标签:row service lib 端口号 启动服务 hub artifact bug 安装部署
Gearman是当年LiveJournal用来做图片resize的,大家也明白图片resize是一个高CPU的操作,如果让web网站去做这个高CPU的功能,有可能会拖垮你的
web应用,那本篇我们来看看gearman是如何解决这个问题的,它的架构图类似下面这样:
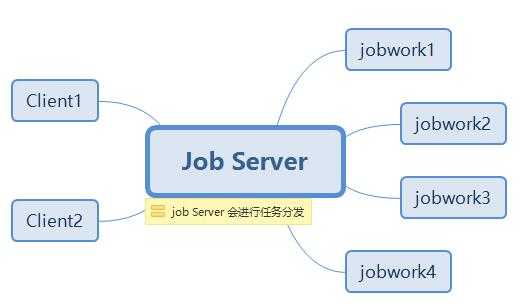
从上面这张图,你应该会看到,Gearman是由三个部分组成:
1. Job Server
这个就是Gearman的Job Server,通过它对Client 和 jobwork 进行桥接,是不是想起来了中介者模式。。。
2. Client
Gearman提供了Client API 给客户端调用,Client只需要将一个高CPU的业务函数名丢给Job Server,然后等待JobServer的返回执行结果。
3. jobwork
Gearman提供了work API 给work客户端进行调用。jobserver会根据后端的work集群的负载情况,分发给一个合适的work去执行,并等待结果。
说到这里,你应该就明白了,本质上它属于那种分布式的RPC调用,而且非常牛逼的地方在于Client 和 Work 可以用不同的语言实现。
一:安装部署
1. 下载地址:https://github.com/gearman/gearmand/releases
目前gearman的JobServer 有C,JAVA,Perl三种语言实现,由于C版本的JobServer是最活跃的,所以这里采用目前最新的1.1.17版本的gearmand在CentOS
上进行安装部署。
2. 快速安装
可以通过官网http://gearman.org/getting-started/中的getting-started进行快速安装。
<1> 基础依赖库安装和gearmand下载
1 yum -y install boost-devel gperf libevent-devel libuuid-devel gcc44 gcc-c++ 2 wget https://github.com/gearman/gearmand/releases/download/1.1.17/gearmand-1.1.17.tar.gz 3 cd gearmand-1.1.17.tar.gz 4 tar xzvf gearmand-1.1.17.tar.gz 5 cd gearmand-1.1.17 6 [root@localhost gearmand-1.1.17]# ls 7 aclocal.m4 build-aux configure.ac gear_config.in libgearman-1.0 libhashkit-1.0 Makefile.am rpm THANKS 8 AUTHORS ChangeLog COPYING gearmand libgearmancore libhostile Makefile.in scripts util 9 benchmark configmake.h docs HACKING libgearman-server libtest man support version.m4 10 bin configure examples libgearman libhashkit m4 NEWS tests
<2> 然后就是常规的./configure --prefix=/usr/myapp/gearman && make && make install 这个过程超级慢,可以出去抽跟烟,
顺便再去拉泡屎。。。
1 ./configure --prefix=/usr/myapp/gearman && make && make install
<3> 若干年后,当你看到这个就算安装成功了。。。还是得恭喜一下。。。。至少没让你踩到缺少各种依赖包的界面。
1 See any operating system documentation about shared libraries for 2 more information, such as the ld(1) and ld.so(8) manual pages. 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 4 /usr/bin/mkdir -p ‘/usr/myapp/gearman/sbin‘ 5 /usr/bin/install -c -m 644 man/gearman_worker_create.3 man/gearman_worker_define_function.3 man/gearman_worker_echo.3 man/gearman_worker_errno.3 man/gearman_worker_error.3 man/gearman_worker_free.3 man/gearman_worker_function_exist.3 man/gearman_worker_grab_job.3 man/gearman_worker_options.3 man/gearman_worker_register.3 man/gearman_worker_remove_options.3 man/gearman_worker_remove_servers.3 man/gearman_worker_set_context.3 man/gearman_worker_set_log_fn.3 man/gearman_worker_set_namespace.3 man/gearman_worker_set_options.3 man/gearman_worker_set_timeout.3 man/gearman_client_has_option.3 man/gearman_client_options_t.3 man/gearman_task_attr_init.3 man/gearman_task_attr_init_background.3 man/gearman_task_attr_init_epoch.3 man/gearman_task_attr_t.3 man/gearman_worker_set_identifier.3 man/gearman_worker_set_workload_free_fn.3 man/gearman_worker_set_workload_malloc_fn.3 man/gearman_worker_st.3 man/gearman_worker_timeout.3 man/gearman_worker_unregister.3 man/gearman_worker_unregister_all.3 man/gearman_worker_wait.3 man/gearman_worker_work.3 man/libgearman.3 ‘/usr/myapp/gearman/share/man/man3‘ 6 /bin/sh ./libtool --mode=install /usr/bin/install -c gearmand/gearmand ‘/usr/myapp/gearman/sbin‘ 7 libtool: install: /usr/bin/install -c gearmand/gearmand /usr/myapp/gearman/sbin/gearmand 8 /usr/bin/mkdir -p ‘/usr/myapp/gearman/bin‘ 9 /bin/sh ./libtool --mode=install /usr/bin/install -c bin/gearman bin/gearadmin ‘/usr/myapp/gearman/bin‘ 10 libtool: install: /usr/bin/install -c bin/.libs/gearman /usr/myapp/gearman/bin/gearman 11 libtool: install: /usr/bin/install -c bin/gearadmin /usr/myapp/gearman/bin/gearadmin 12 make[3]: Leaving directory `/usr/myapp/gearmand-1.1.17‘ 13 make[2]: Leaving directory `/usr/myapp/gearmand-1.1.17‘ 14 make[1]: Leaving directory `/usr/myapp/gearmand-1.1.17‘
