标签:des style blog http color os io 使用 java
Text是Hadoop中的一个Writable类,定义了Hadoop中的其中的数据类型以及操作。

This class stores text using standard UTF8 encoding. It provides methods to serialize, deserialize, and compare texts at byte level. The type of length is integer and is serialized using zero-compressed format.
In addition, it provides methods for string traversal without converting the byte array to a string.Also includes utilities for serializing/deserialing a string,encoding / decoding a string, checking if a byte array contains valid UTF8 code, calculating the length of an encoded string.
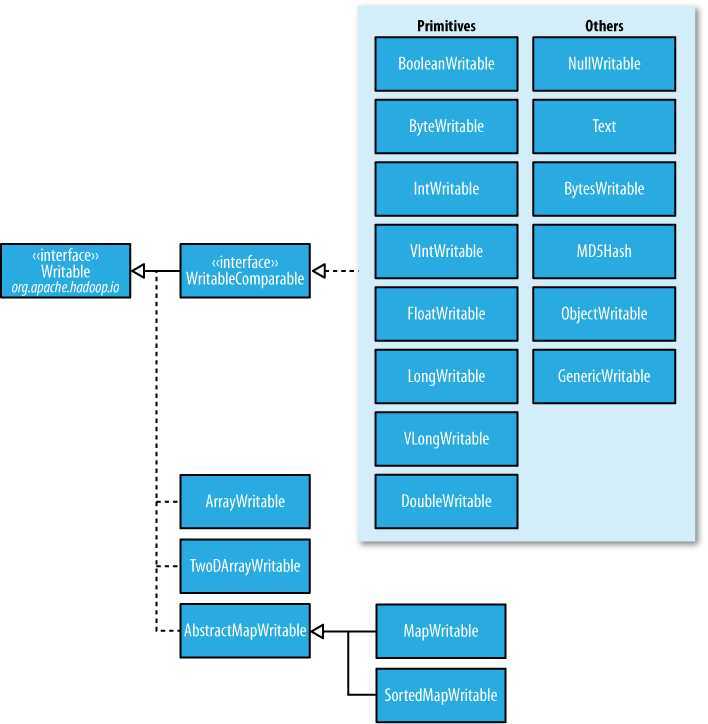
由上图的Writable层次结构图可以看到绝大多数的数据类型都实现了Writable、WritableComparable接口,在此先分析一下这两个接口情况。自顶下下逐步分析。
Writable接口的定义如下:
1 package org.apache.hadoop.io; 2 3 import java.io.DataOutput; 4 import java.io.DataInput; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 public interface Writable { 7 void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException; 8 void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException; 9 }
void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException /* object将自身字段序列化后的的字节流写入输出流out中。 参数: out - 接收object序列化后的字节流的输出流. */
void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException /* 将输入流in中的字节流反序列化然后写入object的字段 参数: 字节流的出处 */
而DataInput、DataOutput是java.io.*中最基本的输入输出流接口,其他输入输出流都需要实现DataInput与DataOutput这两个接口的方法。关于这两个接口,另外开篇分析解读。
到此Writable接口解读完毕,其实这些东西大家看看API文档也可以看懂的,我只是想详细了解一下Writable类所以就写一次更加明白。
WritableComparable接口定义如下:
package org.apache.hadoop.io; public interface WritableComparable<T> extends Writable, comparable<T> { }
咋一看这个WritableComparable没有方法,其实它的方法全都是通过继承而来的,Writable接口上面已经分析了,所以WritableComparable以下两个方法。
void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException;
void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException;
还有来自comparable的方法,comparable是属于java.lang.*中的一个接口,它只有一个方法。
int compareTo( T other); /* 比较此对象与指定对象other的顺序。如果该对象小于、等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数、零或正整数。 参数:o - 要比较的对象。 返回:负整数、零或正整数,根据此对象是小于、等于还是大于指定对象。 */
简单来说实现WritableComparable的类是一个可写可比较的类。
现在来分析基本类Text,声明定义如下
public class Text extends BinaryComparable implements WritableComparable<BinaryComparable>;

1 package org.apache.hadoop.io; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.DataInput; 5 import java.io.DataOutput; 6 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 7 import java.nio.CharBuffer; 8 import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException; 9 import java.nio.charset.Charset; 10 import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder; 11 import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder; 12 import java.nio.charset.CodingErrorAction; 13 import java.nio.charset.MalformedInputException; 14 import java.text.CharacterIterator; 15 import java.text.StringCharacterIterator; 16 17 import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; 18 import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; 19 20 /** This class stores text using standard UTF8 encoding. It provides methods 21 * to serialize, deserialize, and compare texts at byte level. The type of 22 * length is integer and is serialized using zero-compressed format. <p>In 23 * addition, it provides methods for string traversal without converting the 24 * byte array to a string. <p>Also includes utilities for 25 * serializing/deserialing a string, coding/decoding a string, checking if a 26 * byte array contains valid UTF8 code, calculating the length of an encoded 27 * string. 28 */ 29 public class Text extends BinaryComparable 30 implements WritableComparable<BinaryComparable> { 31 private static final Log LOG= LogFactory.getLog(Text.class); 32 33 private static ThreadLocal<CharsetEncoder> ENCODER_FACTORY = 34 new ThreadLocal<CharsetEncoder>() { 35 protected CharsetEncoder initialValue() { 36 return Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder(). 37 onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT). 38 onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 39 } 40 }; 41 42 private static ThreadLocal<CharsetDecoder> DECODER_FACTORY = 43 new ThreadLocal<CharsetDecoder>() { 44 protected CharsetDecoder initialValue() { 45 return Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder(). 46 onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT). 47 onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 48 } 49 }; 50 51 private static final byte [] EMPTY_BYTES = new byte[0]; 52 53 private byte[] bytes; 54 private int length; 55 56 public Text() { 57 bytes = EMPTY_BYTES; 58 } 59 60 /** Construct from a string. 61 */ 62 public Text(String string) { 63 set(string); 64 } 65 66 /** Construct from another text. */ 67 public Text(Text utf8) { 68 set(utf8); 69 } 70 71 /** Construct from a byte array. 72 */ 73 public Text(byte[] utf8) { 74 set(utf8); 75 } 76 77 /** 78 * Returns the raw bytes; however, only data up to {@link #getLength()} is 79 * valid. 