标签:环境 enabled 用户创建 guest 技术 排错 -418 开头 round
(1) RHCSA上午2.5小时,RHCE下午3.5小时,考生需对题目非常熟练。
(2) 5样东西必带(身份证、1支黑色水笔、常用邮箱、姓名拼音、聪明的脑袋)。
(3) 考试的时候有3台机;1台物理机用来看题目/启动/关闭/重启虚拟机,不要动物理机上的任何配置;2台虚拟机用来考试的,所有的操作必需在虚拟机中完成。
(4) 不要尝试SSH到其它人的机器,如果你的机器连过别人的机器,或者被别人连过,这2个人视为作弊。
(5) 考试题目可以选择简体中文,但是建议中英文切换着看,有些地方翻译的不严谨,且中文断句上有问题,某些地方少个逗号意思就变了。
(6) 总分都是300分,>=210分成绩就算通过考试。
(7) 考试中如有不清楚请及时与考官联系。
(8) 考试时一定要看清楚是否要求两台虚拟机都要配置。
(9) 所有操作都设置为永久生效,意味着重启系统还是生效。
(10)所有的服务既要start,同时也记得要enable。
(11)所有的挂载要写到/etc/fstab里。
(12)本题库只作为参考,考试中可能名字不一样,因此需要大家灵活使用。
(13)做完每一题都检查一下,看看自己做的对不对,那么怎么检查?是一个问题,这些在下面的题库中都有哈。
2017.05.28
1) 网络与系统安全:
配置网络
SElinux
改密码,内核升级
2) 基本操作(用户与组/目录和权限):
用户
目录,权限,查找文件,目录压缩
计划任务
文字处理
3) 磁盘分区与卷管理:
lvm扩容,swap,lvm创建
4) 软件安装与配置:
yum
ntp
ldap
autofs
下面我们来模拟RHCSA考试,首先在foundation上将实验环境重置:
1 [root@localhost ~]# rht-vmctl fullreset desktop #重置虚拟机desktop
一台虚拟机system1,网络环境为 desktopX.example.com( 172.25.X.0/24),有一个禁止网络 test.com (172.10.0.0/24)。您可以通过物理机 ssh 到两台虚拟机上进行操作。
您没有物理机的 root 权限。考试服务器为 classroom.example.com(172.25.254.254/24)。
建议大家远程过去做
记得加上-X,表示可以弹出图形化界面(后面配置ldap时需要用到)。
A 重置虚拟机的Root 密码,设置为redhat。
B 设置 system1 的网络和主机名
你的虚拟机的网络应该按照以下要求配置:
1 * Hostname:desktopX.example.com 2 * IP address:172.25.x.10 3 * Netmask:255.255.255.0 4 * Gateway:172.25.x.254 5 * Name server:172.25.254.254 6
1 破解密码: 2 (1)开机,快速的按上下键,选择第一个 3 (2)按下字母e 4 (3)找到linux16开头的行 5 (4)到该行的最后,删除到ro 6 (5)把ro 改成 rw rd.break 7 (6)ctrl+x 8 (7)chroot /sysroot/ 9 (8)这时就可以修改root密码了 10 passwd root 11 (9) SElinux开启时必须需要创建,重打selinux标签,如果没这步,系统起不来 12 touch /.autorelabel 13 (10)exit 14 (11)reboot 15 网络和主机名: 16 (1)hostnamectl set-hostname serverN.example.com 17 (2)vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 18 DEVICE=eth0 19 BOOTPROTO=none 20 ONBOOT=yes 21 TYPE=Ethernet 22 IPADDR1=172.25.0.10 23 PREFIX1=24 24 GATEWAY1=172.25.0.254 25 DNS1=172.25.254.254 26 (3)systemctl restart network 27
下面我们模拟考试环境,破解desktop0的密码。
破解密码:
(1)开机,快速的按上下键,选择第一个
(2)按下字母e
(3)找到linux16开头的行
(4)到该行的最后,删除到ro
(5)把ro 改成 rw rd.break
(6)ctrl+x
(7)chroot /sysroot/,这里将文件系统切换到真正的根上面,可以看到提示符变成了“sh-4.2#”。
(8)这时就可以修改root密码了
1 passwd root
(9)重打selinux标签,如果没这步,系统起不来
1 touch /.autorelabel
(10)exit
(11)reboot
在实验环境中虚拟机是以DHCP的方式获得IP的,因此在本实验环境通过下面方法来修改IP。在考试中需要看清楚题目的要求的IP和网关和DNS,然后再修改网络配置,评分时会登陆你的虚拟机,IP不对将无法评分。
1 (1)ip addr show #查看IP地址与子网掩码并记录下来 2 (2)route #查看网关并记录下来 3 (3)cat /etc/resolv.conf #查看DNS并记录下来 4 (4)hostname #查看主机名
(5)然后写到配置文件中
1 vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 2 DEVICE=eth0 3 BOOTPROTO=none 4 ONBOOT=yes 5 TYPE=Ethernet 6 IPADDR1=172.25.0.10 7 PREFIX1=24 8 GATEWAY1=172.25.0.254 9 DNS1=172.25.254.254 10
(6)重启网络
1 systemctl restart network
注意事项
? 这题做成功没分,没做成功全部为0分。
? 这里改密码后要记得touch /.autorelabel,这里单词经常有同学写错的哈。
保证系统SElinux运行在 enforcing 状态.
