标签:nbsp ret 标签 win param exe setname ges stp
程序结构:src文件夹下存放xml文件
该文件内容:
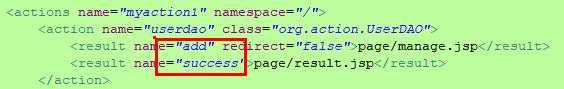
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <mystruts> <actions name="myaction1" namespace="/"> <action name="userdao" class="org.action.UserDAO"> <result name="add" redirect="false">page/manage.jsp</result> <result name="success">page/result.jsp</result> </action> <action name="register" class="cn.jbit.houserent.action.RegisterAction"> <result name="success">page/success.jsp</result> <result name="input">page/register.jsp</result> <result name="error">page/register.jsp</result> </action> </actions> <actions name="myaction2" namespace="/"> <action name="login" class="cn.jbit.houserent.action.LoginAction"> <result name="success" redirect="false">page/manage.jsp</result> <result name="input">page/result.jsp</result> </action> </actions> </mystruts>
定义实体类:




测试类:
package org.frame; import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import org.dom4j.Attribute; import org.dom4j.Document; import org.dom4j.Element; import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; import org.junit.Test; import org.node.Action; import org.node.Actions; import org.node.Result; //本类完成对xml文件的解析工作 返回解析到的list集合 public class Analyze { @Test public void print() throws Exception { List<Actions> listActions = analyzeRoot(); Iterator<Actions> i = listActions.iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { Actions actions = i.next(); System.out.println("actions[Name]:" + actions.getName() + ",actions[namespace]:" + actions.getNamespace()); // 获得action集合 Iterator<Action> i2 = actions.getActionList().iterator(); while (i2.hasNext()) { Action action = i2.next(); System.out.println("action[Name]:" + action.getName() + ",action[class]:" + action.getClassname()); // 遍历result集合 Iterator<Result> i3 = action.getResultList().iterator(); while (i3.hasNext()) { Result result = i3.next(); System.out.println("result[Name]:" + result.getName() + ",result[redirect]:" + result.isRedirect() + ",result[content]:" + result.getContent()); } } } } // 解析根节点<mystruts>的方法 最终返回actions下的所有节点集合 public List<Actions> analyzeRoot() throws Exception { // 用于封装节点数据的集合 List<Actions> listActions = new ArrayList<Actions>(); // 创建文件 File file = new File("src/mystruts.xml"); SAXReader sax = new SAXReader(); // 获得dom结构 Document read = sax.read(file); // 获取根节点 <mystruts> Element elementRoot = read.getRootElement(); // 一层层遍历根节点下的节点 Iterator<Element> iterator = elementRoot.elementIterator(); Actions actions = null; while (iterator.hasNext()) { actions = new Actions(); // 获得actions节点 Element elementActions = iterator.next(); // 获得actions标签的基本属性 Attribute attribute1 = elementActions.attribute("name"); Attribute attribute2 = elementActions.attribute("namespace"); // 设置基本属性到actions对象中 actions.setName(attribute1.getValue()); actions.setNamespace(attribute2.getValue()); // 