<4> 启动gearmand,你也可以用 -d 开启后台运行的模式,这里加上DEBUG只是看一下实时的DEBUG信息,如下所示:
1 [root@localhost myapp]# cd /usr/myapp/gearman 2 [root@localhost gearman]# ls 3 bin include lib sbin share 4 [root@localhost gearman]# cd bin 5 [root@localhost bin]# ls 6 gearadmin gearman 7 [root@localhost bin]# cd /usr/myapp/gearman 8 [root@localhost gearman]# cd sbin 9 [root@localhost sbin]# ls 10 gearmand 11 [root@localhost sbin]# ./gearmand --verbose DEBUG 12 ./gearmand: Could not open log file "/usr/myapp/gearman/var/log/gearmand.log", from "/usr/myapp/gearman/sbin", switching to stderr. (No such file or directory) 13 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.796259 [ main ] THREADS: 4 -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:263 14 INFO 2017-08-29 02:31:10.796374 [ main ] Initializing Gear on port 4730 with SSL: false 15 INFO 2017-08-29 02:31:10.796487 [ main ] Starting up with pid 40299, verbose is set to DEBUG 16 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.796637 [ main ] Method for libevent: epoll -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:364 17 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.798874 [ main ] Trying to listen on 0.0.0.0:4730 -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:646 18 INFO 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800151 [ main ] Listening on 0.0.0.0:4730 (8) 19 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800175 [ main ] Trying to listen on :::4730 -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:646 20 INFO 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800307 [ main ] Listening on :::4730 (9) 21 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800333 [ main ] Creating wakeup pipe -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:915 22 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800344 [ main ] Creating 4 threads -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:378 23 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800357 [ main ] Initializing libevent for IO thread -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:224 24 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800406 [ main ] Creating IO thread wakeup pipe -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:495 25 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800467 [ main ] Thread 1 created -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:273 26 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800507 [ main ] Initializing libevent for IO thread -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:224 27 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800550 [ main ] Creating IO thread wakeup pipe -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:495 28 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800585 [ main ] Thread 2 created -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:273 29 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800594 [ main ] Initializing libevent for IO thread -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:224 30 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800632 [ main ] Creating IO thread wakeup pipe -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:495 31 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800669 [ main ] Thread 3 created -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:273 32 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800677 [ main ] Initializing libevent for IO thread -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:224 33 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800714 [ main ] Creating IO thread wakeup pipe -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:495 