参考步骤
1 (1)vim /etc/selinux/config 2 SELINUX=enforcing 3 (2)setenforce 1 4 (3)getenforce
(1)虚拟机配置selinux后是这样的
注意事项
? setenforce临时生效,其中1为Enforcing状态selinux表示是开启的,0为Permissive状态表示selinux是关闭的。
? /etc/selinux/conf永久生效。
配置你的本地默认 YUM 仓库指向:
http://classroom.example.com/content/rhel7.0/x86_64/dvd/ (考试环境服务器的地址)
1 (1)[root@localhost ~]# yum-config-manager --add-repo=http://classroom.example.com/content/rhel7.0/x86_64/dvd/ --enable --save 2 (2)[root@localhost ~]# echo "gpgcheck=0">> /etc/yum.repos.d/classroom.example.com_content_rhel7.0_x86_64_dvd_.repo 3 (3)[root@localhost ~]# yum repolist 4
(1)我们先将原来的/etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo删除
(2)通过yum-config-manager命令来自动生成,可以看到紫色部分的是自动生成到文件里的。
(3)但这里还少一条gpgcheck=0,通过echo写进去。
这里的>>是追加到刚刚创建的.repo文件中
(4)使用yum clean all清除原来的缓存
(5)使用yum repolist查看yum源的包情况,可以看到有4305个包
注意事项
? yum源的配置文件必须是在/etc/yum.repos.d目录下,并且是以.repo结尾的文件,这里经常有同学不注意的;yum源语法格式如下:
[名字]
name=显示的名字
baseurl=基于哪个yum源
例如基于http的为http://classroom.example.com/content/rhel7.0/x86_64/dvd/;基于本地ISO文件的为file:///mnt/iso(此时iso是挂载在/mnt/iso上的)。
enabled=是否启用这个yum源,1为启用,0为不启用
gpgcheck=是否验证yum源的合法性,1为验证,0为不验证
上面5条即为最基本的YUM源配置。
调整你的本地逻辑卷 lvm1 及其文件系统的大小为 770MiB。
A 确保文件系统当中已存在的内容不能被损坏。注意:实际配置的大小可能会出现误差,只要在 730MiB 与 805MiB之间都是允许的。
B 使其正常挂接的目录不改变,并且其文件系统完整。
参考步骤
1 (1)[root@localhost ~]# lvextend -L 700M /dev/vg1/lv1 2 (2)[root@localhost ~]# resize2fs /dev/vg1/lv1 3
这里我们模拟考试环境,自己先创建一个500M的lvm1,然后挂载给/mnt/lvm1,然后再开始lvm的扩容。
(1) 使用fdisk进行分区,n表示创建分区,p创建一个主分区,1创建的是分区1,+1G分区容量为1G。
(2) 创建完后,p查看分区信息,可以看到多了一个/dev/vdb1的分区,w保存退出。
(3) 查看刚刚的分区是否生效,如果没有/dev/vdb1出来,可用partprobe刷新分区信息。
(4) 创建lvm的顺序为pv-vg-lv也就是物理卷-卷组-逻辑卷,这里先创建pv
(5) 创建vg
(6) 创建lv,-L指定创建的大小为500M,-n指定lv的名字为lvm1
(7) 查看lvm,创建了pv可用pvs来查看,对应的命令为pvs/vgs/lvs,这里可以看到lvm1属于vg1并且lvm1为500M
(8) 创建了lvm后我们要使用这个块设备,也就是挂载,但挂载前需要将它格式化为文件系统,这里我们将它格式化为ext4
(9) 创建挂载目录并挂载lvm,这里/dev/mapper/vg1-lvm1与/dev/vg1/lvm1lvm都表示这个lvm。
(10)通过df -TH查看挂载结果。
------------------------OK,以上为模拟考试环境的步骤,下面开始答题------------------------------
题目说调整你的本地逻辑卷 lvm1 及其文件系统的大小为 770MiB。确保文件系统当中已存在的内容不能被损坏。这里我们的答题思路是这样的先扩容lvm再扩容文件系统。
(1)通过vgs查看vg还有多少容量,可以看到还有520M。
(2)使用lvextend来扩容lv,这里它原来的容量为500M,使用-L将容量扩容到700M,也就是说添加了200M。
(3)用lvs查看扩容结果。
(3)用resize2fs扩容ext的文件系统;如果文件系统为xfs则用xfs_growfs来扩容文件系统,XFS不支持缩小,只支持扩大。
(4)通过df -TH查看扩容结果,可以看到从500M变成了703M。
注意事项
(1)如果创建错了,可参考下列步骤删除,创建是这样:fdisk-pv-vg-lv-mkfs-mount,删除的话反过来操作。
按照以下要求创建用户,组,及用户与组的关系
A 新建一个名为 adminuser 的组,组 id 为 40000
B 新建一个名为 natasha 的用户,并将 adminuser 作为其附属组
C 新建一个名为 harry 的用户,也将 adminuser 作为其附属组
D 新建一个名为 sarah 的用户,其不属于 adminuser 组,并将其 shell 设置为不可登录 shell
E natasha、harry和sarah三用户的密码均设置为 glegunge
参考步骤
1 [root@localhost ~]# groupadd -g 40000 adminuser 2 [root@localhost ~]# useradd -G adminuser natasha 3 [root@localhost ~]# useradd -G adminuser harry 4 [root@localhost ~]# useradd -s /sbin/nologin sarah 5 [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd 6 [root@localhost ~]# passwd natasha 7 [root@localhost ~]# passwd harry 8 [root@localhost ~]# passwd sarah
模拟考试环境
无
注意事项
无
复制文件/etc/fstab到/var/tmp目录中,并按以下要求配置/var/tmp/fstab 文件的权限:
A 文件/var/tmp/fstab 的所属人为 root
B 文件/var/tmp/fstab 的所属组为 root
C 文件/var/tmp/fstab 对任何人均没有执行权限
D 用户 natasha 对文件/var/tmp/fstab 有读和写的权限
E 用户 harry 对文件/var/tmp/fstab 既不能读也不能写
F 所有其他用户( 包换当前用户及未来创建的用户)对文件/var/tmp/fstab 都有读的权限
1 [root@localhost ~]# cp /etc/fstab /var/tmp/ 2 [root@localhost ~]# chown root /var/tmp/fstab 3 [root@localhost ~]# chgrp root /var/tmp/fstab 4 [root@localhost ~]# chmod -x /var/tmp/fstab 5 [root@localhost ~]# setfacl -m u:natasha:rw /var/tmp/fstab 6 [root@localhost ~]# setfacl -m u:harry:-- /var/tmp/fstab 7 [root@localhost ~]# chmod o+r /var/tmp/fstab 8
(1)将/etc/fstab复制到/var/tmp目录下,通过getfacl查看此文件的权限情况
(2)修改所属者/所属组为root
(3)设置任何人都没有执行权限.