80 */ 81 public byte[] getBytes() { 82 return bytes; 83 } 84 85 /** Returns the number of bytes in the byte array */ 86 public int getLength() { 87 return length; 88 } 89 90 /** 91 * Returns the Unicode Scalar Value (32-bit integer value) 92 * for the character at <code>position</code>. Note that this 93 * method avoids using the converter or doing String instatiation 94 * @return the Unicode scalar value at position or -1 95 * if the position is invalid or points to a 96 * trailing byte 97 */ 98 public int charAt(int position) { 99 if (position > this.length) return -1; // too long 100 if (position < 0) return -1; // duh. 101 102 ByteBuffer bb = (ByteBuffer)ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes).position(position); 103 return bytesToCodePoint(bb.slice()); 104 } 105 106 public int find(String what) { 107 return find(what, 0); 108 } 109 110 /** 111 * Finds any occurence of <code>what</code> in the backing 112 * buffer, starting as position <code>start</code>. The starting 113 * position is measured in bytes and the return value is in 114 * terms of byte position in the buffer. The backing buffer is 115 * not converted to a string for this operation. 116 * @return byte position of the first occurence of the search 117 * string in the UTF-8 buffer or -1 if not found 118 */ 119 public int find(String what, int start) { 120 try { 121 ByteBuffer src = ByteBuffer.wrap(this.bytes,0,this.length); 122 ByteBuffer tgt = encode(what); 123 byte b = tgt.get(); 124 src.position(start); 125 126 while (src.hasRemaining()) { 127 if (b == src.get()) { // matching first byte 128 src.mark(); // save position in loop 129 tgt.mark(); // save position in target 130 boolean found = true; 131 int pos = src.position()-1; 132 while (tgt.hasRemaining()) { 133 if (!src.hasRemaining()) { // src expired first 134 tgt.reset(); 135 src.reset(); 136 found = false; 137 break; 138 } 139 if (!(tgt.get() == src.get())) { 140 tgt.reset(); 141 src.reset(); 142 found = false; 143 break; // no match 144 } 145 } 146 if (found) return pos; 147 } 148 } 149 return -1; // not found 150 } catch (CharacterCodingException e) { 151 // can‘t get here 152 e.printStackTrace(); 153 return -1; 154 } 155 } 156 /** Set to contain the contents of a string. 157 */ 158 public void set(String string) { 159 try { 160 ByteBuffer bb = encode(string, true); 161 bytes = bb.array(); 162 length = bb.limit(); 163 }catch(CharacterCodingException e) { 164 throw new RuntimeException("Should not have happened " + e.toString()); 165 } 166 } 167 168 /** Set to a utf8 byte array 169 */ 170 public void set(byte[] utf8) { 171 set(utf8, 0, utf8.length); 172 } 173 174 /** copy a text. */ 175 public void set(Text other) { 176 set(other.getBytes(), 0, other.getLength()); 177 } 178 179 /** 180 * Set the Text to range of bytes 181 * @param utf8 the data to copy from 182 * @param start the first position of the new string 183 * @param len the number of bytes of the new string 184 */ 185 public void set(byte[] utf8, int start, int len) { 186 setCapacity(len, false); 187 System.arraycopy(utf8, start, bytes, 0, len); 188 this.length = len; 189 } 190 191 /** 192 * Append a range of bytes to the end of the given text 193 * @param utf8 the data to copy from 194 * @param start the first position to append from utf8 195 * @param len the number of bytes to append 196 */ 197 public void append(byte[] utf8, int start, int len) { 198 setCapacity(length + len, true); 199 System.arraycopy(utf8, start, bytes, length, len); 200 length += len; 201 } 202 203 /** 204 * Clear the string to empty. 205 */ 206 public void clear() { 207 length = 0; 208 } 209 210 /* 211 * Sets the capacity of this Text object to <em>at least</em> 212 * <code>len</code> bytes. If the current buffer is longer, 213 * then the capacity and existing content of the buffer are 214 * unchanged. If <code>len</code> is larger 215 * than the current capacity, the Text object‘s capacity is 216 * increased to match. 217 * @param len the number of bytes we need 218 * @param keepData should the old data be kept 219 */ 220 private void setCapacity(int len, boolean keepData) { 221 if (bytes == null || bytes.length < len) { 222 byte[] newBytes = new byte[len]; 223 if (bytes != null && keepData) { 224 System.arraycopy(bytes, 0, newBytes, 0, length); 225 } 226 bytes = newBytes; 227 } 228 } 229 230 /** 231 * Convert text back to string 232 * @see java.lang.Object#toString() 233 */ 234 public String toString() { 235 try { 236 return decode(bytes, 0, length); 237 } catch (CharacterCodingException e) { 238 throw new RuntimeException("Should not have happened " + e.toString()); 239 } 240 } 241 242 /** deserialize 243 */ 244 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 245 int newLength = WritableUtils.readVInt(in); 246 setCapacity(newLength, false); 247 in.readFully(bytes, 0, newLength); 248 length = newLength; 249 } 250 251 /** Skips over one Text in the input. */ 252 public static void skip(DataInput in) throws IOException { 253 int length = WritableUtils.readVInt(in); 254 WritableUtils.skipFully(in, length); 255 } 256 257 /** serialize 258 * write this object to out 259 * length uses zero-compressed encoding 260 * @see Writable#write(DataOutput) 261 */ 262 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 263 WritableUtils.writeVInt(out, length); 264 out.write(bytes, 0, length); 265 } 266 267 /** Returns true iff <code>o</code> is a Text with the same contents. */ 268 public boolean equals(Object o) { 269 if (o instanceof Text) 270 return super.equals(o); 271 