调用方法 返回的集合是action节点的集合 List<Action> listAction = analyzeActions(elementActions); // 把action节点集合加入到actions的集合对象中 actions.setActionList(listAction); // 把封装好的actions对象加入到actions集合中 返回给用户 listActions.add(actions); } return listActions; } // 解析actions节点的方法 参数actions节点 最终返回的是action节点集合 public List<Action> analyzeActions(Element elementActions) throws Exception { List<Action> listAction = new ArrayList<Action>(); // 遍历actions节点 得到action节点 Iterator<Element> iterator = elementActions.elementIterator(); Action action = null; while (iterator.hasNext()) { action = new Action(); // 得到每个action节点对象 Element elementAction = iterator.next(); // 获取该节点的基本属性 Attribute attribute1 = elementAction.attribute("name"); Attribute attribute2 = elementAction.attribute("class"); action.setName(attribute1.getValue()); action.setClassname(attribute2.getValue()); // 继续调用方法 返回的是action下的result节点的集合 List<Result> listResult = analyzeAction(elementAction); // 把集合封装进action中的集合属性中 action.setResultList(listResult); // 最后把每个action对象 封装进上边准备的listAction集合中 listAction.add(action); } return listAction; } // 解析action节点的方法 参数action节点 最终返回的是result节点集合 public List<Result> analyzeAction(Element elementAction) throws Exception { List<Result> listResult = new ArrayList<Result>(); // 遍历action节点 得到result节点 Iterator<Element> iterator = elementAction.elementIterator(); Result result = null; while (iterator.hasNext()) { result = new Result(); // 得到每个result对象 Element elementResult = iterator.next(); // 得打属性对象 Attribute attribute1 = elementResult.attribute("name"); Attribute attribute2 = elementResult.attribute("redirect"); // 进行封装 result.setName(attribute1.getValue()); // 但是需要注意的是 redirect属性可能获取不到 如果获取不到 设置默认值为true String redirect = ""; try {// 没有异常 表示可以获取到 redirect = attribute2.getValue(); result.setRedirect(Boolean.parseBoolean(redirect)); } catch (Exception e) { // 表示没有redirect属性 设置默认值 result.setRedirect(true); } // 设置文本属性 result.setContent(elementResult.getTextTrim()); listResult.add(result); } return listResult; } }
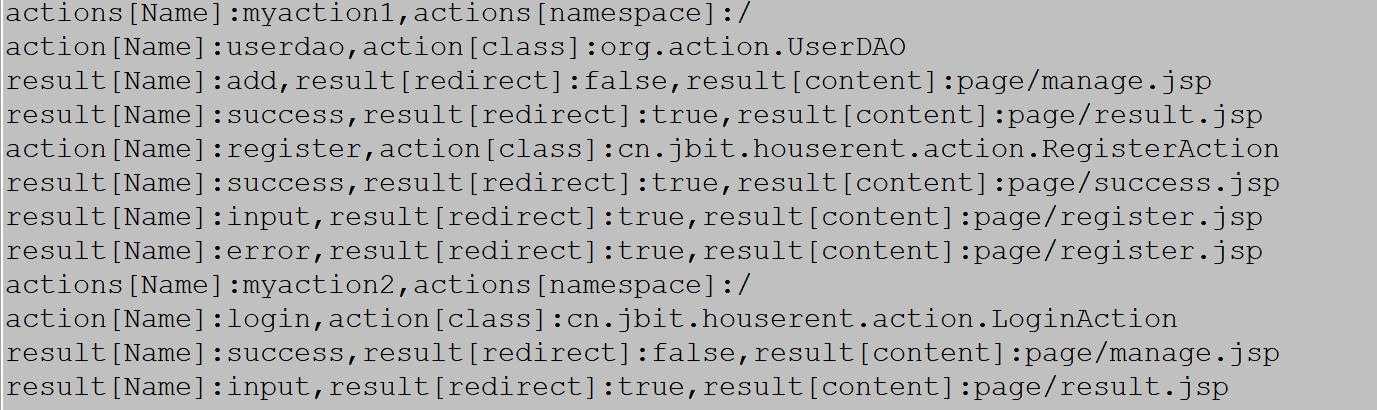
执行单元测试类:节点遍历结果:
有了以上代码的基础上,实现struts2框架中 传递url访问目标方法 并且返回对应视图的名称
框架类(使用反射):
package org.frame; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.List; import org.node.Action; import org.node.Actions; import org.node.Result; //这个类根据用户传入的参数 反射生成对应对象之后 执行对象中用户需要调用的方法 public class FrameMethod { public Object reflect(String classname,String methodname,List<Object> listobj)throws Exception{ //classname完整的包.类名称 通过它我们才能实例化对象 //methodname:需要调用的方法名称 //object[]执行方法 需要传入的参数 Class<?