(4)使用setfacl设置单个用户对此文件的权限,-m表示修改,格式为g/u/o:user:rwx,g表示组,u表示单个用户,o表示其它人
(5)设置所有用户都有读的权限
(6)查看配置结果,可以看到
所属者为root
所属组为root
用户natasha的权限是可读可写
用户harry没有任何权限
其它人只有计的权限
所有人都没有执行的权限
注意事项
无
对 natasha 用户配置计划任务,要求在本地时间的每天 14:23 分执行以下命令
1 [root@localhost ~]# /bin/echo “hi uplooking”
参考步骤
1 [root@localhost ~]# crontab -e -u natasha 2 [root@localhost ~]# crontab -l -u natasha
无
? crontab的格式为:
23 14 * * * /bin/echo "hi uplooking"
对应:分 时 日 月 年
在/home 目录下创建子目录名为 admins,按以下要求设置权限:
A /home/admins 的所属组为 adminuser
B 该目录对 adminuser 组成员可读可写可访问,但对其他用户没有任何权限( root 帐户不
受该限制)
C 在/home/admins 目录下所创建的文件的所属组自动会被设置为 adminuser
参考步骤
1 [root@localhost ~]# chgrp adminuser /home/admins 2 [root@localhost ~]# chmod g=rwx /home/admins 3 [root@localhost ~]# chmod o= /home/admins 4 [root@localhost ~]# chmod g+s /home/admins 5 [root@localhost ~]# ll -d /home/admins
模拟考试环境
(1)题目说所属组是adminuser,于是要先创建adminuser用户
1 [root@desktop0 tmp]# useradd adminuser 2
(2)进到/home目录下创建admin目录,然后查看权限情况,可以看到默认的所属者和所属组是root
(3)修改所属组为adminuser
(4)将所属组的权限改为可读可写可执行,其它人没有任何权限
(5)设置g+s将所创建的文件的所属组自动会被设置为 adminuser
(6)查看结果,可以看到admins目录的所属组为adminuser,并且权限为rwx,其它人的权限为---,在所属组那里的x位置显示的是s。
(7)进入admins目录,创建一个文件,可以看到所属组自动变为adminuser
注意事项
无
按以下要求更新系统的内核
A 新内核的 RPM 包在http://classroom.example.com/content/rhel7.0/x86_64/errata/Packages
B 重新重启时,会默认以新内核启动系统。原始的内核将继续可用。
参考步骤
1 [root@localhost ~]# wget http://classroom.example.com/content/rhel7.0/x86_64/errata/Packages/kernel-3.10.0-123.1.2.el7.x86_64.rpm 2 [root@localhost ~]# uname -r 3 [root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh kernel-3.10.0-123.1.2.el7.x86_64.rpm 4 [root@localhost ~]# reboot 5 [root@localhost ~]# uname –r 6
? 首先SSH到虚拟机里面,这里-X表示可以打开图形化工具
? 然后打开firefox浏览器,将安装包的下载路径复制出来
? 接着wget刚刚复制的路径,将安装包下载到当前目录
? 查看操作系统版本
? 安装新的内核包,然后重启
? 如果安装不成功,可用rpm -ivh --force表示强制安装的参数
在 classroom.example.com 上已部署了一台 LDAP 认证服务器,按以下要求配置你的系统
加入到该 LDAP 服务中,并使用 Kerberos 认证用户密码
该 LDAP 认证服务的Base DN为:dc=example,dc=com .
该 LDAP 认证服务的LADP Server为 :classroom.example.com
该认证服务的 Kerbros Realm 为:EXAMPLE.COM
该认证服务的 Kerbros KDC为:classroom.example.com
该认证服务的 Kerbros Admin Server为:classroom.example.com
认证的会话连接需要被加密,证书的下载地址为 http://classroom.example.com/pub/example-ca.crt
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y authconfig-gtk sssd krb* 2 [root@localhost ~]# authconfig-gtk 3 [root@localhost ~]# getent passwd ldapuser0 4
(1)先装包,题目说要加到LDAP服务器,进行kerbros认证。sssd(访问多种验证服务器,如LDAP,Kerberos等,并提供授权) authconfig-gtk(图形化配置客户端) krb5-workstation(Kerberos客户端软件)
(2)通过SSH登陆,加上-X表示可以打开图形化工具
(4)加入LDAP并进行kerberos认证,用户信息在LDAP,密码认证在Kerberos。下面这些根据题目给出的信息填写即可,注意不要写错哦。
1 User Account database:LDAP
2 LDAP Search Base DN:基准DN,指定LDAP search的起始DN,即从哪个DN下开始搜索
3 LDAP Server:LDAP服务器域名
4 钩上表示使用加密
5 Authentication Method:Kerberos password
6 Realm:Kerberos域(必须大写)
7 KDCs:钥匙分发中心/AD地址
8 Admin Servers:Kerberos管理服务器地址
9 证书路径
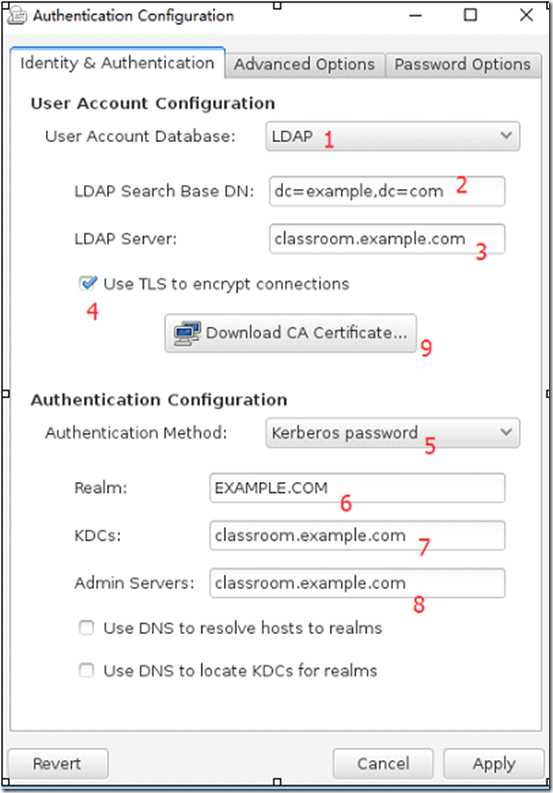
(5)getent passwd 用户名(从passwd库中得到账号信息;支持AD、NIS等用户账号)
(6)切换到ldapuserX检查一下刚刚的配置是否成功,可以看到切换用户成功。但没有家目录,这个问题在下一题可以解决。
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y autofs 2 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/auto.master 3 /home/guests /etc/auto.ldap 4 [root@localhost ~]# cp /etc/auto.misc /etc/auto.ldap 5 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/auto.share 6 ldapuser0 -type=nfs classroom.example.com:/home/guests/ldapuser0 7 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable autofs 8 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart autofs 9 [root@localhost ~]# su - ldapuser0 10
(1)查看服务器的NFS共享
(2)安装autofs软件包
(3)配置autofs的监听目录配置文件
(4)配置autofs子目录配置文件
(5)启动autofs服务
(6)切换到普通用户harry,再切换到ldapuser0,这时输入题目给的密码kerberos,可以看到有家目录出现,表示autofs配置成功
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/auto.ldap 2 * -type=nfs,_netdev,vers=3,rw classroom.example.com:/home/guests/& 3 4 5
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y chrony 2 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf 3 server classroom.example.com 4 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable chronyd 5 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart chronyd.service 6 [root@localhost ~]# chronyc sources -v
(1)安装时间同步软件包,可以看到已安装。
(2)编辑配置文件,将其它的server项都删除,只留1条server classroom.example.com iburst
(3)启动服务
(4)通过chronyc sources -v查看时间同步情况,可以看到同步成功。
1 [root@localhost ~]# tar -cjvf /root/sysconfig.tar.bz2 /etc/sysconfig
(1)使用tar来打包,通过j的参数来压缩为bzip2的格式
(2)查看打包压缩的结果
1 [root@localhost ~]# useradd -u 3456 alex 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# passwd alex
1 [root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/vdb 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# mkswap /dev/vdb6 4 5 [root@localhost ~]# echo "/dev/vdb6 swap swap defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab 6 7 [root@localhost ~]# swapon -a
考试环境的分区情况是这样的,已经存在3个分区,但这题swap需要创建新的分区,后面有一题lvm也需要创建新的分区,现在只能创建一个主分区了,怎么办?其实有很多种方法。
方法一:创建一个扩展分区,然后再创建多个逻辑分区。