return false; 272 } 273 274 public int hashCode() { 275 return super.hashCode(); 276 } 277 278 /** A WritableComparator optimized for Text keys. */ 279 public static class Comparator extends WritableComparator { 280 public Comparator() { 281 super(Text.class); 282 } 283 284 public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, 285 byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) { 286 int n1 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b1[s1]); 287 int n2 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b2[s2]); 288 return compareBytes(b1, s1+n1, l1-n1, b2, s2+n2, l2-n2); 289 } 290 } 291 292 static { 293 // register this comparator 294 WritableComparator.define(Text.class, new Comparator()); 295 } 296 297 /// STATIC UTILITIES FROM HERE DOWN 298 /** 299 * Converts the provided byte array to a String using the 300 * UTF-8 encoding. If the input is malformed, 301 * replace by a default value. 302 */ 303 public static String decode(byte[] utf8) throws CharacterCodingException { 304 return decode(ByteBuffer.wrap(utf8), true); 305 } 306 307 public static String decode(byte[] utf8, int start, int length) 308 throws CharacterCodingException { 309 return decode(ByteBuffer.wrap(utf8, start, length), true); 310 } 311 312 /** 313 * Converts the provided byte array to a String using the 314 * UTF-8 encoding. If <code>replace</code> is true, then 315 * malformed input is replaced with the 316 * substitution character, which is U+FFFD. Otherwise the 317 * method throws a MalformedInputException. 318 */ 319 public static String decode(byte[] utf8, int start, int length, boolean replace) 320 throws CharacterCodingException { 321 return decode(ByteBuffer.wrap(utf8, start, length), replace); 322 } 323 324 private static String decode(ByteBuffer utf8, boolean replace) 325 throws CharacterCodingException { 326 CharsetDecoder decoder = DECODER_FACTORY.get(); 327 if (replace) { 328 decoder.onMalformedInput( 329 java.nio.charset.CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 330 decoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 331 } 332 String str = decoder.decode(utf8).toString(); 333 // set decoder back to its default value: REPORT 334 if (replace) { 335 decoder.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 336 decoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 337 } 338 return str; 339 } 340 341 /** 342 * Converts the provided String to bytes using the 343 * UTF-8 encoding. If the input is malformed, 344 * invalid chars are replaced by a default value. 345 * @return ByteBuffer: bytes stores at ByteBuffer.array() 346 * and length is ByteBuffer.limit() 347 */ 348 349 public static ByteBuffer encode(String string) 350 throws CharacterCodingException { 351 return encode(string, true); 352 } 353 354 /** 355 * Converts the provided String to bytes using the 356 * UTF-8 encoding. If <code>replace</code> is true, then 357 * malformed input is replaced with the 358 * substitution character, which is U+FFFD. Otherwise the 359 * method throws a MalformedInputException. 360 * @return ByteBuffer: bytes stores at ByteBuffer.array() 361 * and length is ByteBuffer.limit() 362 */ 363 public static ByteBuffer encode(String string, boolean replace) 364 throws CharacterCodingException { 365 CharsetEncoder encoder = ENCODER_FACTORY.get(); 366 if (replace) { 367 encoder.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 368 encoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 369 } 370 ByteBuffer bytes = 371 encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap(string.toCharArray())); 372 if (replace) { 373 encoder.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 374 encoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 375 } 376 return bytes; 377 } 378 379 /** Read a UTF8 encoded string from in 380 */ 381 public static String readString(DataInput in) throws IOException { 382 int length = WritableUtils.readVInt(in); 383 byte [] bytes = new byte[length]; 384 in.readFully(bytes, 0, length); 385 return decode(bytes); 386 } 387 388 /** Write a UTF8 encoded string to out 389 */ 390 public static int writeString(DataOutput out, String s) throws IOException { 391 ByteBuffer bytes = encode(s); 392 int length = bytes.limit(); 393 WritableUtils.writeVInt(out, length); 394 out.write(bytes.array(), 0, length); 395 return length; 396 } 397 398 ////// states for validateUTF8 399 400 private static final int LEAD_BYTE = 0; 401 402 private static final int TRAIL_BYTE_1 = 1; 403 404 private static final int TRAIL_BYTE = 2; 405 406 /** 407 * Check if a byte array contains valid utf-8 408 * @param utf8 byte array 409 * @throws MalformedInputException if the byte array contains invalid utf-8 410 */ 411 public static void validateUTF8(byte[] utf8) throws MalformedInputException { 412 validateUTF8(utf8, 0, utf8.length); 413 } 414 415 /** 416 * Check to see if a byte array is valid utf-8 417 * @param utf8 the array of bytes 418 * @param start the offset of the first byte in the array 419 * @param len the length of the byte sequence 420 * @throws MalformedInputException if the byte array contains invalid bytes 421 */ 422 public static void validateUTF8(byte[] utf8, int start, int len) 423 throws MalformedInputException { 424 int count = start; 425 int leadByte = 0; 426 int length = 0; 427 int state = LEAD_BYTE; 428 while (count < start+len) { 429 int aByte = ((int) utf8[count] & 0xFF); 430 431 switch (state) { 432 case LEAD_BYTE: 433 leadByte = aByte; 434 length = bytesFromUTF8[aByte]; 435 436 switch (length) { 437 case 0: // check for ASCII 438 if (leadByte > 0x7F) 439 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 440 break; 441 case 1: 442 if (leadByte < 0xC2 || leadByte > 0xDF) 443 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 444 state = TRAIL_BYTE_1; 445 break; 446 case 2: 447 if (leadByte < 0xE0 || leadByte > 0xEF) 448 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 449 state = TRAIL_BYTE_1; 450 break; 451 case 3: 452 if (leadByte < 0xF0 || leadByte > 0xF4) 453 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 454 state = TRAIL_BYTE_1; 455 break; 456 default: 457 // too long! Longest valid UTF-8 is 4 bytes (lead + three) 458 // or if < 0 we got a trail byte in the lead byte position 459 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 460 } // switch (length) 461 break; 462 463 case TRAIL_BYTE_1: 464 if (leadByte == 0xF0 && aByte < 0x90) 465 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 466 if (leadByte == 0xF4 && aByte > 0x8F) 467 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 468 if (leadByte == 0xE0 && aByte < 0xA0) 469 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 470 if (leadByte == 0xED && aByte > 0x9F) 471 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 472 // falls through to regular trail-byte test!! 473 case TRAIL_BYTE: 474 if (aByte < 0x80 || aByte > 0xBF) 475 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 476 if (--length == 0) { 477 state = LEAD_BYTE; 478 } else { 479 state = TRAIL_BYTE; 480 } 481 break; 482 } // switch (state) 483 count++; 484 } 485 } 486 487 /** 488 * Magic numbers for UTF-8. These are the number of bytes 489 * that <em>follow</em> a given lead byte. Trailing bytes 490 * have the value -1. The values 4 and 5 are presented in 491 * this table, even though valid UTF-8 cannot include the 492 * five and six byte sequences. 493 */ 494 static final int[] bytesFromUTF8 = 495 { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 496 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 497 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 498 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 499 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 500 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 501 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 502 // trail bytes 503 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 504 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 505 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 506 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 507 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 508 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 509 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5 }; 510 511 /** 512 * Returns the next code point at the current position in 513 * the buffer. The buffer‘s position will be incremented. 514 * Any mark set on this buffer will be changed by this method! 515 */ 516 public static int bytesToCodePoint(ByteBuffer bytes) { 517 bytes.mark(); 518 byte b = bytes.get(); 519 bytes.reset(); 520 int extraBytesToRead = bytesFromUTF8[(b & 0xFF)]; 521 if (extraBytesToRead < 0) return -1; // trailing byte! 522 int ch = 0; 523 524 switch (extraBytesToRead) { 525 case 5: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; /* remember, illegal UTF-8 */ 526 case 4: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; /* remember, illegal UTF-8 */ 527 case 3: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; 528 case 2: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; 529 case 1: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; 530 case 0: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); 531 } 532 ch -= offsetsFromUTF8[extraBytesToRead]; 533 534 return ch; 535 } 536 537 538 static final int offsetsFromUTF8[] = 539 { 0x00000000, 0x00003080, 540 0x000E2080, 0x03C82080, 0xFA082080, 0x82082080 }; 541 542 /** 543 * For the given string, returns the number of UTF-8 bytes 544 * required to encode the string. 545 * @param string text to encode 546 * @return number of UTF-8 bytes required to encode 547 */ 548 public static int utf8Length(String string) { 549 CharacterIterator iter = new StringCharacterIterator(string); 550 char ch = iter.first(); 551 int size = 0; 552 while (ch != CharacterIterator.DONE) { 553 if ((ch >= 0xD800) && (ch < 0xDC00)) { 554 // surrogate pair? 555 char trail = iter.next(); 556 if ((trail > 0xDBFF) && (trail < 0xE000)) { 557 // valid pair 558 size += 4; 559 } else { 560 // invalid pair 561 size += 3; 562 iter.previous(); // rewind one 563 } 564 } else if (ch < 0x80) { 565 size++; 566 } else if (ch < 0x800) { 567 size += 2; 568 } else { 569 // ch < 0x10000, that is, the largest char value 570 size += 3; 571 } 572 ch = iter.next(); 573 } 574 return size; 575 } 576 }
它继承了BinaryComparable基类、实现了WritableComparable<BinaryComparable>接口
WritableComparable已经在上面讲述,现来分析BinaryComparable基类,定义如下:

1 package org.apache.hadoop.io; 2 public abstract class BinaryComparable implements Comparable<BinaryComparable> { 3 public abstract int getLength(); 4 public abstract byte[] getBytes(); 5 public int compareTo(BinaryComparable other) { 6 if (this == other) 7 return 0; 8 return WritableComparator.compareBytes(getBytes(), 0, getLength(), 9 other.getBytes(), 0, other.getLength()); 10 } 11 public int compareTo(byte[] other, int off, int len) { 12 return WritableComparator.compareBytes(getBytes(), 0, getLength(), 13 other, off, len); 14 } 15 public boolean equals(Object other) { 16 if (!(other instanceof BinaryComparable)) 17 return false; 18 BinaryComparable that = (BinaryComparable)other; 19 if (this.getLength() != that.getLength()) 20 return false; 21 return this.compareTo(that) == 0; 22 } 23 public int hashCode() { 24 return WritableComparator.hashBytes(getBytes(), getLength()); 25 } 26 27 }
BinaryComparable是一个抽象类,主要是提供一个在二进制流这一层次直接比较两个对象的功能
其中
WritableComparator.compareBytes(getBytes(), 0, getLength(), other.getBytes(), 0, other.getLength());
是根据字典序排序返回比较结果。
而
WritableComparator.hashBytes(getBytes(), getLength());
则是返回字节流的hashCode;
现在总括看看Text的方法
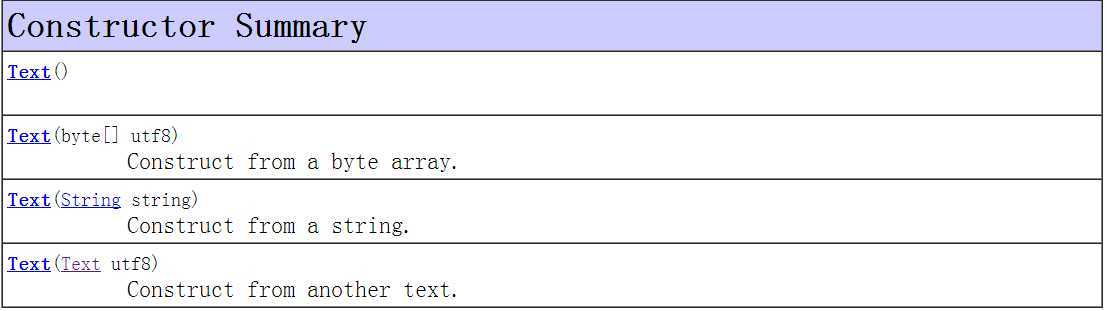
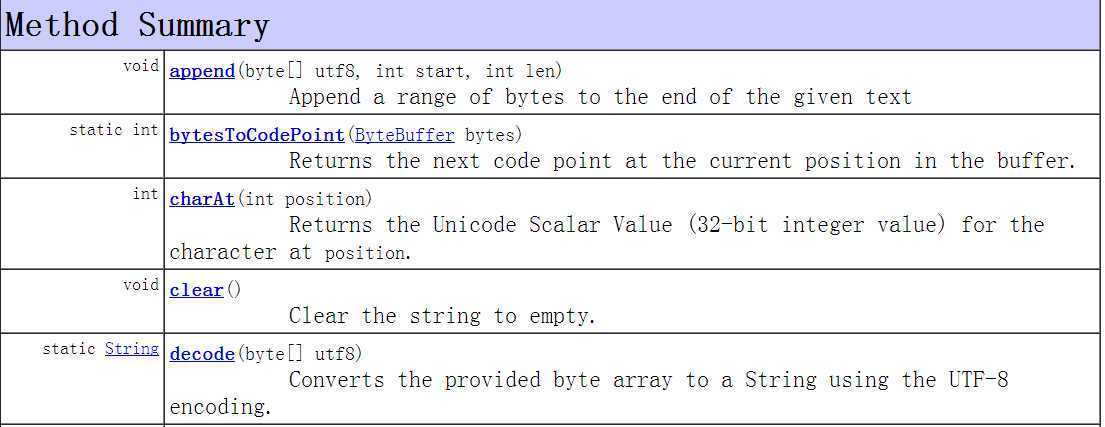

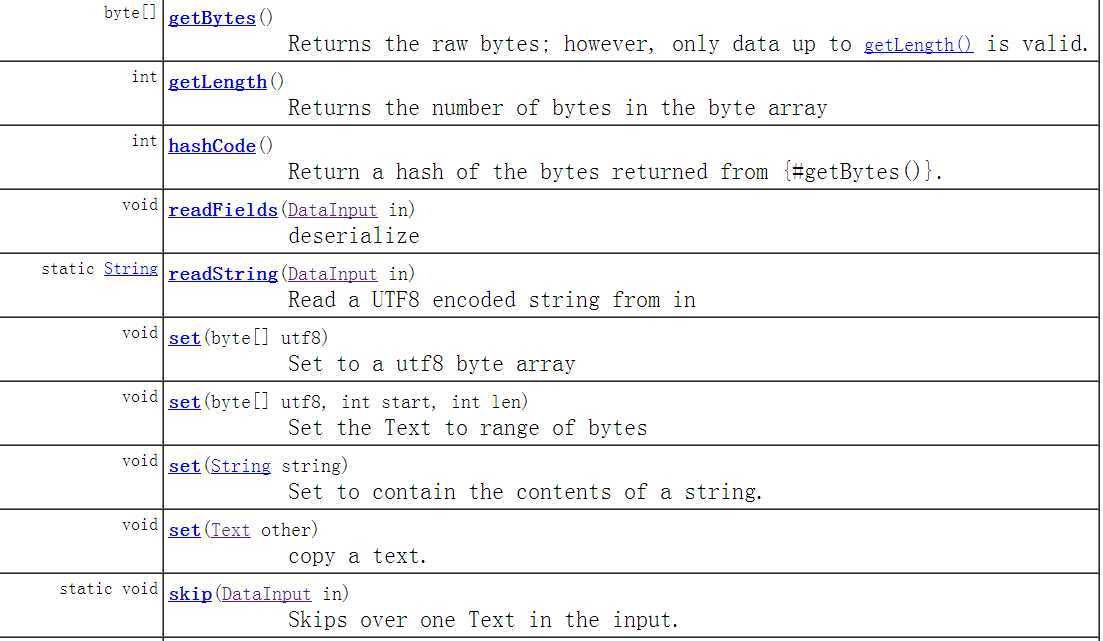



1 /** 2 * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one 3 * or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file 4 * distributed with this work for additional information 5 * regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file 6 * to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the 7 * "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance 8 * with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at 9 * 10 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 11 * 12 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 13 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 14 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 15 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 16 * limitations under the License. 17 */ 18 19 package org.apache.hadoop.io; 20 21 import java.io.IOException; 22 import java.io.DataInput; 23 import java.io.DataOutput; 24 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 25 import java.nio.CharBuffer; 26 import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException; 27 import java.nio.charset.Charset; 28 import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder; 29 import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder; 30 import java.nio.charset.CodingErrorAction; 31 import java.nio.charset.MalformedInputException; 32 import java.text.CharacterIterator; 33 import java.text.StringCharacterIterator; 34 35 import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; 36 import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; 37 38 /** This class stores text using standard UTF8 encoding. It provides methods 39 * to serialize, deserialize, and compare texts at byte level. The type of 40 * length is integer and is serialized using zero-compressed format. <p>In 41 * addition, it provides methods for string traversal without converting the 42 * byte array to a string. <p>Also includes utilities for 43 * serializing/deserialing a string, coding/decoding a string, checking if a 44 * byte array contains valid UTF8 code, calculating the length of an encoded 45 * string. 46 */ 47 public class Text extends BinaryComparable 48 implements WritableComparable<BinaryComparable> { 49 private static final Log LOG= LogFactory.getLog(Text.class); 50 51 private static ThreadLocal<CharsetEncoder> ENCODER_FACTORY = 52 new ThreadLocal<CharsetEncoder>() { 53 protected CharsetEncoder initialValue() { 54 return Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder(). 55 onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT). 56 onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 57 } 58 }; 59 60 private static ThreadLocal<CharsetDecoder> DECODER_FACTORY = 61 new ThreadLocal<CharsetDecoder>() { 62 protected CharsetDecoder initialValue() { 63 return Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder(). 64 onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT). 65 onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 66 } 67 }; 68 69 private static final byte [] EMPTY_BYTES = new byte[0]; 70 71 private byte[] bytes; 72 private int length; 73 74 public Text() { 75 bytes = EMPTY_BYTES; 76 } 77 78 /** Construct from a string. 79 */ 80 public Text(String string) { 81 set(string); 82 } 83 84 /** Construct from another text. */ 85 public Text(Text utf8) { 86 set(utf8); 87 } 88 89 /** Construct from a byte array. 90 */ 91 public Text(byte[] utf8) { 92 set(utf8); 93 } 94 95 /** 96 * Returns the raw bytes; however, only data up to {@link #getLength()} is 97 * valid. 