> clazz=Class.forName(classname); Object o=clazz.newInstance();//创建的反射对象 //判断参数 如果不为空执行对应方法 并且传递参数 如果为空 默认执行action类中的execute方法(仿struts2) Object obj=null;//执行方法执行 保存方法的返回值 if(listobj==null){ //执行默认方法execute 不需要参数 //返回指定的方法 第一个参数方法名 第二个参数 该方法需要的参数类型 Method method=clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodname, null); //执行该方法 第一个参数实例化的对象 第二个参数传递的参数 这里无参 obj=method.invoke(o, null);//该方法可能存在返回值 }else{ Method method=clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodname, List.class); obj=method.invoke(o,listobj); } //执行方法之后 把方法返回的值 返回给调用者 return obj; } //根据用户(访问)传入的url 执行对应的方法 并且返回出xml中result标签 对应的文本内容 xx.jsp public Object returnView(String url,List<Object> listParm)throws Exception{ String className=null; String methodName=null; Analyze analyze=new Analyze(); //首先得到解析到的xml标签集合 List<Actions> listActions=analyze.analyzeRoot(); //解析用户访问的url xxxDao!method xxxDao 得到访问的action类名 以及方法名称 int index=url.indexOf("!"); if(index>0){//说明是xxxDao!method的形式 String[] str=url.split("!"); className=str[0]; methodName=str[1]; }else{//说明是xxxDao的形式 执行的方法是默认方法execute() className=url; methodName="execute"; } //下面输入返回值对应的视图名称 Object viewName=null; for(Actions actions:listActions){ //得到actions节点 //通过actions节点 继续向下遍历action节点 for(Action action:actions.getActionList()){ //或得action节点 //进行判断 然后找到对应的result节点 打印该节点中的文本 就是视图名称 if(action.getName().equals(className)){ //下面调用反射方法 传递参数执行对应方法 className=action.getClassname(); Object rtnobj=reflect(className,methodName,listParm);//得到action中方法的返回值 //找到 就或得该节点下的所有result节点 List<Result> listResult=action.getResultList(); //继续遍历 for(Result r:listResult){ if(r.getName().equals(rtnobj)){ //action中方法的返回值 与result节点中的name值对应 那么获取该节点的文本节点 viewName=r.getContent(); } } } } } return viewName; } }
action类:
package org.action; import java.util.List; public class UserDAO { public void hello() { System.out.println("我是hello"); } public String execute() { System.out.println("我是execute"); return "success"; } public String add(List<Object> param) { System.out.println("我是add"); for (Object obj : param) { System.out.println(obj); } return "add"; } }
测试代码:
package org.frame; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.junit.Test; import org.model.Student; public class testFrame { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { t1(); System.out.println("-------------------------"); t2(); } public static void t1() throws Exception { FrameMethod rm = new FrameMethod(); List<Object> listObj = new ArrayList<Object>(); listObj.add("张三"); listObj.add("李四"); // 第三次 加入一个对象进去 Student stu = new Student("jay", "123"); listObj.add(stu); Object obj = rm.returnView("userdao!add", listObj); // 输入返回的视图名称 System.out.println("访问该url,返回的视图名称为:" + obj); } public static void t2() throws Exception { FrameMethod rm = new FrameMethod(); // 访问默认的execute方法 Object obj = rm.returnView("userdao", null); // 输入返回的视图名称 System.out.println("访问该url,返回的视图名称为:" + obj); } }
测试结果:
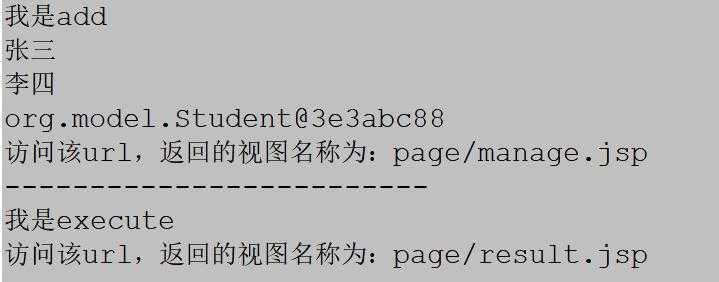
以上就基本模仿实现了struts2框架机制,根据用户访问的url地址 解析xml 执行对应action中的方法 然后返回视图名称 对比xml中的result节点中的name属性 找到对应的视图路径
解析xml文件,遍历输出xml文件中的所有节点, 最终模仿实现struts2框架
标签:nbsp ret 标签 win param exe setname ges stp
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Joke-Jay/p/7464040.html