数。并在最后以实例来演示这些函数的具体用法。
类名操作的函数主要有:
|
1
2
3
|
// 获取类的类名const char * class_getName ( Class cls ); |
● 对于class_getName函数,如果传入的cls为Nil,则返回一个字字符串。
父类和元类操作的函数主要有:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// 获取类的父类Class class_getSuperclass ( Class cls );// 判断给定的Class是否是一个元类BOOL class_isMetaClass ( Class cls ); |
● class_getSuperclass函数,当cls为Nil或者cls为根类时,返回Nil。不过通常我们可以使用NSObject类的superclass方法来达到同样的目的。
● class_isMetaClass函数,如果是cls是元类,则返回YES;如果否或者传入的cls为Nil,则返回NO。
实例变量大小操作的函数有:
|
1
2
3
|
// 获取实例大小size_t class_getInstanceSize ( Class cls ); |
在objc_class中,所有的成员变量、属性的信息是放在链表ivars中的。ivars是一个数组,数组中每个元素是指向Ivar(变量信息)的指针。runtime提供了丰富的函数来操作这一字段。大体上可以分为以下几类:
1.成员变量操作函数,主要包含以下函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
// 获取类中指定名称实例成员变量的信息Ivar class_getInstanceVariable ( Class cls, const char *name );// 获取类成员变量的信息Ivar class_getClassVariable ( Class cls, const char *name );// 添加成员变量BOOL class_addIvar ( Class cls, const char *name, size_t size, uint8_t alignment, const char *types );// 获取整个成员变量列表Ivar * class_copyIvarList ( Class cls, unsigned int *outCount ); |
● class_getInstanceVariable函数,它返回一个指向包含name指定的成员变量信息的objc_ivar结构体的指针(Ivar)。
● class_getClassVariable函数,目前没有找到关于Objective-C中类变量的信息,一般认为Objective-C不支持类变量。注意,返回的列表不包含父类的成员变量和属性。
● Objective-C不支持往已存在的类中添加实例变量,因此不管是系统库提供的类,还是我们自定义的类,都无法动态添加成员变量。但如果我们通过运行时来创建一个类的话,又应该如何给它添加成员变量呢?这时我们就可以使用class_addIvar函数了。不过需要注意的是,这个方法只能在objc_allocateClassPair函数与objc_registerClassPair之间调用。另外,这个类也不能是元类。成员变量的按字节最小对齐量是1<<alignment。这取决于ivar的类型和机器的架构。如果变量的类型是指针类型,则传递log2(sizeof(pointer_type))。
● class_copyIvarList函数,它返回一个指向成员变量信息的数组,数组中每个元素是指向该成员变量信息的objc_ivar结构体的指针。这个数组不包含在父类中声明的变量。outCount指针返回数组的大小。需要注意的是,我们必须使用free()来释放这个数组。
2.属性操作函数,主要包含以下函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
// 获取指定的属性objc_property_t class_getProperty ( Class cls, const char *name );// 获取属性列表objc_property_t * class_copyPropertyList ( Class cls, unsigned int *outCount );// 为类添加属性BOOL class_addProperty ( Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount );// 替换类的属性void class_replaceProperty ( Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount ); |
这一种方法也是针对ivars来操作,不过只操作那些是属性的值。我们在后面介绍属性时会再遇到这些函数。
3.在MAC OS X系统中,我们可以使用垃圾回收器。runtime提供了几个函数来确定一个对象的内存区域是否可以被垃圾回收器扫描,以处理strong/weak引用。这几个函数定义如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
const uint8_t * class_getIvarLayout ( Class cls );void class_setIvarLayout ( Class cls, const uint8_t *layout );const uint8_t * class_getWeakIvarLayout ( Class cls );void class_setWeakIvarLayout ( Class cls, const uint8_t *layout ); |
但通常情况下,我们不需要去主动调用这些方法;在调用objc_registerClassPair时,会生成合理的布局。在此不详细介绍这些函数。
方法操作主要有以下函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
// 添加方法BOOL class_addMethod ( Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types );// 获取实例方法Method class_getInstanceMethod ( Class cls, SEL name );// 获取类方法Method class_getClassMethod ( Class cls, SEL name );// 获取所有方法的数组Method * class_copyMethodList ( Class cls, unsigned int *outCount );// 替代方法的实现IMP class_replaceMethod ( Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types );// 返回方法的具体实现IMP class_getMethodImplementation ( Class cls, SEL name );IMP class_getMethodImplementation_stret ( Class cls, SEL name );// 类实例是否响应指定的selectorBOOL class_respondsToSelector ( Class cls, SEL sel ); |
class_addMethod的实现会覆盖父类的方法实现,但不会取代本类中已存在的实现,如果本类中包含一个同名的实现,则函数会返回NO。如果要修改已存在实现,可以使用method_setImplementation。一个Objective-C方法是一个简单的C函数,它至少包含两个参数—self和_cmd。所以,我们的实现函数(IMP参数指向的函数)至少需要两个参数,如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
void myMethodIMP(id self, SEL _cmd){ // implementation ....} |
与成员变量不同的是,我们可以为类动态添加方法,不管这个类是否已存在。
另外,参数types是一个描述传递给方法的参数类型的字符数组,这就涉及到类型编码,我们将在后面介绍。
● class_getInstanceMethod、class_getClassMethod函数,与class_copyMethodList不同的是,这两个函数都会去搜索父类的实现。
● class_copyMethodList函数,返回包含所有实例方法的数组,如果需要获取类方法,则可以使用class_copyMethodList(object_getClass(cls), &count)(一个类的实例方法是定义在元类里面)。该列表不包含父类实现的方法。outCount参数返回方法的个数。在获取到列表后,我们需要使用free()方法来释放它。
● class_replaceMethod函数,该函数的行为可以分为两种:如果类中不存在name指定的方法,则类似于class_addMethod函数一样会添加方法;如果类中已存在name指定的方法,则类似于method_setImplementation一样替代原方法的实现。
