标签:个学生 记录 分享 das es2017 mit from 分数 用户注册
思考:
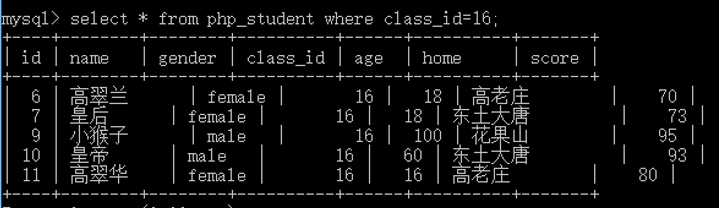
如何得到php_student表中成绩最高的学生的记录?
1 select * from php_student order by score desc limit 1;
但是,存在一个逻辑问题,如果最高分有很多人,怎么办!
1 insert into php_student values 2 (null,‘观世音‘,‘female‘,17,5000,‘南海‘,100), 3 (null,‘如来‘,‘male‘,17,6000,‘西天‘,100);
所以,必须换一个思维方式,分成两个步骤:
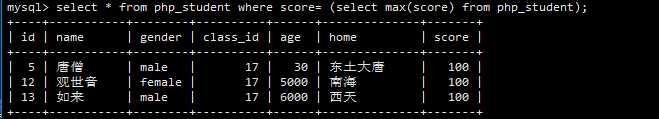
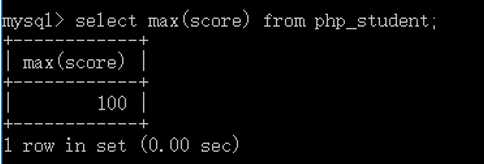
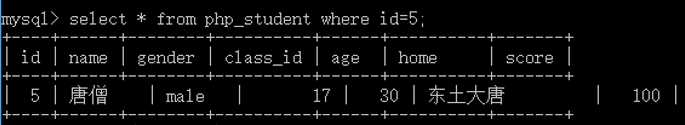
1 -- 1.先得到成绩的最高分 2 select max(score) from php_student; 3 -- 2.把成绩为最高分的人全部查询出来 4 select * from php_student where score = (select max(score) from php_student);
所谓的子查询,其实就是在一条select语句中又出现了另一条select语句!
子查询有一个最基本的语法要求,就是子查询语句需要用一对括号括起来!
一般的,有两种不同的分类方式:
分类:
一般的两种不同的分类方式:
子查询依然是一条完整的查询语句,只要是查询语句,其返回值就四种形式:
1.单一值
上面四条select语句乳沟放在另一条select语句中,都叫做子查询语句
分别如下:
返回单一值的子查询叫: 标量子查询
返回一列的子查询: 列子查询
返回一行的子查询: 行子查询
返回多行多列的子查询: 表子查询
当然以上是人为的逻辑分类,对应mysql服务器,无论返回形式如何都是资源结果集
from型: 子查询语句出现在from之后,通常作为一个数据源出现
where型: 子查询语句出现在where之后,通常用来做条件判断
exists型: 子查询语句出现在exists之后
通常,就是把标量子查询的结果当成是一个值来使用,可以用来参与运算,或者用来做条件判断!
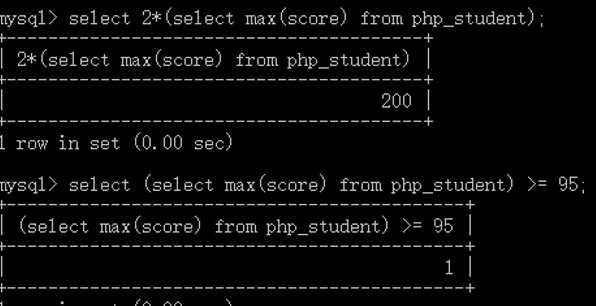
子查询的结果是一列数据的集合!也是一类数据的集合!
所以,通常就是配合in 和not in集合运算符来使用!
