标签:反射机制 兼容问题 数字 alt end ons 初步 demo 对象
反射原理主要是为了做框架用的,但是了解底层原理对以后深入理解框架概念还是蛮有帮助的。
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
JAVA反射(放射)机制:“程序运行时,允许改变程序结构或变量类型,这种语言称为动态语言”。从这个观点看,Perl,Python,Ruby是动态语言,C++,Java,C#不是动态语言。但是JAVA有着一个非常突出的动态相关机制:Reflection,用在Java身上指的是我们可以于运行时加载、探知、使用编译期间完全未知的classes。换句话说,Java程序可以加载一个运行时才得知名称的class,获悉其完整构造(但不包括methods定义),并生成其对象实体、或对其fields设值、或唤起其methods。
首先,先创建一个实体类Student,然后在里面定义2个属性和若干方法
1 package reflect; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 public void setName(String name) { 7 this.name = name; 8 } 9 public void setAge(int age) { 10 this.age = age; 11 } 12 public Student(String name) { 13 super(); 14 this.name = name; 15 } 16 public Student(int age) { 17 super(); 18 this.age = age; 19 } 20 public Student() { 21 System.out.println("无参构造器"); 22 } 23 public String getName() { 24 return name; 25 } 26 public int getAge() { 27 return age; 28 } 29 30 /* 31 * 下面为方法 32 */ 33 34 public void methodTest(){ 35 System.out.println("methodTest()"); 36 } 37 38 public void methodTest(int num){ 39 System.out.println("methodTest()"); 40 } 41 42 private void methodTest(String str){ 43 System.out.println("methodTest()"); 44 } 45 46 private int methodTest(String str,int num){ 47 return 1; 48 } 49 50 public static void methodTest(int[] num){ 51 System.out.println("静态methodTest()"); 52 } 53 public static void main(String[] args) { 54 System.out.println("main方法"); 55 } 56 }
在测试类中实现获得实体类的属性和方法
1 package reflect; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 5 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 6 import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; 7 8 import org.junit.Before; 9 import org.junit.Test; 10 11 12 13 public class Demo1 { 14 private Class c; 15 16 @Before 17 public void testBefore() throws Exception { 18 // System.out.println("before"); 19 c = Class.forName("reflect.Student");// 通过类名找到该类 20 } 21 22 @Test 23 public void test1() throws Exception { 24 Constructor s = c.getConstructor(null); // 获得无参构造方法 25 Student st1 = (Student) s.newInstance(null); // 调用该构造方法,因为调用后返回的是object类型,所以需要强转 26 System.out.println(st1); 27 } 28 29 @Test 30 public void test2() throws Exception { 31 Constructor s = c.getConstructor(String.class); 32 Student st2 = (Student) s.newInstance("lilei"); 33 System.out.println(st2.getName()); 34 st2.setName("lilei*****"); 35 System.out.println(st2.getName()); 36 } 37 38 @Test 39 public void test3() throws Exception { 40 Student st3 = (Student) c.newInstance(); 41 st3.setAge(0); 42 System.out.println(st3.getAge()); 43 // Assert.assertEquals(false, false); 44 } 45 46 /* 47 * 调用有参的方法 public void methodTest(int num){ 48 * System.out.println("methodTest()"); } 49 */ 50 @Test 51 public void test4() throws Exception { 52 Student s = new Student(); 53 Method method = c.getMethod("methodTest", int.class);// 获得方法 54 method.invoke(s, 1); 55 } 56 57 /* 58 * 调用无参无返回值的方法 public void methodTest(){ System.out.println("methodTest()"); 59 * } 60 */ 61 @Test 62 public void test5() throws Exception { 63 Student s = new Student(); 64 Method method = c.getMethod("methodTest", null);// 获得方法 65 method.invoke(s, null); // 无参的就写null 66 } 67 68 /* 69 * 调用私有方法 private int methodTest(String str,int num){ return 1; } 70 */ 71 @Test 72 public void test6() throws Exception { 73 Student s = new Student(); 74 // 想要获得的方法为private修饰的,所以需要用getDeclaredMethod来调用 75 Method method = c.getDeclaredMethod("methodTest", String.class, int.class); 76 // 调用后需要设置打开Accessible为可用 77 method.setAccessible(true); 78 int num = (int) method.invoke(s, "xixi", 2); 79 System.out.println(num); 80 } 81 82 /* 83 * 调用静态方法 public static void methodTest(int[] num){ 84 * System.out.println("methodTest()"); } 85 */ 86 @Test 87 public void test7() throws Exception { 88 // Student s= new Student(); 89 Method method = c.getMethod("methodTest", int[].class);// 获得方法 90 method.invoke(null, new int[] { 1, 20 }); // 静态方法直接写null 91 } 92 93 /* 94 * 调用main方法 public static void main(String[] args) { 95 * System.out.println("main方法"); } 96 */ 97 @Test 98 public void test8() throws Exception { 99 Method method = c.getMethod("main", String[].class); 100 /* 101 * 因为JDK版本兼容问题这样写会发生数字长度错误,旧版本是把数组里的数拆开来分别调main方法 102 */ 103 // method.invoke(null, new String[]{"a","b"}); 104 105 // 第一种解决办法,将String数组外面套一个Object数组,拆开后还是String数组,满足main方法的要求 106 method.invoke(null, new Object[] { new String[] { "a", "b" } }); 107 // 第二种解决方法,强转为object类型,不是数组,这样就不会拆了 108 method.invoke(null, (Object) new String[] { "a", "b" }); 109 } 110 111 @Test 112 public void test9() { 113 Field[] field = c.getDeclaredFields(); 114 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 115 //属性为类就可以直接使用getSimpleName()来获得类名 116 sb.append(Modifier.toString(c.getModifiers()) + " class " + c.getSimpleName() + "{\n"); 117 for (Field f : field) { 118 sb.append("\t");// 空格 119 /* 120 * 获得属性的修饰符,例如public,static等等,这里getModifiers()方法获得的值为int类型,每个int值 121 * 对应了不同的修饰符类型,必须再用toString将其对应出来,才能正确显示为String,不然只有数字 122 */ 123 sb.append(Modifier.toString(f.getModifiers()) + " "); 124 /* 125 * 属性的类型的名字,先使用getType()方法获得类型,返回:class java.lang.String 126 * 再调用getSimpleName() ,返回:String 127 * 如果使用getName(),返回:java.lang.String 128 * 我们只想获得String,那么则使用getType().getSimpleName() 129 */ 130 sb.append(f.getType().getSimpleName() + " "); 131 sb.append(f.getName() + ";\n");// 属性的名字+回车 132 } 133 sb.append("}"); 134 System.out.println(sb); 135 } 136 137 }
test9打印结果: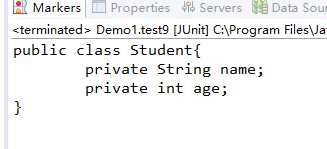
标签:反射机制 兼容问题 数字 alt end ons 初步 demo 对象
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/loseheart/p/7440202.html