● class_getMethodImplementation函数,该函数在向类实例发送消息时会被调用,并返回一个指向方法实现函数的指针。这个函数会比method_getImplementation(class_getInstanceMethod(cls, name))更快。返回的函数指针可能是一个指向runtime内部的函数,而不一定是方法的实际实现。例如,如果类实例无法响应selector,则返回的函数指针将是运行时消息转发机制的一部分。
● class_respondsToSelector函数,我们通常使用NSObject类的respondsToSelector:或instancesRespondToSelector:方法来达到相同目的。
协议相关的操作包含以下函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// 添加协议BOOL class_addProtocol ( Class cls, Protocol *protocol );// 返回类是否实现指定的协议BOOL class_conformsToProtocol ( Class cls, Protocol *protocol );// 返回类实现的协议列表Protocol * class_copyProtocolList ( Class cls, unsigned int *outCount ); |
class_conformsToProtocol函数可以使用NSObject类的conformsToProtocol:方法来替代。
● class_copyProtocolList函数返回的是一个数组,在使用后我们需要使用free()手动释放。
版本相关的操作包含以下函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// 获取版本号int class_getVersion ( Class cls );// 设置版本号void class_setVersion ( Class cls, int version ); |
其它
runtime还提供了两个函数来供CoreFoundation的tool-free bridging使用,即:
|
1
2
3
|
Class objc_getFutureClass ( const char *name );void objc_setFutureClass ( Class cls, const char *name ); |
通常我们不直接使用这两个函数。
上面列举了大量类操作的函数,下面我们写个实例,来看看这些函数的实例效果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
|
//-----------------------------------------------------------// MyClass.h@interface MyClass : NSObject <NSCopying, NSCoding>@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *array;@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *string;- (void)method1;- (void)method2;+ (void)classMethod1;@end//-----------------------------------------------------------// MyClass.m#import "MyClass.h"@interface MyClass () { NSInteger _instance1; NSString * _instance2;}@property (nonatomic, assign) NSUInteger integer;- (void)method3WithArg1:(NSInteger)arg1 arg2:(NSString *)arg2;@end@implementation MyClass+ (void)classMethod1 {}- (void)method1 { NSLog(@"call method method1");}- (void)method2 {}- (void)method3WithArg1:(NSInteger)arg1 arg2:(NSString *)arg2 { NSLog(@"arg1 : %ld, arg2 : %@", arg1, arg2);}@end//-----------------------------------------------------------// main.h#import "MyClass.h"#import "MySubClass.h"#import <objc/runtime.h>int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { MyClass *myClass = [[MyClass alloc] init]; unsigned int outCount = 0; Class cls = myClass.class; // 类名 NSLog(@"class name: %s", class_getName(cls)); NSLog(@"=========================================================="); // 父类 NSLog(@"super class name: %s", class_getName(class_getSuperclass(cls))); NSLog(@"=========================================================="); // 是否是元类 NSLog(@"MyClass is %@ a meta-class", (class_isMetaClass(cls) ? @"" : @"not")); NSLog(@"=========================================================="); Class meta_class = objc_getMetaClass(class_getName(cls)); NSLog(@"%s‘s meta-class is %s", class_getName(cls), class_getName(meta_class)); NSLog(@"=========================================================="); // 变量实例大小 NSLog(@"instance size: %zu", class_getInstanceSize(cls)); NSLog(@"=========================================================="); // 成员变量 Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList(cls, &outCount); for (int i = 0; i < outCount; i++) { Ivar ivar = ivars[i]; NSLog(@"instance variable‘s name: %s at index: %d", ivar_getName(ivar), i); } free(ivars); Ivar string = class_getInstanceVariable(cls, "_string"); if (string != NULL) { NSLog(@"instace variable %s", ivar_getName(string)); } NSLog(@"=========================================================="); // 属性操作 objc_property_t * properties = class_copyPropertyList(cls, &outCount); for (int i = 0; i < outCount; i++) { objc_property_t property = properties[i]; NSLog(@"property‘s name: %s", property_getName(property)); } free(properties); objc_property_t array = class_getProperty(cls, "array"); if (array != NULL) { NSLog(@"property %s", property_getName(array)); } NSLog(@"=========================================================="); // 方法操作 Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(cls, &outCount); for (int i = 0; i < outCount; i++) { Method method = methods[i]; NSLog(@"method‘s signature: %s", method_getName(method)); } free(methods); Method method1 = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, @selector(method1)); if (method1 != NULL) { NSLog(@"method %s", method_getName(method1)); } Method classMethod = class_getClassMethod(cls, @selector(classMethod1)); if (classMethod != NULL) { NSLog(@"class method : %s", method_getName(classMethod)); } NSLog(@"MyClass is%@ responsd to selector: method3WithArg1:arg2:", class_respondsToSelector(cls, @selector(method3WithArg1:arg2:)) ? @"" : @" not"); IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(cls, @selector(method1)); imp(); NSLog(@"=========================================================="); // 协议 Protocol * __unsafe_unretained * protocols = class_copyProtocolList(cls, &outCount); Protocol * protocol; for (int i = 0; i < outCount; i++) { protocol = protocols[i]; NSLog(@"protocol name: %s", protocol_getName(protocol)); } NSLog(@"MyClass is%@ responsed to protocol %s", class_conformsToProtocol(cls, protocol) ? @"" : @" not", protocol_getName(protocol)); NSLog(@"=========================================================="); } return 0;} |
这段程序的输出如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
2014-10-22 19:41:37.452 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] class name: MyClass2014-10-22 19:41:37.453 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.454 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] super class name: NSObject2014-10-22 19:41:37.454 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.454 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] MyClass is not a meta-class2014-10-22 19:41:37.454 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.454 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] MyClass‘s meta-class is MyClass2014-10-22 19:41:37.455 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.455 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] instance size: 482014-10-22 19:41:37.455 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.455 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] instance variable‘s name: _instance1 at index: 02014-10-22 19:41:37.455 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] instance variable‘s name: _instance2 at index: 12014-10-22 19:41:37.455 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] instance variable‘s name: _array at index: 22014-10-22 19:41:37.455 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] instance variable‘s name: _string at index: 32014-10-22 19:41:37.463 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] instance variable‘s name: _integer at index: 42014-10-22 19:41:37.463 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] instace variable _string2014-10-22 19:41:37.463 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.463 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] property‘s name: array2014-10-22 19:41:37.463 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] property‘s name: string2014-10-22 19:41:37.464 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] property‘s name: integer2014-10-22 19:41:37.464 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] property array2014-10-22 19:41:37.464 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.464 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: method12014-10-22 19:41:37.464 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: method22014-10-22 19:41:37.464 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: method3WithArg1:arg2:2014-10-22 19:41:37.465 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: integer2014-10-22 19:41:37.465 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: setInteger:2014-10-22 19:41:37.465 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: array2014-10-22 19:41:37.465 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: string2014-10-22 19:41:37.465 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: setString:2014-10-22 19:41:37.465 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: setArray:2014-10-22 19:41:37.466 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method‘s signature: .cxx_destruct2014-10-22 19:41:37.466 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] method method12014-10-22 19:41:37.466 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] class method : classMethod12014-10-22 19:41:37.466 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] MyClass is responsd to selector: method3WithArg1:arg2:2014-10-22 19:41:37.467 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] call method method12014-10-22 19:41:37.467 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ==========================================================2014-10-22 19:41:37.467 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] protocol name: NSCopying2014-10-22 19:41:37.467 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] protocol name: NSCoding2014-10-22 19:41:37.467 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] MyClass is responsed to protocol NSCoding2014-10-22 19:41:37.468 RuntimeTest[3189:156810] ========================================================== |
runtime的强大之处在于它能在运行时创建类和对象。
动态创建类涉及到以下几个函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// 创建一个新类和元类Class objc_allocateClassPair ( Class superclass, const char *name, size_t extraBytes );// 销毁一个类及其相关联的类void objc_disposeClassPair ( Class cls );// 在应用中注册由objc_allocateClassPair创建的类void objc_registerClassPair ( Class cls ); |
objc_allocateClassPair函数:如果我们要创建一个根类,则superclass指定为Nil。extraBytes通常指定为0,该参数是分配给类和元类对象尾部的索引ivars的字节数。
为了创建一个新类,我们需要调用objc_allocateClassPair。然后使用诸如class_addMethod,class_addIvar等函数来为新创建的类添加方法、实例变量和属性等。完成这些后,我们需要调用objc_registerClassPair函数来注册类,之后这个新类就可以在程序中使用了。
实例方法和实例变量应该添加到类自身上,而类方法应该添加到类的元类上。
● objc_disposeClassPair函数用于销毁一个类,不过需要注意的是,如果程序运行中还存在类或其子类的实例,则不能调用针对类调用该方法。
在前面介绍元类时,我们已经有接触到这几个函数了,在此我们再举个实例来看看这几个函数的使用。
|
1
|
Class cls = objc_allocateClassPair(MyClass.class, "MySubClass", 0); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class_addMethod(cls, @selector(submethod1), (IMP)imp_submethod1, "v@:");class_replaceMethod(cls, @selector(method1), (IMP)imp_submethod1, "v@:");class_addIvar(cls, "_ivar1", sizeof(NSString *), log(sizeof(NSString *)), "i");objc_property_attribute_t type = {"T", "@\"NSString\""};objc_property_attribute_t ownership = { "C", "" };objc_property_attribute_t backingivar = { "V", "_ivar1"};objc_property_attribute_t attrs[] = {type, ownership, backingivar};class_addProperty(cls, "property2", attrs, 3);objc_registerClassPair(cls);id instance = [[cls alloc] init];[instance performSelector:@selector(submethod1)];[instance performSelector:@selector(method1)]; |
程序的输出如下:
|
1
2
3
|
2014-10-23 11:35:31.006 RuntimeTest[3800:66152] run sub method 12014-10-23 11:35:31.006 RuntimeTest[3800:66152] run sub method 1 |
动态创建对象的函数如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// 创建类实例id class_createInstance ( Class cls, size_t extraBytes );// 在指定位置创建类实例id objc_constructInstance ( Class cls, void *bytes );// 销毁类实例void * objc_destructInstance ( id obj ); |
class_createInstance函数:创建实例时,会在默认的内存区域为类分配内存。extraBytes参数表示分配的额外字节数。这些额外的字节可用于存储在类定义中所定义的实例变量之外的实例变量。该函数在ARC环境下无法使用。
调用class_createInstance的效果与+alloc方法类似。不过在使用class_createInstance时,我们需要确切的知道我们要用它来做什么。在下面的例子中,我们用NSString来测试一下该函数的实际效果:
|
1
|
id theObject = class_createInstance(NSString.class, sizeof(unsigned)); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
id str1 = [theObject init];NSLog(@"%@", [str1 class]);id str2 = [[NSString alloc] initWithString:@"test"];NSLog(@"%@", [str2 class]); |
输出结果是:
|
1
2
3
|
2014-10-23 12:46:50.781 RuntimeTest[4039:89088] NSString2014-10-23 12:46:50.781 RuntimeTest[4039:89088] __NSCFConstantString |
可以看到,使用class_createInstance函数获取的是NSString实例,而不是类簇中的默认占位符类__NSCFConstantString。
● objc_constructInstance函数:在指定的位置(bytes)创建类实例。
● objc_destructInstance函数:销毁一个类的实例,但不会释放并移除任何与其相关的引用。
实例操作函数主要是针对我们创建的实例对象的一系列操作函数,我们可以使用这组函数来从实例对象中获取我们想要的一些信息,如实例对象中变量的值。这组函数可以分为三小类:
1.针对整个对象进行操作的函数,这类函数包含
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// 返回指定对象的一份拷贝id object_copy ( id obj, size_t size );// 释放指定对象占用的内存id object_dispose ( id obj ); |