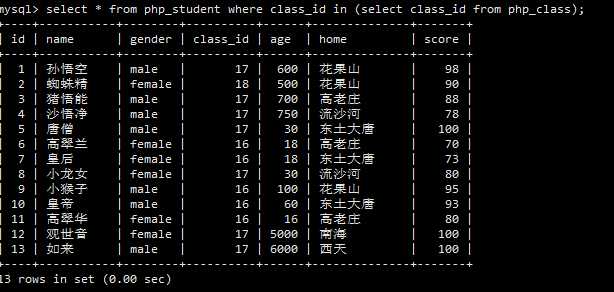
找出php_student表中所有已经开班了的学生的信息!
1 --案例: 2 -- 找出php_student表中所有已经开班的学生的信息 3 -- 1、找出所有已经开班的班级号(班级的集合) 4 select class_id from php_class; 5 -- 2、 找出符合条件的学生 6 select * from php_student where class_id in (select class_id from php_class); 7 8 in 就是=any 或=some 9 10 select * from php_student where class_id in (select class_id from php_class); 11 select * from php_student where class_id =any(select class_id from php_class); 12 select * from php_student where class_id =some(select class_id from php_class);
概念:
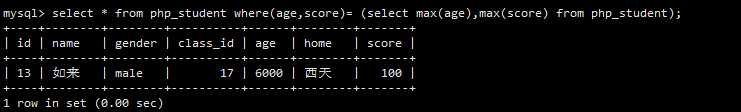
子查询的结果是一行的子查询叫做行子查询!
行子查询使用的不是很多,因为必须在查询的过程中,构造一个行元素才能与子查询的结果进行比较!
所谓的构造行元素,就是一个由多个字段组成的元素,形式上就将多个字段用一对小括号括起来!
1 -- 语法 2 select *|字段列表 from 表名 where(字段1,字段2 ...) = (行子查询语句); 3 4 -- 查询php_student 总年龄最大并且分数最高的记录 5 select * from php_student where(age,score) = (select max(age),max(score) from php_student);

返回的结果是多行多列的子查询就叫做表子查询!
表子查询一般就是用在from语句之后,当成一个数据源来使用,所以最常见的语法格式:
1 select * | 字段列表 from (表子查询语句) as 别名 where子句等五子句;
/*特别强调: 当子查询语句出现在from之后作为一个数据源使用的时候,该语句必须起一个别名! 案例: 不使用任何的统计函数找出php_student 表中每个家乡home中分数score最低的一个学生! */ select * from php_student group by home; -- 无法达到目的 -- 1.先以score字段进行升序排序 select * from php_student order by score asc; -- 2.对排序之后的数据表根据home字段进行分组(分组只拿第一条数据) select * from(select * from php_student order by score asc) as s group by home;
exists主要是用来判断的,返回的是一个布尔值:true或者false,1或者0;
判断依据:
如果子查询的结果有数据返回(查询到了结果),用exists去判断的结果就为true!
如果子查询的结果没有数据返回(没有查询到结果),用exists去判断的结果就为false!
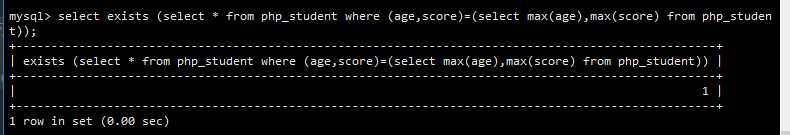
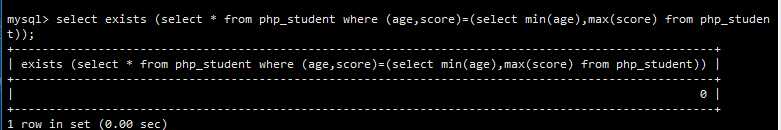
1 -- 案例: 2 -- 查询年龄最大分数最高是否存在 3 select exists(select * from php_student where(age,score) = (select max(age),max(score) from php_student)); 4 5 -- 查询年龄最小分数最高是否存在 6 select exists(select * from php_student where(age,score) = (select min(age),max(score) from php_student)); 7 8 处理用户注册的时候判断用户输入的用户名是否语句存在! 9 -- 假如用户输入的用户名是flybird,要作如下的判断 10 select exists(select * from user where user_name = ‘flybird‘);
查询年龄最大分数最高是否存在
查询年龄最小分数最高是否存在
标签:个学生 记录 分享 das es2017 mit from 分数 用户注册
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mrszhou/p/7471319.html