标签:最好 创建 product red component gauss 带宽 eset 技术
学习利用sklearn的几个聚类方法:
一.几种聚类方法
1.高斯混合聚类(mixture of gaussians)
2.k均值聚类(kmeans)
3.密度聚类,均值漂移(mean shift)
4.层次聚类或连接聚类(ward最小离差平方和)
二.评估方法
1.完整性:值:0-1,同一个类别所有数据样本是否划分到同一个簇中
2.同质性:值:0-1,每个簇是否只包含同一个类别的样本
3.上面两个的调和均值
4.以上三种在评分时需要用到数据样本的真正标签,但实际很难做到。轮廓系数(1,-1):只使用聚类的数据,它计算的是每个数据样本与同簇数据样本和其它簇数据样本之间的相似度,因为从平均来看,与同簇比较起来,比其它簇更相似。
三.说明
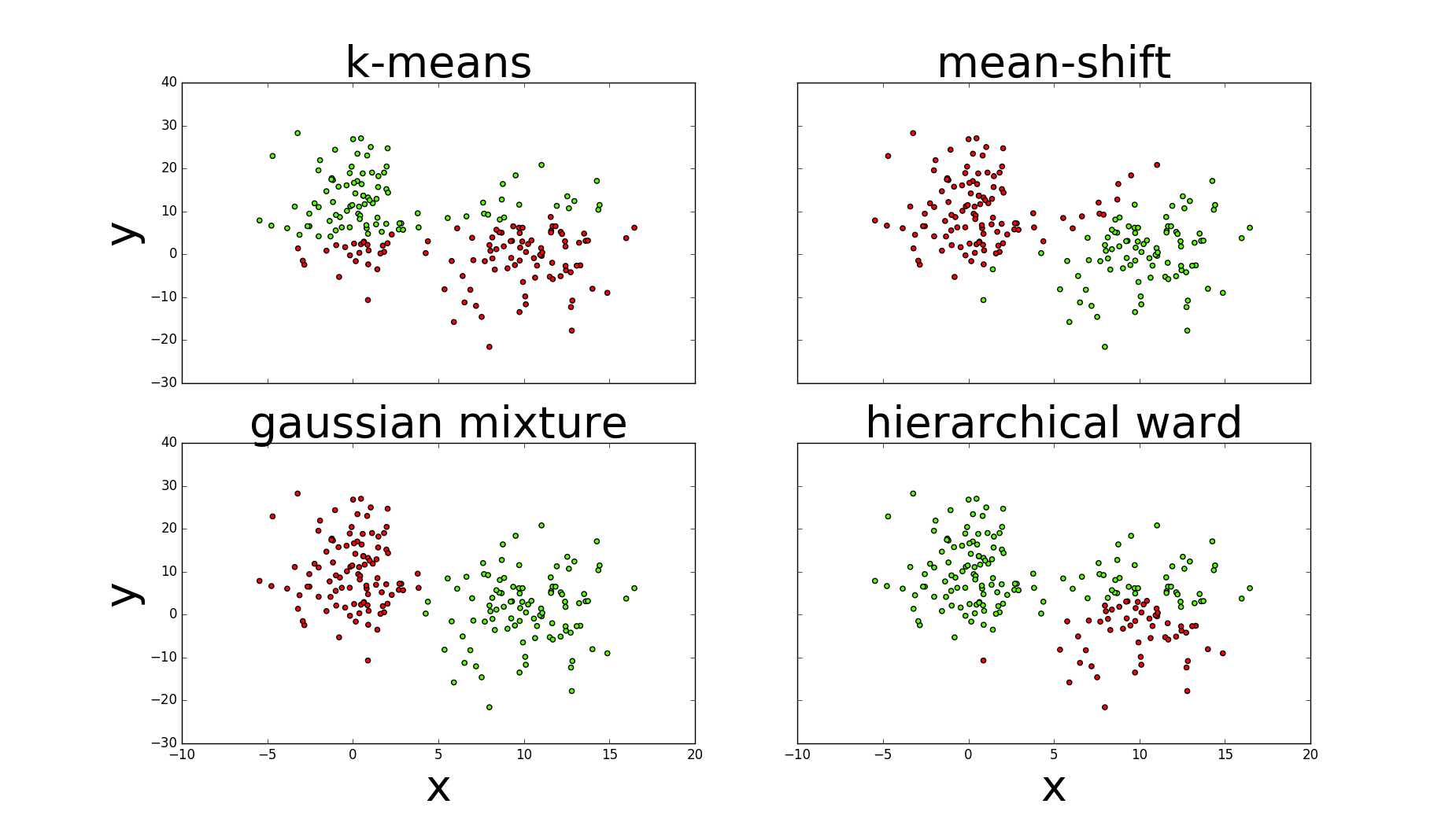
1.kmeans与高斯需要指定簇的数量(n_clusters=2,n_components=2);均值漂移指定带宽(bandwidth=7);层次使用ward链接定义合并代价(距离),终止最大距离max_d。
2.图中可以看出高斯的评估指标最好,其次是均值漂移,k均值与层次较差
四.sklearn聚类
1 #!/usr/bin/python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 import numpy as np 5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 6 from sklearn.cluster import KMeans 7 from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift 8 from sklearn.metrics import homogeneity_completeness_v_measure 9 from sklearn import mixture 10 from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import linkage 11 from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import fcluster 12 13 class ClusterMethod: 14 15 def __init__(self): 16 l1=np.zeros(100) 17 l2=np.ones(100) 18 self.labels=np.concatenate((l1,l2),) 19 20 #随机创建两个二维正太分布,形成数据集 21 def dataProduction(self): 22 # 随机创建两个二维正太分布,形成数据集 23 np.random.seed(4711) 24 c1 = np.random.multivariate_normal([10, 0], [[3, 1], [1, 4]], size=[100, ]) 25 l1 = np.zeros(100) 26 l2 = np.ones(100) 27 # 一个100行的服从正态分布的二维数组 28 c2 = np.random.multivariate_normal([0, 10], [[3, 1], [1, 4]], size=[100, ]) 29 # 加上一些噪音 30 np.random.seed(1) 31 noise1x = np.random.normal(0, 2, 100) 32 noise1y = np.random.normal(0, 8, 100) 33 noise2 = np.random.normal(0, 8, 100) 34 c1[:, 0] += noise1x # 第0列加入噪音数据 35 c1[:, 1] += noise1y 36 c2[:, 1] += noise2 37 38 # 定义绘图 39 self.fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15)) 40 # 添加子图,返回Axes实例,参数:子图总行数,子图总列数,子图位置 41 ax = self.fig.add_subplot(111) 42 # x轴 43 ax.set_xlabel(‘x‘, fontsize=30) 44 # y轴 45 ax.set_ylabel(‘y‘, fontsize=30) 46 # 标题 47 self.fig.suptitle(‘classes‘, fontsize=30) 48 # 连接 49 labels = np.concatenate((l1, l2), ) 50 X = np.concatenate((c1, c2), ) 51 # 散点图 52 pp1 = ax.scatter(c1[:, 0], c1[:, 1], cmap=‘prism‘, s=50, color=‘r‘) 53 pp2 = ax.scatter(c2[:, 0], c2[:, 1], cmap=‘prism‘, s=50, color=‘g‘) 54 ax.legend((pp1, pp2), (‘class 1‘, ‘class 2‘), fontsize=35) 55 self.fig.savefig(‘scatter.png‘) 56 return X 57 58 def clusterMethods(self): 59 X=self.dataProduction() 60 self.fig.clf()#reset plt 61 