有这样一种场景,假设我们有类A和类B,且类B是类A的子类。类B通过添加一些额外的属性来扩展类A。现在我们创建了一个A类的实例对象,并希望在运行时将这个对象转换为B类的实例对象,这样可以添加数据到B类的属性中。这种情况下,我们没有办法直接转换,因为B类的实例会比A类的实例更大,没有足够的空间来放置对象。此时,我们就要以使用以上几个函数来处理这种情况,如下代码所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
NSObject *a = [[NSObject alloc] init];id newB = object_copy(a, class_getInstanceSize(MyClass.class));object_setClass(newB, MyClass.class);object_dispose(a); |
2.针对对象实例变量进行操作的函数,这类函数包含
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
// 修改类实例的实例变量的值Ivar object_setInstanceVariable ( id obj, const char *name, void *value );// 获取对象实例变量的值Ivar object_getInstanceVariable ( id obj, const char *name, void **outValue );// 返回指向给定对象分配的任何额外字节的指针void * object_getIndexedIvars ( id obj );// 返回对象中实例变量的值id object_getIvar ( id obj, Ivar ivar );// 设置对象中实例变量的值void object_setIvar ( id obj, Ivar ivar, id value ); |
如果实例变量的Ivar已经知道,那么调用object_getIvar会比object_getInstanceVariable函数快,相同情况下,object_setIvar也比object_setInstanceVariable快。
3.针对对象的类进行操作的函数,这类函数包含:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// 返回给定对象的类名const char * object_getClassName ( id obj );// 返回对象的类Class object_getClass ( id obj );// 设置对象的类Class object_setClass ( id obj, Class cls ); |
Objective-C动态运行库会自动注册我们代码中定义的所有的类。我们也可以在运行时创建类定义并使用objc_addClass函数来注册它们。runtime提供了一系列函数来获取类定义相关的信息,这些函数主要包括:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
// 获取已注册的类定义的列表int objc_getClassList ( Class *buffer, int bufferCount );// 创建并返回一个指向所有已注册类的指针列表Class * objc_copyClassList ( unsigned int *outCount );// 返回指定类的类定义Class objc_lookUpClass ( const char *name );Class objc_getClass ( const char *name );Class objc_getRequiredClass ( const char *name );// 返回指定类的元类Class objc_getMetaClass ( const char *name ); |
objc_getClassList函数:获取已注册的类定义的列表。我们不能假设从该函数中获取的类对象是继承自NSObject体系的,所以在这些类上调用方法是,都应该先检测一下这个方法是否在这个类中实现。
下面代码演示了该函数的用法:
|
1
2
3
|
int numClasses;Class * classes = NULL; |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
numClasses = objc_getClassList(NULL, 0);if (numClasses > 0) { classes = malloc(sizeof(Class) * numClasses); numClasses = objc_getClassList(classes, numClasses); NSLog(@"number of classes: %d", numClasses); for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) { Class cls = classes[i]; NSLog(@"class name: %s", class_getName(cls)); } free(classes);} |
输出结果如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
2014-10-23 16:20:52.589 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] number of classes: 12822014-10-23 16:20:52.589 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: DDTokenRegexp2014-10-23 16:20:52.590 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: _NSMostCommonKoreanCharsKeySet2014-10-23 16:20:52.590 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: OS_xpc_dictionary2014-10-23 16:20:52.590 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: NSFileCoordinator2014-10-23 16:20:52.590 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: NSAssertionHandler2014-10-23 16:20:52.590 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: PFUbiquityTransactionLogMigrator2014-10-23 16:20:52.591 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: NSNotification2014-10-23 16:20:52.591 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: NSKeyValueNilSetEnumerator2014-10-23 16:20:52.591 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: OS_tcp_connection_tls_session2014-10-23 16:20:52.591 RuntimeTest[8437:188589] class name: _PFRoutines......还有大量输出 |
获取类定义的方法有三个:objc_lookUpClass, objc_getClass和objc_getRequiredClass。如果类在运行时未注册,则objc_lookUpClass会返回nil,而objc_getClass会调用类处理回调,并再次确认类是否注册,如果确认未注册,再返回nil。而objc_getRequiredClass函数的操作与objc_getClass相同,只不过如果没有找到类,则会杀死进程。
● objc_getMetaClass函数:如果指定的类没有注册,则该函数会调用类处理回调,并再次确认类是否注册,如果确认未注册,再返回nil。不过,每个类定义都必须有一个有效的元类定义,所以这个函数总是会返回一个元类定义,不管它是否有效。
本文转自 http://southpeak.github.io/blog/2014/10/25/objective-c-runtime-yun-xing-shi-zhi-lei-yu-dui-xiang/
Objective-C Runtime 运行时之一:类与对象
标签:过程 prot containe == string -- 内存区域 required 不包含
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/feng9exe/p/7230639.html