34 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800753 [ main ] Thread 4 created -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:273 35 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800761 [ main ] replaying queue: begin -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:391 36 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800766 [ main ] __replay -> libgearman-server/plugins/queue/default/queue.cc:101 37 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800774 [ main ] replaying queue: end -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:397 38 INFO 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800780 [ main ] Adding event for listening socket (8) 39 INFO 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800787 [ main ] Adding event for listening socket (9) 40 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800794 [ main ] Adding event for wakeup pipe -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:966 41 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.800801 [ main ] Entering main event loop -> libgearman-server/gearmand.cc:406 42 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.801186 [ 2 ] Entering thread event loop -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:463 43 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.801277 [ 3 ] Entering thread event loop -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:463 44 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.801507 [ main ] staring up Epoch thread -> libgearman-server/timer.cc:61 45 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.801635 [ 1 ] Entering thread event loop -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:463 46 DEBUG 2017-08-29 02:31:10.802426 [ 4 ] Entering thread event loop -> libgearman-server/gearmand_thread.cc:463
<5> 最后通过netstat,lsof, ps -ef 三板斧可以找出来gearmand大概占用的端口号,就如你看到的默认占用的4370端口,
当然你也可以在启动的时候用help命令也是能够知道的。
1 [root@localhost ~]# netstat -tln 2 Active Internet connections (only servers) 3 Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State 4 tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6 tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7 tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:4730 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 9 tcp6 0 0 :::8009 :::* LISTEN 10 tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 11 tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 12 tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 13 tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 14 tcp6 0 0 :::4730 :::* LISTEN 15 tcp6 0 0 127.0.0.1:8005 :::* LISTEN 16 [root@localhost ~]# ps -ef | grep gearmand 17 root 40299 15869 0 02:31 pts/1 00:00:00 ./gearmand --verbose DEBUG 18 root 40364 40327 0 02:33 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto gearmand 19 [root@localhost ~]# lsof -i :4730 20 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME 21 gearmand 40299 root 8u IPv4 322550 0t0 TCP *:gearman (LISTEN) 22 gearmand 40299 root 9u IPv6 322551 0t0 TCP *:gearman (LISTEN) 23 [root@localhost ~]#
二:Java Driver 在 Gearman上的使用
为了演示,我可以做一个简单的 “字符串.ToUpper”的业务逻辑来验证一下这个架构是否可以跑的起来。
1. java 充当 Gearman 的 work
首先需要在mvn仓库中拉一下jar包:http://www.mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.gearman/gearman-java/0.6。
<1> UpperFunction类,这个类用于定义work具体的业务逻辑:
1 package com.datamip.gearmanwork; 2 3 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 4 import java.util.Date; 5 6 import org.gearman.client.GearmanJobResult; 7 import org.gearman.client.GearmanJobResultImpl; 8 import org.gearman.util.ByteUtils; 9 import org.gearman.worker.AbstractGearmanFunction; 10 11 //字符串大写的业务Function 12 public class UpperFunction extends AbstractGearmanFunction { 13 14 @Override 15 public GearmanJobResult executeFunction() { 16 17 String param = ByteUtils.fromUTF8Bytes((byte[]) this.data); 18 19 byte[] mybytes = param.toUpperCase().getBytes(); 20 21 GearmanJobResultImpl result = new GearmanJobResultImpl(mybytes, true, mybytes, null, null, -1, -1); 22 23 SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); 24 25 String dateString = formatter.format(new Date()); 26 27 System.out.println(String.format("当前时间:%s, 过来的字符串:%s,返回的字符串:%s", dateString, param,new String(mybytes))); 28 29 return result; 30 } 31 }
<2> 将UpperFunction注册到gearmand中,从红色代码可以看到,其实是一个kv模式,这里的key="myUpperFunc”的对应执行业务就是new UpperFunction。
这样Client只需要传递一个"myUpperFunc",Gearmand就知道这个“字符串”对应是哪一个处理函数。。。
1 public class App { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 4 GearmanWorker worker = new GearmanWorkerImpl(); 5 6 GearmanNIOJobServerConnection conn = new GearmanNIOJobServerConnection("192.168.23.170", 4730); 7 worker.addServer(conn); 8 9 // 将‘将转大写的函数注册’ 到gearmand中 10 worker.registerFunctionFactory(new GearmanFunctionFactory() { 11 12 public String getFunctionName() { 13 return "myUpperFunc"; 14 } 15 16 public GearmanFunction getFunction() { 17 return new UpperFunction(); 18 } 19 }); 20 21 System.out.println("启动服务。。。。"); 22 23 worker.work(); 24 } 25 }
2. java 充当 Gearman 的 client
<1> GearSubmit类【简单的一个包装类,随便定义】
1 package com.datamip.gearmanclient; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 5 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 6 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 7 8 import org.gearman.client.GearmanClient; 9 import org.gearman.client.GearmanClientImpl; 10 import org.gearman.client.GearmanJob; 11 import org.gearman.client.GearmanJobImpl; 12 import org.gearman.client.GearmanJobResult; 13 import org.gearman.common.GearmanJobServerConnection; 14 import org.gearman.common.GearmanNIOJobServerConnection; 15 import org.gearman.util.ByteUtils; 16 17 public class Gearsubmit { 18 19 public void process() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 20 21 GearmanJobServerConnection conn = new GearmanNIOJobServerConnection("192.168.23.170", 4730); 22 23 GearmanClient client = new GearmanClientImpl(); 24 25 client.addJobServer(conn); // 添加连接 26 27 String functionName = "myUpperFunc"; 28 29 byte[] data = ByteUtils.toUTF8Bytes("hello,world"); 30 31 // 创建后台任务 32 GearmanJob job = GearmanJobImpl.createJob(functionName, data, null); 33 34 GearmanJobResult jobResult = null; 35 36 Future<GearmanJobResult> gearmanJobResult = client.submit(job); 37 38 jobResult = gearmanJobResult.get(); 39 40 byte[] resultBytes = jobResult.getResults(); 41 42 // 获取job的返回值 43 String value = ByteUtils.fromUTF8Bytes(resultBytes); 44 45 System.out.println(value); 46 47 System.out.println("执行结束"); 48 49 client.shutdown(); 50 } 51 }
<2> 主程序,开多线程并发的去执行。
1 public class App { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, IOException { 3 4 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100); 5 6 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { 7 executorService.execute(new Runnable() { 8 9 @Override 10 public void run() { 11 Gearsubmit submit=new Gearsubmit(); 12 13 try { 14 submit.process(); 15 } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 } 20 }); 21 } 22 23 System.in.read(); 24 } 25 }
好了,一切都准备好了,接下来为了演示,演示就是解释,我用Jar2Exe把work程序导出成jar再转换成exe,如下图:
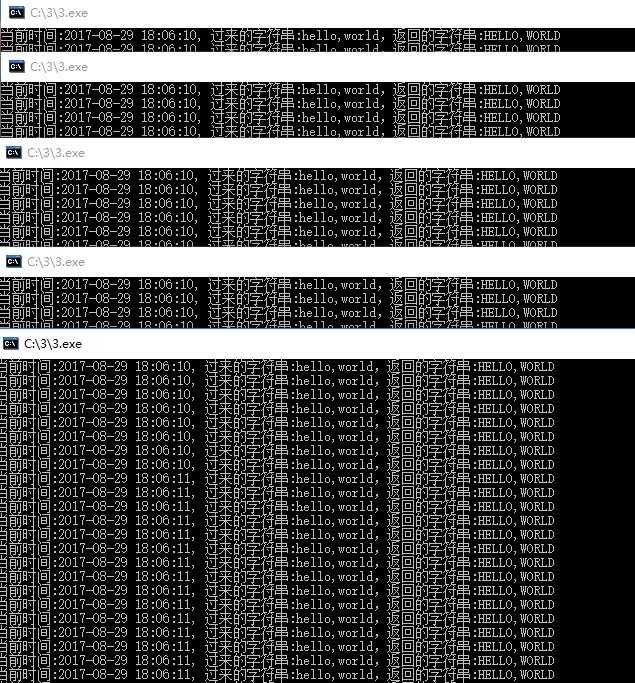
然后我把3.exe开成5个实例,client用100个线程的线程池并发调用,当然一切都是模拟。。。。可以看到,当我client启动的时候,5个work都在执行,
如果这个时候,你把某一个work停止了,jobserver也不再将任务丢给它,而是转给其他负载相对小的work继续执行。
好了,本篇就说到这里,希望对你有帮助。
标签:row service lib 端口号 启动服务 hub artifact bug 安装部署
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/p/7449722.html