98 */ 99 public byte[] getBytes() { 100 return bytes; 101 } 102 103 /** Returns the number of bytes in the byte array */ 104 public int getLength() { 105 return length; 106 } 107 108 /** 109 * Returns the Unicode Scalar Value (32-bit integer value) 110 * for the character at <code>position</code>. Note that this 111 * method avoids using the converter or doing String instatiation 112 * @return the Unicode scalar value at position or -1 113 * if the position is invalid or points to a 114 * trailing byte 115 */ 116 public int charAt(int position) { 117 if (position > this.length) return -1; // too long 118 if (position < 0) return -1; // duh. 119 120 ByteBuffer bb = (ByteBuffer)ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes).position(position); 121 return bytesToCodePoint(bb.slice()); 122 } 123 124 public int find(String what) { 125 return find(what, 0); 126 } 127 128 /** 129 * Finds any occurence of <code>what</code> in the backing 130 * buffer, starting as position <code>start</code>. The starting 131 * position is measured in bytes and the return value is in 132 * terms of byte position in the buffer. The backing buffer is 133 * not converted to a string for this operation. 134 * @return byte position of the first occurence of the search 135 * string in the UTF-8 buffer or -1 if not found 136 */ 137 public int find(String what, int start) { 138 try { 139 ByteBuffer src = ByteBuffer.wrap(this.bytes,0,this.length); 140 ByteBuffer tgt = encode(what); 141 byte b = tgt.get(); 142 src.position(start); 143 144 while (src.hasRemaining()) { 145 if (b == src.get()) { // matching first byte 146 src.mark(); // save position in loop 147 tgt.mark(); // save position in target 148 boolean found = true; 149 int pos = src.position()-1; 150 while (tgt.hasRemaining()) { 151 if (!src.hasRemaining()) { // src expired first 152 tgt.reset(); 153 src.reset(); 154 found = false; 155 break; 156 } 157 if (!(tgt.get() == src.get())) { 158 tgt.reset(); 159 src.reset(); 160 found = false; 161 break; // no match 162 } 163 } 164 if (found) return pos; 165 } 166 } 167 return -1; // not found 168 } catch (CharacterCodingException e) { 169 // can‘t get here 170 e.printStackTrace(); 171 return -1; 172 } 173 } 174 /** Set to contain the contents of a string. 175 */ 176 public void set(String string) { 177 try { 178 ByteBuffer bb = encode(string, true); 179 bytes = bb.array(); 180 length = bb.limit(); 181 }catch(CharacterCodingException e) { 182 throw new RuntimeException("Should not have happened " + e.toString()); 183 } 184 } 185 186 /** Set to a utf8 byte array 187 */ 188 public void set(byte[] utf8) { 189 set(utf8, 0, utf8.length); 190 } 191 192 /** copy a text. */ 193 public void set(Text other) { 194 set(other.getBytes(), 0, other.getLength()); 195 } 196 197 /** 198 * Set the Text to range of bytes 199 * @param utf8 the data to copy from 200 * @param start the first position of the new string 201 * @param len the number of bytes of the new string 202 */ 203 public void set(byte[] utf8, int start, int len) { 204 setCapacity(len, false); 205 System.arraycopy(utf8, start, bytes, 0, len); 206 this.length = len; 207 } 208 209 /** 210 * Append a range of bytes to the end of the given text 211 * @param utf8 the data to copy from 212 * @param start the first position to append from utf8 213 * @param len the number of bytes to append 214 */ 215 public void append(byte[] utf8, int start, int len) { 216 setCapacity(length + len, true); 217 System.arraycopy(utf8, start, bytes, length, len); 218 length += len; 219 } 220 221 /** 222 * Clear the string to empty. 223 */ 224 public void clear() { 225 length = 0; 226 } 227 228 /* 229 * Sets the capacity of this Text object to <em>at least</em> 230 * <code>len</code> bytes. If the current buffer is longer, 231 * then the capacity and existing content of the buffer are 232 * unchanged. If <code>len</code> is larger 233 * than the current capacity, the Text object‘s capacity is 234 * increased to match. 235 * @param len the number of bytes we need 236 * @param keepData should the old data be kept 237 */ 238 private void setCapacity(int len, boolean keepData) { 239 if (bytes == null || bytes.length < len) { 240 byte[] newBytes = new byte[len]; 241 if (bytes != null && keepData) { 242 System.arraycopy(bytes, 0, newBytes, 0, length); 243 } 244 bytes = newBytes; 245 } 246 } 247 248 /** 249 * Convert text back to string 250 * @see java.lang.Object#toString() 251 */ 252 public String toString() { 253 try { 254 return decode(bytes, 0, length); 255 } catch (CharacterCodingException e) { 256 throw new RuntimeException("Should not have happened " + e.toString()); 257 } 258 } 259 260 /** deserialize 261 */ 262 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 263 int newLength = WritableUtils.readVInt(in); 264 setCapacity(newLength, false); 265 in.readFully(bytes, 0, newLength); 266 length = newLength; 267 } 268 269 /** Skips over one Text in the input. */ 270 public static void skip(DataInput in) throws IOException { 271 int length = WritableUtils.readVInt(in); 272 WritableUtils.skipFully(in, length); 273 } 274 275 /** serialize 276 * write this object to out 277 * length uses zero-compressed encoding 278 * @see Writable#write(DataOutput) 279 */ 280 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 281 WritableUtils.writeVInt(out, length); 282 out.write(bytes, 0, length); 283 } 284 285 /** Returns true iff <code>o</code> is a Text with the same contents. */ 286 public boolean equals(Object o) { 287 if (o instanceof Text) 288 return super.equals(o); 289 return false; 290 } 291 292 public int hashCode() { 293 return super.hashCode(); 294 } 295 296 /** A WritableComparator optimized for Text keys. */ 297 public static class Comparator extends WritableComparator { 298 public Comparator() { 299 super(Text.class); 300 } 301 302 public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, 303 byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) { 304 int n1 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b1[s1]); 305 int n2 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b2[s2]); 306 return compareBytes(b1, s1+n1, l1-n1, b2, s2+n2, l2-n2); 307 } 308 } 309 310 static { 311 // register this comparator 312 WritableComparator.define(Text.class, new Comparator()); 313 } 314 315 /// STATIC UTILITIES FROM HERE DOWN 316 /** 317 * Converts the provided byte array to a String using the 318 * UTF-8 encoding. If the input is malformed, 319 * replace by a default value. 