方法二:创建一个主分区,将这个分区做成pv,然后创建2个lv。
方法三:通过dd命令创建一个文件,然后通过这个文件来创建swap。
这里我们只讲第一种方法,其它的感兴趣的同学可以自己玩一下。
(1)查看磁盘信息,这里我们找一块未使用的磁盘来练习,可以看到一个/dev/vdb
(2)通过fdisk对这块磁盘分区,p查看分区情况,n创建新的分区,这里创建一个1G的分区
(3)按照上面的方法创建3个分区出来
(1)创建扩展分区,这里的Last sector我们默认回车,表示剩下的容量作全部分给扩展分区
(3)通过p查看,可以看到扩展分区的System是Extended,然后在扩展分区的基础上创建逻辑分区,这里创建一个512M的
(4)通过p查看分区情况
(5)通过lsblk查看分区的使用情况,如果用lsblk看不到分区,就用partprobe刷新,再不行就重启
(6)将分区格式化成swap
(7)启用swap
(8)查看swap信息
(9)配置永久挂载,重启后再查看swap是否配置成功
1 [root@localhost ~]# find / -user ira -exec cp {} /root/findfiles/ \;
(1)首先切换为ira的用户,然后通过ira用户创建几个文件,方便等一下检查,考试中不用做此操作。
(2)通过find查找根目录,要求用户为ira,并且找出的文件要cp到/root/findfiles目录中,这里需要用到find的exec参数
(3)查看find的执行结果,可以看到刚刚通过ira用户创建的文件都在
1 [root@localhost ~]# grep seismic /usr/share/dict/words >> /root/wordlist
(1)通过grep将今有seismic的过滤出来
(2)查看执行结果
1 [root@localhost ~]# Partprobe 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# pvcreate /dev/vdb6 4 5 [root@localhost ~]# vgcreate -s 16M datastor /dev/vdb6 6 7 [root@localhost ~]# lvcreate -l 8 datastor -n lvm2 8 9 [root@localhost ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/datastor/lvm2 10 11 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /exam/lvm2 12 13 [root@localhost ~]# echo "/dev/datastor/lvm2 /exam/lvm2 xfs defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab 14 15 [root@localhost ~]# mount -a
? 网络与安全:
? 服务类:
? shell类:
1 [root@localhost ~]# rht-vmctl fullreset desktop 2 [root@localhost ~]# rht-vmctl fullreset server
您有三台主机,分别为物理机 foundationX.example.com。及两台 kvm 虚拟机分别为 desktopX.example.com(172.25.X.10/24)及serverX.example.com(172.25.X.11/24)。
两台虚拟机网络和主机名已经配置好,均位于 example.com(172.25.X.0/24)域中。
您的所有题目要求都将在两台虚拟机上完成。您可以通过物理机 ssh 到两台虚拟机上进行操作。
您没有物理机的 root 权限。考试服务器为 classroom.example.com(172.25.254.254/24)。
建议大家远程过去做
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config 2 3 SELINUX=enforcing 4 5 setenforce 1 6 7 getenforce
下面2台虚拟机配置selinux后是这样的。
desktop的步骤同上。
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/hosts.allow 2 3 sshd: example.com 4 5 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/hosts.deny 6 7 sshd: deny.com
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/bashrc 2 3 alias show=‘ls -al;pwd;echo ok‘
1 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule=‘rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.0.0/24 forward-port port=5423 protocol=tcp to-por=80‘ 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
下面模拟考试环境,在server上安装http,然后配置端口转发,通过desktop来验证。
确认防火墙是开的
配置端口转发,并将防火墙重新加载
通过desktop访问5423端口验证
首先将2台虚拟机的eth0配置成静态IP,方法如下:
1 [root@localhost ~]# ip addr show #查看IP地址与子网掩码并记录下来 2 [root@localhost ~]# route #查看网关并记录下来 3 [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf #查看DNS并记录下来
然后写到配置文件中:
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 2 DEVICE=eth0 3 BOOTPROTO=none 4 ONBOOT=yes 5 TYPE=Ethernet 6 IPADDR1=172.25.0.11 7 PREFIX1=24 8 GATEWAY1=172.25.0.254 9 DNS1=172.25.254.254
重启网络:
1 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart network
最后开始配置链路聚合:
1 [root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection add type team con-name team1 ifname team1 config ‘{"runner":{"name":"activebackup"}}‘ 2 [root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection add type team-slave con-name team1-slave1 ifname eth1 master team1 3 [root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection add type team-slave con-name team1-slave2 ifname eth2 master team1 4 [root@localhost ~]# teamdctl team1 state 5 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-team1 6IPADDR=192.168.0.111 7 PREFIX=24 8 ONBOOT=yes
9 [root@localhost ~]#systemctl restart network
10 11 12
配置静态IP
重启网络服务
desktop的配置同上。
下面在foundation上添加2张网卡给虚拟机。
首先切换到root用户,打开virt-manager
下面这个就是virt-manager界面
下面添加2张网卡到虚拟机上
desktop的步骤同上。
可以看到2张网卡是没有配置的
下面创建team1并查看网卡状态。
可以看到多了一个CONNECTION为team1的,和DEVICE为team1的。
将2张网卡添加到这个team1中
配置team1的IP地址
desktop的配置同上。
下面进行验证,server ping desktop
1 [root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection modify "System eth0" ipv6.method auto 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection modify "System eth0" ipv6.addresses 2001::1/64 4 5 [root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection modify "System eth0" ipv6.method manual 6 7 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart network 8 9 [root@localhost ~]# ping6 2001::10
在2台虚拟机通过命令配置IPV6并验证,首先需要先设置为auto再配置IP再设置为manual。
desktop的步骤同上。
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y postfix 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/postfix/main.cf 4 5 inet_interfaces = loopback-only #监听本地 6 7 myorigin = example.com #发送的邮件显示为example.com 8 9 relayhost = [foundationX.example.com] #转发 10 11 mydestination = #不接受任何邮件 12 13 local_transport = error:local delivery disabled #不会把邮件邮放MDA 14 15 mynetworks = 127.0.0.1/8 #中继哪些网段 16 17 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart postfix 18 19 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable postfix
