标签:def clu numbers using 递推 eve ++ type color
A bit is a binary digit, taking a logical value of either 1 or 0 (also referred to as "true" or "false" respectively). And every decimal number has a binary representation which is actually a series of bits. If a bit of a number is 1 and its next bit is also 1 then we can say that the number has a 1 adjacent bit. And you have to find out how many times this scenario occurs for all numbers up to N.
Examples:
Number Binary Adjacent Bits
12 1100 1
15 1111 3
27 11011 2
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 10000), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case contains an integer N (0 ≤ N < 231).
Output
For each test case, print the case number and the summation of all adjacent bits from 0 to N.
Sample Input
7
0
6
15
20
21
22
2147483647
Sample Output
Case 1: 0
Case 2: 2
Case 3: 12
Case 4: 13
Case 5: 13
Case 6: 14
Case 7: 16106127360
详解:http://www.cnblogs.com/jianglangcaijin/archive/2012/10/10/2719029.html
好厉害,能这样找递推公式!!!!!!
F[ i ]表示[ 0,(2^i)-1 ]这个区间上的数字的adjacent bits之和。
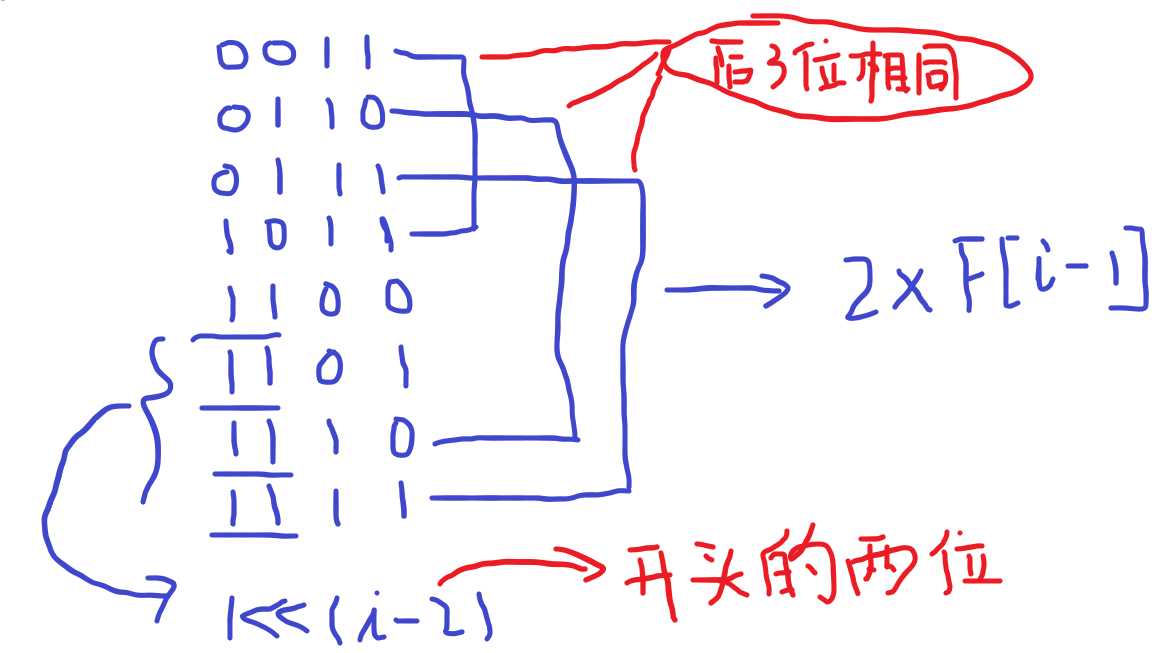
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 typedef long long ll; 7 8 int n; 9 ll F[40]; 10 11 void Inite(){ 12 F[1]=0;F[2]=1; 13 for(int i=3;i<=31;i++) F[i]=F[i-1]*2+(1<<(i-2)); 14 } 15 16 ll Solve(int x){ 17 ll ans=0; 18 for(int i=31;i>=0;i--){ 19 if(x&(1<<i)){ 20 x=x-(1<<i); 21 ans=ans+F[i]+max(0,x-(1<<(i-1))+1); 22 } 23 } 24 return ans; 25 } 26 27 int main() 28 { Inite(); 29 30 int kase; 31 cin>>kase; 32 for(int t=1;t<=kase;t++){ 33 cin>>n; 34 printf("Case %d: %lld\n",t,Solve(n)); 35 } 36 return 0; 37 }
Fast Bit Calculations LightOJ - 1032
标签:def clu numbers using 递推 eve ++ type color
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zgglj-com/p/7501206.html