标签:get 技术分享 com 分享 str blog alt getc space
笛卡尔树就是你给两维限制,一维堆R,一维二叉搜索树K,平地拔起一棵Treap,最广范的应用:用LCA求区间最值,建Treap,还有个什么范围top k我表示并不会查都查不到。它最妙最高的地方在于用栈来建树:我们可以先排序K然后一个个插入,那么我们都是最右端,横容易被卡,那么我们不从上到下,我们从下到上,用栈维护,那就把时间复杂度从O(n^2)降到O(n),具体过程见下图从图一到图二就是这么一个过程,我们在把K为13的点插入时要找到一个合适的位置,上比他大,下比他小(假设大根堆)
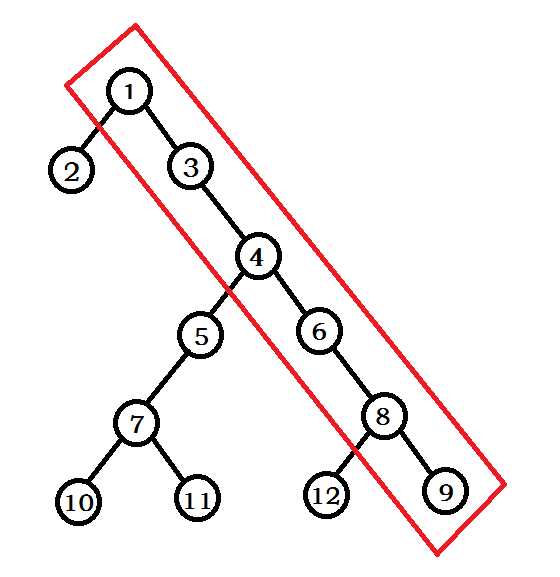
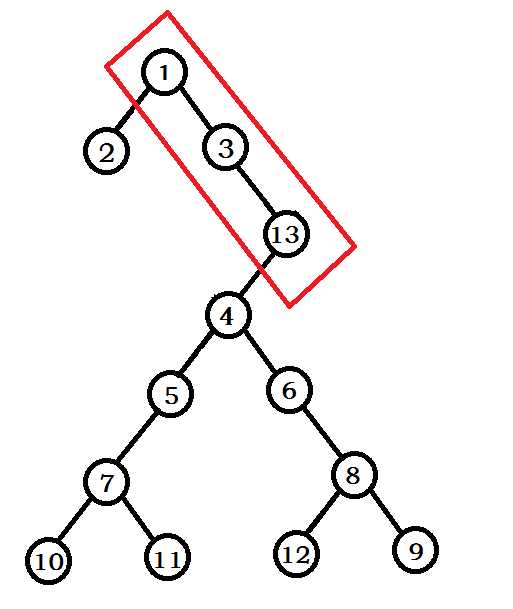
下面见代码
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #define MAXN 500010 using namespace std; inline int read() { int sum=0; char ch=getchar(); while(ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘)ch=getchar(); while(ch>=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘) { sum=(sum<<1)+(sum<<3)+ch-‘0‘; ch=getchar(); } return sum; } struct Treap { int key,r; Treap *ch[2]; }*stack[MAXN],node[MAXN],*root; int top; int n; int comp(const Treap a,const Treap b) { return a.key<b.key; } inline void Init() { n=read(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)node[i].key=read(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)node[i].r=read(); sort(node+1,node+n+1,comp); } inline void Build() { stack[++top]=node+1; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) { Treap *last=NULL; while(top&&stack[top]->r>node[i].r) last=stack[top--]; if(top)stack[top]->ch[1]=node+i; node[i].ch[0]=last; stack[++top]=node+i; } root=stack[1]; } void dfs(Treap *p) { if(!p)return; printf("%d ",p->key); dfs(p->ch[0]); dfs(p->ch[1]); } int main() { int __size__=128<<20; char *__p__=(char*)malloc(__size__)+__size__; __asm__("movl %0, %%esp\n"::"r"(__p__)); freopen("treap.in","r",stdin); freopen("treap.out","w",stdout); Init(); Build(); dfs(root); return 0; }
[COGS 2421] [HZOI 2016] 简单的Treap 笛卡尔树
标签:get 技术分享 com 分享 str blog alt getc space
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/TSHugh/p/7242090.html