8.通过SMB共享目录
在server X上配置SMB服务
您的SMB服务器必须是STAFF工作组的一个成员
共享/common目录共享名必须为common
只有example.com域内的客户端可以访问common共享
common必须是可以浏览的
用户andy必须能够读取共享中的内容,如果需要的话,验证的密码是redhat
参考步骤
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y samba samba-common samba-client 2 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart smb nmb 3 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable smb nmb 4 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule=’rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.0.0/24 service name=samba accept’ 5 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload 6 [root@localhost ~]# useradd andy 7 [root@localhost ~]# smbpasswd -a andy 8 [root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t “/common(/.*)?” 9 [root@localhost ~]# restorecon -Rv /common/ 10 [root@localhost ~]# ll -dZ /common/ 11 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/samba/smb.conf 12 [root@localhost ~]# workgroup = STAFF 13 [common] 14 path = /common 15 browseable = yes 16 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart smb nmb 17 [root@localhost ~]# su - andy 18 [root@localhost ~]# ll /common
模拟考试环境
这里模拟考试环境,考试的时候可能common已经有了。本题思路如下:
? 装包
? start和enable服务
? 防火墙
? 创建用户
? 创建目录/目录权限
? selinux
? 修改配置文件
? 重启服务
此题目没有要求客户端挂载,这里不讲。首先是常规操作(装包,start和enable服务,防火墙),samba要装3个包,samba是控制smb和nmb服务的,samba-common是samba相关命令,samba-client是samba客户端用于测试。
题目说:只有example.com域内的客户端可以访问common共享
首先通过ping 域名得出网段,然后通过防火墙规则来实现只有172.25.0.0/24可以访问共享。
接下来创建用户与目录并配置selinux。因为默认就有读的权限,因此不用做权限的修改。
下面按照题目要求修改配置文件,修改配置文件的workgroup,添加common共享目录信息。
下面我们来测试一下哈,题目说andy有读的权限是吧,那在服务器端通过andy来访问这个common共享目录,看看是否有读的权限。
1 server: 2 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule=’rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.0.0/24 service name=samba accept’ 3 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload 4 [root@localhost ~]# useradd kenji 5 [root@localhost ~]# useradd chihiro 6 [root@localhost ~]# smbpasswd kenji 7 [root@localhost ~]# smbpasswd chihiro 8 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /devops 9 [root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t “/devops(/.*)?” 10 [root@localhost ~]# restorecon -Rv /devops/ 11 [root@localhost ~]# ll -dZ /devops/ 12 [root@localhost ~]# setfacl -R -m u:chihiro:rwx /devops/ 13 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/samba/smb.conf 14[devops] 15 path = /devops 16 browseable = yes 17 write list = chihiro
18 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart smb nmb 19 desktop: 20 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y samba-client 21 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y cifs-utils.x86_64 22 [root@localhost ~]# echo "//172.25.0.11/devops /mnt/dev cifs username=kenji,password=redhat,multiuser,sec=ntlmssp 0 0" >> /etc/fstab 23 [root@localhost ~]# mount -a 24 [root@localhost ~]# su - student 25 [root@localhost ~]# cifscreds add 172.25.0.11 -u chihiro 26 [root@localhost ~]# touch /mnt/dev/test5
模拟考试环境
这里模拟考试环境,考试的时候可能devops已经有了,装包和防火墙前面那题已经配置了。本题思路如下:
? 创建用户
? 创建目录/目录权限
? selinux
? 修改配置文件
? 重启服务
? 客户端(装包,创建挂载目录,永久挂载,提升凭证测试)
下面模拟考试环境,server为samba服务器,desktop为客户端进行samba多用户挂载与提升凭证测试。首先创建用户,创建目录/配置目录权限与selinux,由于这里是多个用户场景,因此使用setfacl对单个用户进行权限的设置。
题目说:用户chihiro必须能以读写的方式访问此共享,访问密码是atenorth。
前面我们使用setfacl对chihiro用户进行了权限设置后配置文件里也要有写的权限,下面配置共享目录/devops的共享参数,write list = chihiro表示哪些用户有写的权限。
使用testparm命令测试配置的语法是否有错
接下来通过desktop客户端来测试,首先要装2个包samba-client(用于samba客户端测试)和cifs-utils(用于samba挂载),创建挂载目录,然后配置基于kenji的samba多用户挂载,通过chihiro用户来提升凭证,获得写devops目录的权限。
手动挂载测试一下,没问题后,再配置永久挂载
配置永久挂载
cifscreds add 172.25.0.11 -u chihiro表示提升到chihiro的凭证,因为这个用户有写的权限,因此需要用到写功能时,就提升下权限来写。
注意事项
? 挂载的时候要写multiuser多用户挂载,才可提升凭证,写权限才能生效。
? 一定要使用普通用户来提升凭证,在客户端提升凭证使用cifscreds add 172.25.0.11 -u chihiro,清除凭证使用cifscreds clearall。
? 使用testparm可以检查samba配置文件的语法。
? 永久挂载时
//172.25.0.11/devops /mnt/dev cifs username=kenji,password=redhat,multiuser,sec=ntlmssp 0 0
这里表示使用kenji这个用户来挂载,密码为redhat,挂载参数是multiuser(多用户),加载方式是sec=ntlmssp。
以只读的方式共享目录/public同时只能被example.com域中的系统访问
以读写的方式共享目录/protected能被example.com域中的系统访问
访问/protected需要通过kerberos安全加密,您可以使用下面的URL提供的密钥
http://classroom.example.com/pub/keytabs/server0.keytab
目录/protected应该包含名为project拥有人为ldapuserX的子目录
用户ldapuserX能以读写方式访问/protected/project
1 [root@localhost ~]# wget -O /etc/krb5.keytab http://classroom.example.com/pub/keytabs/server0.keytab 2 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nfs-server rpcbind 3 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable nfs-server rpcbind 4 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nfs-secure-server 5 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable nfs-secure-server 6 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=nfs 7 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=mountd 8 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=rpc-bind 9 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload 10 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /public 11 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /protected 12 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /protected/project 13 [root@localhost ~]# setfacl -m u:ldapuser0:rwx /protected/ 14 [root@localhost ~]# chown ldapuser0 /protected/project/ 15 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/exports 16/public 172.25.0.0/24(ro) 17 /protected 172.25.0.0/24(rw,sec=krb5p) 18 exportfs -rv