320 */ 321 public static String decode(byte[] utf8) throws CharacterCodingException { 322 return decode(ByteBuffer.wrap(utf8), true); 323 } 324 325 public static String decode(byte[] utf8, int start, int length) 326 throws CharacterCodingException { 327 return decode(ByteBuffer.wrap(utf8, start, length), true); 328 } 329 330 /** 331 * Converts the provided byte array to a String using the 332 * UTF-8 encoding. If <code>replace</code> is true, then 333 * malformed input is replaced with the 334 * substitution character, which is U+FFFD. Otherwise the 335 * method throws a MalformedInputException. 336 */ 337 public static String decode(byte[] utf8, int start, int length, boolean replace) 338 throws CharacterCodingException { 339 return decode(ByteBuffer.wrap(utf8, start, length), replace); 340 } 341 342 private static String decode(ByteBuffer utf8, boolean replace) 343 throws CharacterCodingException { 344 CharsetDecoder decoder = DECODER_FACTORY.get(); 345 if (replace) { 346 decoder.onMalformedInput( 347 java.nio.charset.CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 348 decoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 349 } 350 String str = decoder.decode(utf8).toString(); 351 // set decoder back to its default value: REPORT 352 if (replace) { 353 decoder.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 354 decoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 355 } 356 return str; 357 } 358 359 /** 360 * Converts the provided String to bytes using the 361 * UTF-8 encoding. If the input is malformed, 362 * invalid chars are replaced by a default value. 363 * @return ByteBuffer: bytes stores at ByteBuffer.array() 364 * and length is ByteBuffer.limit() 365 */ 366 367 public static ByteBuffer encode(String string) 368 throws CharacterCodingException { 369 return encode(string, true); 370 } 371 372 /** 373 * Converts the provided String to bytes using the 374 * UTF-8 encoding. If <code>replace</code> is true, then 375 * malformed input is replaced with the 376 * substitution character, which is U+FFFD. Otherwise the 377 * method throws a MalformedInputException. 378 * @return ByteBuffer: bytes stores at ByteBuffer.array() 379 * and length is ByteBuffer.limit() 380 */ 381 public static ByteBuffer encode(String string, boolean replace) 382 throws CharacterCodingException { 383 CharsetEncoder encoder = ENCODER_FACTORY.get(); 384 if (replace) { 385 encoder.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 386 encoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPLACE); 387 } 388 ByteBuffer bytes = 389 encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap(string.toCharArray())); 390 if (replace) { 391 encoder.onMalformedInput(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 392 encoder.onUnmappableCharacter(CodingErrorAction.REPORT); 393 } 394 return bytes; 395 } 396 397 /** Read a UTF8 encoded string from in 398 */ 399 public static String readString(DataInput in) throws IOException { 400 int length = WritableUtils.readVInt(in); 401 byte [] bytes = new byte[length]; 402 in.readFully(bytes, 0, length); 403 return decode(bytes); 404 } 405 406 /** Write a UTF8 encoded string to out 407 */ 408 public static int writeString(DataOutput out, String s) throws IOException { 409 ByteBuffer bytes = encode(s); 410 int length = bytes.limit(); 411 WritableUtils.writeVInt(out, length); 412 out.write(bytes.array(), 0, length); 413 return length; 414 } 415 416 ////// states for validateUTF8 417 418 private static final int LEAD_BYTE = 0; 419 420 private static final int TRAIL_BYTE_1 = 1; 421 422 private static final int TRAIL_BYTE = 2; 423 424 /** 425 * Check if a byte array contains valid utf-8 426 * @param utf8 byte array 427 * @throws MalformedInputException if the byte array contains invalid utf-8 428 */ 429 public static void validateUTF8(byte[] utf8) throws MalformedInputException { 430 validateUTF8(utf8, 0, utf8.length); 431 } 432 433 /** 434 * Check to see if a byte array is valid utf-8 435 * @param utf8 the array of bytes 436 * @param start the offset of the first byte in the array 437 * @param len the length of the byte sequence 438 * @throws MalformedInputException if the byte array contains invalid bytes 439 */ 440 public static void validateUTF8(byte[] utf8, int start, int len) 441 throws MalformedInputException { 442 int count = start; 443 int leadByte = 0; 444 int length = 0; 445 int state = LEAD_BYTE; 446 while (count < start+len) { 447 int aByte = ((int) utf8[count] & 0xFF); 448 449 switch (state) { 450 case LEAD_BYTE: 451 leadByte = aByte; 452 length = bytesFromUTF8[aByte]; 453 454 switch (length) { 455 case 0: // check for ASCII 456 if (leadByte > 0x7F) 457 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 458 break; 459 case 1: 460 if (leadByte < 0xC2 || leadByte > 0xDF) 461 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 462 state = TRAIL_BYTE_1; 463 break; 464 case 2: 465 if (leadByte < 0xE0 || leadByte > 0xEF) 466 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 467 state = TRAIL_BYTE_1; 468 break; 469 case 3: 470 if (leadByte < 0xF0 || leadByte > 0xF4) 471 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 472 state = TRAIL_BYTE_1; 473 break; 474 default: 475 // too long! Longest valid UTF-8 is 4 bytes (lead + three) 476 // or if < 0 we got a trail byte in the lead byte position 477 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 478 } // switch (length) 479 break; 480 481 case TRAIL_BYTE_1: 482 if (leadByte == 0xF0 && aByte < 0x90) 483 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 484 if (leadByte == 0xF4 && aByte > 0x8F) 485 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 486 if (leadByte == 0xE0 && aByte < 0xA0) 487 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 488 if (leadByte == 0xED && aByte > 0x9F) 489 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 490 // falls through to regular trail-byte test!! 491 case TRAIL_BYTE: 492 if (aByte < 0x80 || aByte > 0xBF) 493 throw new MalformedInputException(count); 494 if (--length == 0) { 495 state = LEAD_BYTE; 496 } else { 497 state = TRAIL_BYTE; 498 } 499 break; 500 } // switch (state) 501 count++; 502 } 503 } 504 505 /** 506 * Magic numbers for UTF-8. These are the number of bytes 507 * that <em>follow</em> a given lead byte. Trailing bytes 508 * have the value -1. The values 4 and 5 are presented in 509 * this table, even though valid UTF-8 cannot include the 510 * five and six byte sequences. 511 */ 512 static final int[] bytesFromUTF8 = 513 { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 514 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 515 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 516 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 517 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 518 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 519 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 520 // trail bytes 521 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 522 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 523 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 524 -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 525 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 526 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 527 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5 }; 528 529 /** 530 * Returns the next code point at the current position in 531 * the buffer. The buffer‘s position will be incremented. 532 * Any mark set on this buffer will be changed by this method! 533 */ 534 public static int bytesToCodePoint(ByteBuffer bytes) { 535 bytes.mark(); 536 byte b = bytes.get(); 537 bytes.reset(); 538 int extraBytesToRead = bytesFromUTF8[(b & 0xFF)]; 539 if (extraBytesToRead < 0) return -1; // trailing byte! 540 int ch = 0; 541 542 switch (extraBytesToRead) { 543 case 5: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; /* remember, illegal UTF-8 */ 544 case 4: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; /* remember, illegal UTF-8 */ 545 case 3: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; 546 case 2: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; 547 case 1: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); ch <<= 6; 548 case 0: ch += (bytes.get() & 0xFF); 549 } 550 ch -= offsetsFromUTF8[extraBytesToRead]; 551 552 return ch; 553 } 554 555 556 static final int offsetsFromUTF8[] = 557 { 0x00000000, 0x00003080, 558 0x000E2080, 0x03C82080, 0xFA082080, 0x82082080 }; 559 560 /** 561 * For the given string, returns the number of UTF-8 bytes 562 * required to encode the string. 563 * @param string text to encode 564 * @return number of UTF-8 bytes required to encode 565 */ 566 public static int utf8Length(String string) { 567 CharacterIterator iter = new StringCharacterIterator(string); 568 char ch = iter.first(); 569 int size = 0; 570 while (ch != CharacterIterator.DONE) { 571 if ((ch >= 0xD800) && (ch < 0xDC00)) { 572 // surrogate pair? 573 char trail = iter.next(); 574 if ((trail > 0xDBFF) && (trail < 0xE000)) { 575 // valid pair 576 size += 4; 577 } else { 578 // invalid pair 579 size += 3; 580 iter.previous(); // rewind one 581 } 582 } else if (ch < 0x80) { 583 size++; 584 } else if (ch < 0x800) { 585 size += 2; 586 } else { 587 // ch < 0x10000, that is, the largest char value 588 size += 3; 589 } 590 ch = iter.next(); 591 } 592 return size; 593 } 594 }
Text是针对UTF-8序列的Writable类,一般可以认为它等价于java.lang.String 的 Writable,为了与输入流输出流DataInput、DataOutput兼容,Text是使用Java的UTF-8修改版来进行编码。关于UTF-8修改版如下:


本文基于知识共享署名-非商业性使用 3.0 许可协议进行许可。欢迎转载、演绎,但是必须保留本文的署名林羽飞扬,若需咨询,请给我发信
标签:des style blog http color os io 使用 java
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhengyuhong/p/3952954.html