标签:clu div 之间 路径压缩 set get ima 维护 ++
看了标答感觉思路清晰了许多,用并查集来维护全联通块的点数和边权和。
用另一个up[]数组(也是并查集)来保证每条边不会被重复附权值,这样我们只要将询问按权值从小到大排序,一定能的到最小的边权和与联通块中的点数。
下面是过程分析。过程中一共运用了两个并查集。
[数据]
1
10 3
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6
3 7
4 8
5 9
5 10
9 6 3 1 50
1 4 2 5 20
9 10 8 10 40
[分析]
首先我们将图构建出来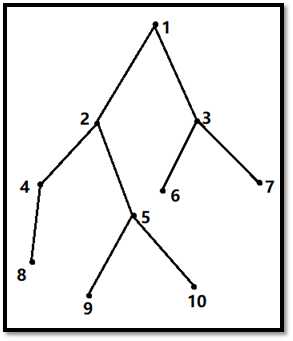
我们将m次询问按权值从小到大排序后:
1 4 2 5 20
9 10 8 10 40
9 6 3 1 50
对于(1,4) (2,5) 20 这一组询问:
我们做如下操作, 首先查找1,4的lca(此例中lca即为1),先合并4与lca之间的边:利用up[] 往上合并直到超过或者到达lca。在往上合并的过程中,可以把下面的边权合并至父节点。利用up[]的路径压缩性质,下次再访问up[4],up[2]时会直接跳至1。此时cnt[1]已经加上了了从4到1路径中点的个数,cost[1]里面加上了了从4到1所有边权的和(利用一个并查集维护)。经过上述操作 parent[4] = parent[2] = 1, up[4] = up[2] = 1。同理我们继续合并1与lca(lca=1);
合并完之后,我们处理2,5这一对点,lca(2,5)=2; 首先我们合并5与lca之间的边,利用up[5]=5,我们在并查集中合并5与anc[5][0](是倍增lca,所以即为5的2^0级父节点) 我们知道anc[5][0]=2;所以在merge(5,anc[5][0],cost)的过程中,实际上是把边权和点数附加到了anc[5][0]的父节点上,即1(详见上一段操作中,2已经被合并至1上,即parent[2] = 1),也就是说cnt[1]记录了5到lca路径中点的个数,cost[1]里面加上了5到lca所有边权的和,且经过这一段操作,up[5] = 1, parent[5] = 1。同理,我们继续合并2与lca(lca=2)。
对于9 10 8 10 40 这一组询问,
lca[9,10]=5,照上面的过程合并中将{1,2,4,5,9 ,10}都加进了父节点中,在处理8,10(lca(8,10)=2)中我们发现,在8,10路径之中有已经被赋值的边,且肯定比当前要赋的值(因为询问是按权值从小到大来的)小,这个时候 up数组 就要发挥作用了。第一次询问up[8] = 8,合并[8,anc[8][0]=4],下一次询问up[8] = 4,合并[4 , anc[4][0]=2],这个时候就,因为parent[2] = 1,所以8被记录进了cnt[1],且边权也被加到了cost[1],再之后up[4] = 1,直接跳到了lca=2节点的上面,提示我们不需要再继续合并了(deep[1]<deep[2])。之后都进行相似的操作就可以得出答案 [9, 280]。
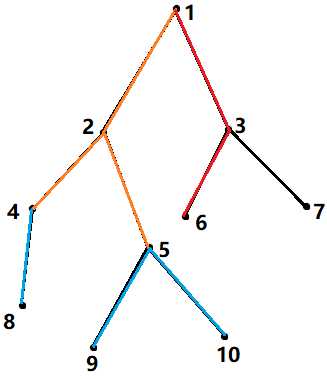 就像这样 , 9 10 8 10 50这组询问实际上只将3条蓝色边赋值成了40,橙色的边早已赋值成了更优的20。
就像这样 , 9 10 8 10 50这组询问实际上只将3条蓝色边赋值成了40,橙色的边早已赋值成了更优的20。
实际上,up数组保存的是与自己不在一个联通块(另一个并查集维护联通快性质)的且最接近自己的父节点,比如此例子中up[4]=1,up[8]=1,(此例子中较特殊,已经不存在深度更小的顶点了,假如第一组询问换成2 4 2 5 20,那么up[2] = up[4] = 1)直接跳到了最高点,提示我们不需要继续合并了,之后的边肯定都已经赋过值了,且值更优。
/*hdu6074[并查集+LCA+思维] 2017多校4*/ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; struct node { int a, b, c, d; LL w; bool operator < (node& x) { return w < x.w; } } q[100005]; vector<int> G[100005]; int T, m, n; int up[100005], p[100005], deep[100005], anc[100005][22]; LL cnt[100005], cost[100005]; void init() { for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { G[i].clear(); } memset(deep, 0, sizeof(deep)); for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) cost[i]=0,cnt[i]=1,p[i] = up[i] = i; } int getfa(int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = getfa(p[x]); } int getup(int x) { return up[x] == x ? x : up[x] = getup(up[x]); } void dfs(int u, int fa) { anc[u][0] = fa; for (int i = 1; i < 21; i++) { anc[u][i] = anc[anc[u][i - 1]][i - 1]; } for (int i = 0; i < (int)G[u].size(); i++) { int v = G[u][i]; if (v == fa) continue; deep[v] = deep[u] + 1; dfs(v, u); } } int lca(int u, int v) { if (deep[u] < deep[v]) swap(u, v); for (int i = 21; ~i; i--) { if (deep[v] <= deep[anc[u][i]]) { u = anc[u][i]; } } if (u == v) return u; for (int i = 21; ~i; i--) { if (anc[u][i] != anc[v][i]) { u = anc[u][i]; v = anc[v][i]; } } return anc[u][0]; } void merge(int u, int v, LL w) { int x = getfa(u); int y = getfa(v); if (x == y) return; p[x] = y; cnt[y] += cnt[x]; cost[y] += cost[x] + w; } void jump(int u, int v, LL w) { for (;;) { u = getup(u); if (deep[u] <= deep[v]) return; merge(u, anc[u][0], w); up[u] = anc[u][0]; } } void solve() { dfs(1, 1); sort(q + 1, q + m + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int k = lca(q[i].a, q[i].b); //cout << q[i].w << endl; jump(q[i].a, k, q[i].w); jump(q[i].b, k, q[i].w); k = lca(q[i].c, q[i].d); jump(q[i].c, k, q[i].w); jump(q[i].d, k, q[i].w); merge(q[i].a, q[i].c, q[i].w); } printf("%lld %lld\n",cnt[getfa(1)],cost[getfa(1)]); } int main() { scanf("%d", &T); while (T--) { int u, v; scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); init(); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); G[u].push_back(v); G[v].push_back(u); } for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { scanf("%d%d%d%d%lld", &q[i].a, &q[i].b, &q[i].c, &q[i].d, &q[i].w); } solve(); } return 0; } /* 2 10 3 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 3 6 3 7 4 8 5 9 5 10 1 4 2 5 20 9 10 8 10 40 9 6 3 1 50 10 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 3 6 3 7 4 8 5 9 5 10 1 7 9 10 20 */
标签:clu div 之间 路径压缩 set get ima 维护 ++
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/UnderSilenceee/p/7294545.html