模拟考试环境
考试的时候2台虚拟机已通过kerberos认证,这里模拟考试环境因此需要手动添加kerberos认证,本题配置思路:
? kerberos认证,下载密钥
? 装包
? start和enable服务
? 防火墙
? 创建目录/目录权限
? 修改配置文件
? 重启服务
首先将server加入kerberos认证,这里server的密钥在
http://classroom.example.com/pub/keytabs/server0.keytab
接下来是常规操作,在server上装包,start和enable服务,配置防火墙
目录/protected应该包含名为project拥有人为ldapuserX的子目录
用户ldapuserX能以读写方式访问/protected/project
通过ldapuserX测试是否对/protected/project可读写
注意事项
? 记得是nfs-secure-server。因为是通过kerberos安全加密的,所以服务器使用的是nfs-secure-server这个服务。
? kerberos认证原理:
首先server和desktop都要成为kerberos的client才能进行安全加密传输。
然后kerberos会将加进来的client都生成密钥。
server和desktop有自己的密钥。
如果desktop要和server通信,desktop怎么才能知道server就是真server呢?
kerberos将server的密钥进行加密生成一个凭证发给desktop。
desktop会拿着kerberos发给它的凭证和server通信。
server收到凭证后通过自己的密钥来解密,如果解密成功,说明这是真server。
/public挂载在下面的目录上/mnt/nfsmount
/protected挂载在下面的目录上/mnt/nfssecure并使用安全的方式。密钥下载URL如下:
http://classroom.example.com/pub/keytabs/desktop0.keytab
ldapuserX能够在/mnt/nfssecure/project上创建文件
这此文件系统在系统启动时自动挂载
1 [root@localhost ~]# wget -O /etc/krb5.keytab http://classroom.example.com/pub/keytabs/desktop0.keytab 2 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nfs-secure 3 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable nfs-secure 4 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /mnt/nfsmount 5 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /mnf/nfssecure 6 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/fstab 7server0.example.com:/public /mnt/nfsmount nfs defaults,vers=3 0 0 8 server0.example.com:/protected /mnt/nfssecure nfs defaults,vers=3,sec=krb5p 0 0
9 [root@localhost ~]# mount -a 10 [root@localhost ~]# df -TH
考试的时候2台虚拟机已通过kerberos认证,这里模拟考试环境因此需要手动添加kerberos认证,本题配置思路:
? kerberos认证,下载密钥
? 装包
? start和enable服务
? 创建目录
? 挂载
? 测试
首先将desktop加入kerberos认证, desktop的密钥在
http://classroom.example.com/pub/keytabs/desktop0.keytab
加入kerberos与下载密钥步骤请参考上题。
接下来在desktop上装包,start和enable服务,创建目录。为什么客户端也要安装nfs-utils的包呢?因为nfs是c/s架构,nfs-utils包含了服务器的包和客户端工具(client-tools)。
serverX上配置一个站点http://serverX.example.com然后执行下述步骤:
从ftp://172.25.254.250/pub/RHCE/12.html下载文件,并且将文件重命名index.html不要修改此文件的内容
将文件index.html拷贝到您的web服务器的documentroot目录下
来自于example.com域的客户端可以访问此web服务
来自于deny.com域的客户端拒绝访问此web的服务
1 server: 2 [root@localhost ~]# yum install httpd -y 3 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start httpd 4 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable httpd 5 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule=‘rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.0.0/24 port port=80 protocol=tcp accept‘ 6 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload 7 [root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/share/doc/httpd-2.4.6/httpd-vhosts.conf #在模板文件中8yy复制,然后在server0.conf中p粘贴 8 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/server0.conf 9<VirtualHost *:80> 10 ServerAdmin root@server0.example.com 11 DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" 12 ServerName server0.example.com 13 ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/server0.example.com-error_log" 14 CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/server0.example.com-access_log" common 15 </VirtualHost>
16 [root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html/ 17 [root@localhost ~]# wget ftp://172.25.254.250/pub/RHCE/12.html #进入站点目录将主页wget下来 18 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd 19 desktop: 20 [root@localhost ~]# curl http://server0.example.com
测试
为站点http://serverX.example.com配置
TLS加密一个已签名证书从http://classroom.example.com/pub/tls/certs/www0.crt获取,
此证书的密钥从http://classroom.example.com/pub/tls/private/www0.key获取,
此证书的签名授权信息从http://classroom.example.com/pub/example-ca.crt获取。
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install mod_ssl -y 2 [root@localhost ~]# wget -O /etc/pki/tls/certs/www0.crt http://classroom.example.com/pub/tls/certs/www0.crt 3 [root@localhost ~]# wget -O /etc/pki/tls/private/www0.key http://classroom.example.com/pub/tls/private/www0.key 4 [root@localhost ~]# wget -O /etc/pki/tls/certs/example-ca.crt http://classroom.example.com/pub/example-ca.crt 5 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/server0.conf6 <VirtualHost *:443> 7 ServerAdmin root@server0.example.com 8 DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" 9 ServerName server0.example.com 10 ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/server0_443.example.com-error_log" 11 CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/server0_443.example.com-access_log" common 12 SSLEngine on 13 SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3 14 SSLCipherSuite HIGH:MEDIUM:!aNULL:!MD5 15 SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/www0.crt 16 SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/www0.key 17 SSLCACertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/example-ca.crt 18 </VirtualHost>