self.fig,((axis1,axis2),(axis3,axis4))=plt.subplots(2,2,sharex=‘col‘,sharey=‘row‘)#函数返回一个figure图像和一个子图ax的array列表 62 63 #k-means 64 self.kMeans(X,axis1) 65 #mean-shift 66 self.meanShift(X,axis2) 67 #gaussianMix 68 self.gaussianMix(X,axis3) 69 #hierarchicalWard 70 self.hierarchicalWard(X,axis4) 71 72 def kMeans(self,X,axis1): 73 kmeans=KMeans(n_clusters=2)#聚类个数 74 kmeans.fit(X)#训练 75 pred_kmeans=kmeans.labels_#每个样本所属的类 76 print(‘kmeans:‘,np.unique(kmeans.labels_)) 77 print(‘kmeans:‘,homogeneity_completeness_v_measure(self.labels,pred_kmeans))#评估方法,同质性,完整性,两者的调和平均 78 #plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=kmeans.labels_,cmap=‘prism‘) 79 axis1.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=kmeans.labels_,cmap=‘prism‘) 80 axis1.set_ylabel(‘y‘,fontsize=40) 81 axis1.set_title(‘k-means‘,fontsize=40) 82 #plt.show() 83 84 def meanShift(self,X,axis2): 85 ms=MeanShift(bandwidth=7)#带宽 86 ms.fit(X) 87 pred_ms=ms.labels_ 88 axis2.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=pred_ms,cmap=‘prism‘) 89 axis2.set_title(‘mean-shift‘,fontsize=40) 90 print(‘mean-shift:‘,np.unique(ms.labels_)) 91 print(‘mean-shift:‘,homogeneity_completeness_v_measure(self.labels,pred_ms)) 92 93 def gaussianMix(self,X,axis3): 94 gmm=mixture.GMM(n_components=2) 95 gmm.fit(X) 96 pred_gmm=gmm.predict(X) 97 axis3.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=pred_gmm, cmap=‘prism‘) 98 axis3.set_xlabel(‘x‘, fontsize=40) 99 axis3.set_ylabel(‘y‘, fontsize=40) 100 axis3.set_title(‘gaussian mixture‘, fontsize=40) 101 print(‘gmm:‘,np.unique(pred_gmm)) 102 print(‘gmm:‘,homogeneity_completeness_v_measure(self.labels,pred_gmm)) 103 104 def hierarchicalWard(self,X,axis4): 105 ward=linkage(X,‘ward‘)#训练 106 max_d=110#终止层次算法最大的连接距离 107 pred_h=fcluster(ward,max_d,criterion=‘distance‘)#预测属于哪个类 108 axis4.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=pred_h, cmap=‘prism‘) 109 axis4.set_xlabel(‘x‘,fontsize=40) 110 axis4.set_title(‘hierarchical ward‘,fontsize=40) 111 print(‘ward:‘,np.unique(pred_h)) 112 print(‘ward:‘,homogeneity_completeness_v_measure(self.labels,pred_h)) 113 114 self.fig.set_size_inches(18.5,10.5) 115 self.fig.savefig(‘comp_clustering.png‘,dpi=100)#保存图 116 117 if __name__==‘__main__‘: 118 cluster=ClusterMethod() 119 cluster.clusterMethods()
五.评估图
参考:1.Machine.Learning.An.Algorithmic.Perspective.2nd.Edition.
2.Machine Learning for the Web
标签:最好 创建 product red component gauss 带宽 eset 技术
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/little-horse/p/7367407.html