标签:english php 自己的 信息 where 标识 常见 必须 手机
数据的操作也叫做CRUD
C:Create
R:Read
U:Update
D:Delete
标准语法:
1 insert into 表名[字段列表] values(值列表);
思考:
1,如何以最快的速度向数据表中插入100万条数据?
含义:在已有的数据的基础之上,将原来的数据进行复制,插入到对应的表中(也可以插入到自己的表中);
1 -- 蠕虫复制 2 insert into 表名 select *|字段列表 from 表名; 3 4 create table ruchong1( 5 a int , 6 b int 7 ); 8 9 10 insert into ruchong1 values(12,23),(9,18),(34,56),(13,35); 11 12 create table ruchong2( 13 a int , 14 b int 15 ); 16 17 insert into ruchong2 select * from ruchong1; --重复插入10多次就行了
作用:
1, 以最快的速度将一张表的数据复制到另一张表中,前提是后面查询结果的结构与前面插入数据表的结构是一样的!
2, 短期内产生大量的数据,以测试服务器的压力!
常见的一个场景:
在进行数据插入的时候,主键已经存在,但是又需要将最新的数据更新到记录中,怎么办?
比如,更新手机号码的机主信息:
1 create table tel_info( 2 tel_no char(11) primary key, 3 tel_name varchar(20), 4 tel_id char(18) 5 ); 6 7 insert into tel_info values(‘13612345678‘,‘张三‘,‘440921199411080845‘); 8 insert into tel_info values(‘13612345678‘,‘李四‘,‘440921199411080883‘);-- 出错了
此时,有两种解决方案:
1 -- 方案一: 2 -- 如果主键冲突,直接更新: 3 insert into 表名(字段列表) values(值列表) on duplicate key update 字段1=值1,字段2=值2...; 4 5 -- 执行流程:先执行插入语句,如果遇到主键重复,就变成执行一条更新语句。 6 7 insert into tel_info values(‘13612345678‘,‘李四‘,‘440921199411080883‘) on duplicate key update tel_name = ‘李四‘,tel_id=‘440921199411080883‘; 8 -- 方案二: 9 -- 如果主键冲突,就直接删除原记录,再插入 10 replace into 表名(字段列表) values(值列表); 11 12 replace into tel_info values(‘13612345678‘,‘张三‘,‘440921199411080845‘); 13 14 --执行流程:先判断主键有没有重复,如果没有,就执行正常的插入语句,如果有就先执行删除之前的再插入新的! 15
1 -- 修改数据: 2 -- 标准语法: 3 4 update 表名 set 字段1 = 值1, 字段2 = 值2..where 条件; 5 6 7 -- 其他语法: 8 update 表名 set 段1 = 值1, 字段2 = 值2..where 条件 order by 字段名[asc|desc] limit 数据量; 9 -- asc是升序 默认值 10 -- desc 是降序 11 create table user_info( 12 user_id int unsigned primary key auto_increment, 13 user_name varchar(20), 14 user_tel char(11), 15 is_vip enum(‘Y‘,‘N‘), 16 last_buy_time int unsigned, 17 user_score int unsigned 18 ); 19 20 -- 应用场景:商家做活动,给前最先到的100名的vip用户的积分增加500分! 21 22 update user_info set user_score = user_score + 500 where is_vip=‘Y‘ order by last_buy_time asc limit 100 23 24 /* 也就是说,修改数据的时候可以使用order by关键字进行排序然后再限制修改的数量! 25 注意:where修改条件、order by子句以及limit子句的顺序不能发生改变! 26 27 同样的,删除数据的时候也可以加上order by子句和limit子句: 28 */
1 -- 标准语法: 2 delete from 表名 where 删除条件 3 4 -- 其他语法: 5 delete from 表名 where 删除条件 order by 字段名[asc|desc] limit 数量;
1 -- 查询数据是业务逻辑中使用的最多的也是最复杂的! 2 -- 以前的语法: 3 select *|字段列表 from 表名 where 查询条件; 4 -- 比较完整的语法: 5 6 7 select [select选项] *|字段列表 [as 别名] from 数据源 [where子句] [group by子句][having子句][order by子句][limit子句]; 8 9 /* 10 注意: 11 1, from后面的子句往往叫做五子查询,也叫做五子句 12 2, 五子查询的选项都可以没有,但是如果有,必须按顺序写! 13 */
1 /* 2 就是查询到数据之后,该如何保留查询结果! 3 一共有两个值: 4 all:也是默认值,保留所有的查询结果! 5 distinct:去重,去掉重复的记录,这里的重复是指所有的字段的值完全一样! 6 7 一般来说,如果查询的是所有的字段,用缺省值(省略即可)就行, 8 如果查询的是部分字段,可以进行去重操作! 9 */ 10 11 insert into ruchong2 values(23,24),(35,36),(10,35);
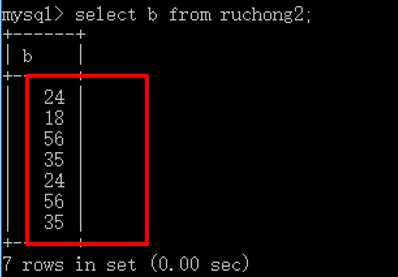
1 select b from ruchong2;
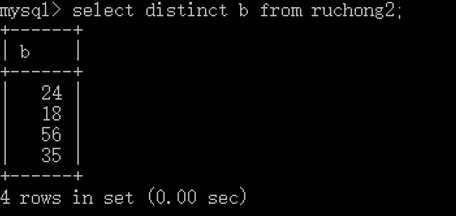
1 select distinct b from ruchong2; -- 去重
1 -- 所谓的别名就是给字段或者其他表达式等标识符起一个别名.基本语法: 2 -- 别名 3 字段名|表达式|表|子查询语句[as] 别名 4 -- 其中as可以省略,但是建议写上
1, 为什么给字段起别名呢?
因为在进行联表查询的时候,两张表可能会出现相同的字段名:
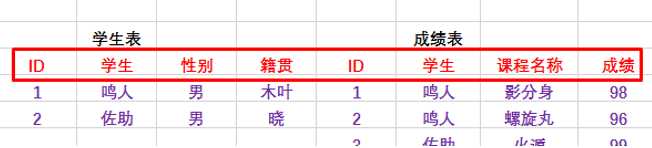
比如上面的学生表中的学生字段和成绩表中的学生字段!这样将来PHP在提取记录的时候,后面的数组元素会覆盖前面的(下标值是一样的),所以,有必须给她们两个中至少一个起一个别名!
2,为什么要给表达式起别名?
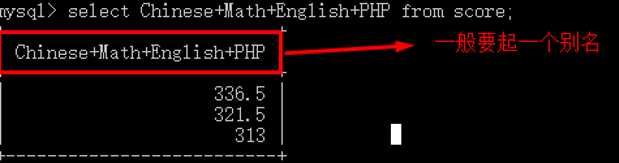
1 create table score( 2 chinese float, 3 Math float, 4 English float, 5 PHP float 6 ); 7 8 insert into score values 9 (78.5,89,76,93), 10 (77,69,70,98), 11 (76.5,79,96,90), 12 (75.5,99,96,93); 13 14 select Chinese+Math+English+PHP from score;
1 select Chinese+Math+English+PHP as sum from score;
标签:english php 自己的 信息 where 标识 常见 必须 手机
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mrszhou/p/7468190.html