19 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd
这里可以进入/etc/pki/tls/certs后再wget,这样selinux不需要修改,或者wget -O 指定路径
通过grep ssl.conf将https配置参数复制出来,这里的最后一条记得把#去掉。
在serverX上扩展您的web服务器,为站点http://14.example.com创建一个虚拟主机,然后执行下述步骤:
设置DocumentRoot为/var/www/virtual
从ftp://172.25.254.250/pub/RHCE/14.html下载文件并重命名为index.html不要对文件index.html的内容做任何修改
将文件index.html放到虚拟主机的DocumentRoot目录下
确保floyd用户能够在/var/www/virtual目录下创建文件
注意:原始站点http://server0.example.com必须仍然能够访问
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/server0.conf 2 3<VirtualHost *:80> 4 5 ServerAdmin root@server0.example.com 6 7 DocumentRoot "/var/www/virtual" 8 9 ServerName 14.example.com 10 11 ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/server0_14.example.com-error_log" 12 13 CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/server0_14.example.com-access_log" common 14 15 </VirtualHost> 16 17 <Directory "/var/www/virtual"> 18 19 AllowOverride None 20 21 Require all granted 22 23 </Directory>
24 25 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd 26
其中<Directory>这个在/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf里面复制
为您的serverX上的web服务器的DocumentRoot目录下创建一个名为private的目录,要求如下:
从ftp://172.25.254.250/pub/RHCE/15.html下载一个文件副本到这个目录,并且重命名为index.html
不要对这个文件的内容做任何修改
在serverX上任何人都可以浏览private的内容,但是从其他系统不能访问这个目录的内容
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/server0.conf 2 3 <VirtualHost *:80> 4 5 ServerAdmin root@server0.example.com 6 7 DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" 8 9 ServerName server0.example.com 10 11 ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/server0.example.com-error_log" 12 13 CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/server0.example.com-access_log" common 14 15 </VirtualHost> 16 17 <Directory "/var/www/html/private"> #在第一个站点后面添加 18 19 Require all denied 20 21 Require local 22 23 </Directory> 24 25 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd 26
这里说的DocumentRoot,我们就在默认的/var/www/html里创建就OK
其中<Directory>这个在/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf里面复制
desktop测试
server测试
1. 下载文件时,先cd到要保存的位置,再wget;或者使用wget -O指定绝对路径。
在serverX上配置提供动态web内容,要求如下:
动态内容为16.example.com的虚拟主机提供
虚拟主机侦听在端口8909
从ftp://172.25.254.250/pub/RHCE/webinfo.wsgi下载一个脚本,然后放在适当的位置,无论如何都不要修改此文件的内容
客户端访问http://14.example.com:8909时应该接到动态生成的WEB页面
此http://14.example.com:8900必须被example.com域内的所有系统访问
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y mod_wsgi 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule=‘rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.0.0/24 port port=8990 protocol=tcp accept‘ 4 5 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload 6 7 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/server0.conf 8 9Listen 8909 10 11 <VirtualHost *:8909> 12 13 ServerName 16.example.com 14 15 WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/html/webapp.wsgi 16 17 </VirtualHost>
18 19 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd 20 21 [root@localhost ~]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 8909 22 23 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd 24
当运行/root/foo.sh redhat,输出为fedora
当运行/root/foo.sh fedora,输出为redhat
1 [root@localhost ~]# /root/foo.sh redhat|fedora 2 3 #参考步骤 4 5 [root@localhost ~]# vim /root/foo.sh 6 7#!/bin/bash 8 9 case $1 in 10 11 redhat) 12 13 echo “fedora”; 14 15 ;; 16 17 fedora) 18 19 echo “redhat”; 20 21 ;; 22 23 *) 24 25 echo ‘/root/foo.sh redhat|fedora’ 26 27 ;; 28 29 esac
30 31 [root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /root/foo.sh 32
在serverX上创建一个脚本,名为/root/batchusers,此脚本能实现为系统server创建本地用户,并且这些用户的用户名来自一个包含用户名列表的文件。同时满足下列要求:
此脚本要求提供一个参数,此参数就是包含用户名列表的文件
如果没有提供参数,此脚本应该给出下面的提示信息Usage:/root/bachuser然后退出并返回相应的值
如果提供一个不存在的文件名,此脚本应该给出下面的提示信息input file not found然后退出并返回相应的值
创建的用户登录shell为/bin/false
此脚本不需要为用户设置密码
你可以从下面的URL获取用户名列表作为测试用 http://172.25.254.250/pub/RHCE/userlist
1 [root@localhost ~]# vim /root/batchusers 23 #!/bin/bash 4 5 if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then 6 7 echo "Usage:/root/bachusers"; 8 9 exit 1; 10 11 fi 12 13 if [ ! -f $1 ] ; then 14 15 echo "input file not found"; 16 17 exit 2; 18 19 fi 20 21 for USERNAME in $(cat $1) ; 22 23 do 24 25 useradd -s /bin/false $USERNAME 26 27 id $USERNAME 28 29 done
30 31 [root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /root/foo.sh 32
配置serverX提供一个iSCSI服务磁盘名为iqn.2017-05.com.example:serverX并符合下列要求
服务器端口为3260
使用iscsi——store作其后端卷其大小为3G
从服务只能被desktopX.example.com访问
1 [root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/vdb 2 3 Command (m for help): p 4 5 Command (m for help): n 6 7 Select (default p): p 8 9 Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 10 11 First sector (2048-20971519, default 2048): 12 13 Using default value 2048 14 15 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-20971519, default 20971519): +3G 16 17 Command (m for help): w 18 19 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y targetcli 20 21 [root@localhost ~]# targetcli 2223 /> backstores/block create disk1 /dev/vdb1 24 25 /> iscsi/ create iqn.2017-05.com.example:server0 26 27 /> iscsi/iqn.2017-05.com.example:server0/tpg1/acls create iqn.2017-05.com.example:desktop0 28 29 /> iscsi/iqn.2017-05.com.example:server0/tpg1/luns create /backstores/block/disk1 30 31 /> iscsi/iqn.2017-05.com.example:server0/tpg1/portals create 172.25.0.11
32 33 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start target 34 35 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable target 36 37 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3260/tcp 38 39 [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload 40
配置desktopX使其能连接在serverX上提供的iqn.2017-05.com.example:serverX并符合以下要求
iSCSI设备在系统启动的期间自动加载
块设备iSCSI上包含一个大小为2100MIB的分区,并格式化为ext4
此分区挂载在/mnt/data上同时在系统启动的期间自动挂载
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum install iscsi* -y 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi 4 5 InitiatorName=iqn.2017-05.com.example:desktop0 6 7 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart iscsi 8 9 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart iscsid 10 11 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable iscsid 12 13 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable iscsi 14 15 [root@localhost ~]# man iscsiadm |grep EXAMPLE -A 10 16 17 [root@localhost ~]# iscsiadm --mode discoverydb --type sendtargets --portal 172.25.0.11 --discover 18 19 [root@localhost ~]# iscsiadm --mode node --targetname iqn.2017-05.com.example:server0 --portal 172.25.0.11:3260 --login 20 21 [root@localhost ~]# lsblk 22 23 [root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sda 24 25 Command (m for help): p 26 27 Command (m for help): n 28 29 Select (default p): p 30 31 Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 32 33 First sector (8192-6291455, default 2048): 34 35 Using default value 8192 36 37 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (8192-6291455, default 6291455): +2100M 38 39 Command (m for help): w 40 41 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /mnt/data 42 43 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/fstab 44 45 [root@localhost ~]# /dev/sda1 /mnt/data ext4 defaults,_netdev 0 0 46 47 [root@localhost ~]# mount -a 48 49 [root@localhost ~]# df -TH 50 51 [root@localhost ~]# shutdown -h 0 52
在serverX上创建一个MariaDB数据库,名为Contacts,并符合以下要求
数据库应该包含来自数据库复制的内容,复制文件的URL为
ftp://172.25.254.250/pub/RHCE/user.mdb
数据库只能被localhost访问
除了root用户,此数据库只能被用户Raikon查询,此用户的密码为atenorth
root用户的密码为atenorth,同时不允许空密码登录
1 [root@localhost ~]# yum groupinstall mariadb mariadb-client -y 2 3 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start mariadb 4 5 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable mariadb 6 7 [root@localhost ~]# mysql_secure_installation 8 9 Set root password? [Y/n] y 10 11 New password: 12 13 Re-enter new password: 14 15 Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y 16 17 Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y 18 19 Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y 20 21 Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y 22 23 [root@localhost ~]# ll /root/users.mdb 24 25 [root@localhost ~]# cd /root/ #进入users.mdb所在的目录,方便后面source 26 27 [root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -p 28 29 create database Contacts; 30 31 use Contacts; 32 33 source users.mdb #source一下,前提当前目录有这个文件 34 35 create user r1@localhost identified by ‘redhat‘; 36 37 grant select on Contacts.* to r1@localhost; 38
这里我们将foundation0上的users.mdb复制到server上。
在serverX上创建一个MariaDB数据库,名为Contacts
root用户的密码为atenorth,同时不允许空密码登录
数据库应该包含来自数据库复制的内容, user.mdb
数据库只能被localhost访问
除了root用户,此数据库只能被用户Raikon查询,此用户的密码为atenorth
在系统serverX上使用数据库Contacts,并使用相应的SQL查询以回答下列问题:
密码是tangerine的人的名字?
有多少人的姓名是John同时居住在guangzhou?
1 [root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -p 2 3 use Contacts; 4 5 show tables; 6 7 desc pass; 8 9 select * from pass where password="tangerine"; #根据题目要求 10 11 desc name; 12 13 select * from name where aid=3; #根据上面查询结果 14 15 desc loc; 16 17 select * from name inner join loc where name.aid=loc.cid and loc.loction=‘guangzhou‘; 18
密码是tangerine的人的名字?通过上面的2次查询看到mary的密码是这个。
有多少人的姓名是John同时居住在guangzhou?
这里1 row in set,表示即叫John又住在广州的有1个人。
标签:环境 enabled 用户创建 guest 技术 排错 -418 开头 round
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ios9/p/RedHat_linux_RHCA.html