标签:gcd context 学习 ++ ring not round 1.5 一起
四则运算题目生成程序
coding地址:https://git.coding.net/conding_hjy/project-01.git
需求分析
1. 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数,例如
Myapp.exe -n 10 -o Exercise.txt
将生成10个题目。
2. 使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围,例如
Myapp.exe -r 10
将生成10以内(不包括10)的四则运算题目。该参数可以设置为1或其他自然数。该参数必须给定,否则程序报错并给出帮助信息。
3. 生成的题目中如果存在形如e1 ÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数。
4. 每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
5. 程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。例如,23 + 45 = 和45 + 23 = 是重复的题目,6 × 8 = 和8 × 6 = 也是重复的题目。3+(2+1)和1+2+3这两个题目是重复的,由于+是左结合的,1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,也就是3+(1+2),也就是3+(2+1)。但是1+2+3和3+2+1是不重复的两道题,因为1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,而3+2+1等价于(3+2)+1,它们之间不能通过有限次交换变成同一个题目。
生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件,格式如下:
1. 四则运算题目1
2. 四则运算题目2
……
其中真分数在输入输出时采用如下格式,真分数五分之三表示为3/5,真分数二又八分之三表示为2’3/8。
6. 在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件,格式如下:
1. 答案1
2. 答案2
特别的,真分数的运算如下例所示:1/6 + 1/8 = 7/24。
7. 程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
8. 程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,并会输出所有题目中重复的题目,输入参数如下:
Myapp.exe -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt -o Grade.txt
统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
Repeat:2
RepeatDetail:
(1) 2,45+32 Repeat 3,32+45
(2) 5,3+(2+1) Repeat 7,1+2+3
解释:
Correct: 5 ----5道题目正确,正确的题号 1,3,5,7,9
Wrong:5 -----5道题目错误,错误的题号 2,4,6,8,10
Repeat:2 2---组题目重复
(1) 第一组 题号2,题目 45+32 与题号3的题目重复,题号3为 32+45
(2)第二组 题号5,题目 3+(2+1) 与题号7的题目重复,题号7为 1+2+3
其中“:”后面的数字5表示对/错的题目的数量,括号内的是对/错题目的编号。为简单起见,假设输入的题目都是按照顺序编号的符合规范的题目。
功能设计
设计实现
Szys.class
1.根据输入的特定的命令行,执行特定的功能 2.截取输入字符串获得需要的参数 3.生成四则运算题目及答案 4.给定四则运算题目和答案比较,判断答案的正确数,错误数,题目的重复数及详细的说明
ReversePolishNotation.class
1.将表达式转换成逆波兰表达式进行计算
TestFractory.class
1.分数的四则运算
代码说明
Szys.class根据用户输入的命令行进行操作,生成四则运算题目和答案并保存在不同的文件中,
对每个表达式调用ReversePolishNotation.class中的evaluate(String[] tokens)方法实现逆波兰式计算。两个操作数进行计算时,要先转换成分数的形式,然后分别调用TestFractory.class中实现的分数的加减乘除的四个方法进行分数计算。
Szys.class
1 // 任务一 2 public static void task1(String input) throws IOException { 3 // n题目数,r数值位数 4 int n, r; 5 // 题目文件名 6 String o = ""; 7 // 答案文件名 8 String a = "Answers.txt"; 9 // 随机数对象 10 Random random = new Random(); 11 // 文件内容 12 String o_context = ""; 13 // 答案内容 14 String a_context = ""; 15 // 每个表达式操作符数量 16 int operator_num; 17 18 n = Integer.parseInt(hasNum(‘n‘, ‘-‘, input)); 19 r = Integer.parseInt(hasNum(‘r‘, ‘-‘, input)); 20 o = hasNum(‘o‘, ‘-‘, input); 21 22 File file = new File(o); 23 File file1 = new File(a); 24 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true); 25 FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream(file1, true); 26 boolean right, left; 27 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 28 right = false; 29 left = false; 30 o_context = ""; 31 a_context = (i+1)+". "; 32 operator_num = random.nextInt(3) + 1; 33 34 if (left == false && operator_num > 1) { 35 if (random.nextInt(2) == 1) { 36 o_context += "("; 37 left = true; 38 } 39 } 40 o_context += randomNumber(r); 41 for (int j = 0; j < operator_num; j++) { 42 String add1 = "", add2 = ""; 43 if (left == true && right == false && operator_num > 1) { 44 if (operator_num == 2) { 45 add2 = ")"; 46 right = true; 47 } else { 48 if (random.nextInt(2) == 1) { 49 add2 = ")"; 50 right = true; 51 } 52 } 53 54 } else if (left == false && operator_num > 1) { 55 if (random.nextInt(2) == 1) { 56 add1 = "("; 57 left = true; 58 // right = true; 59 } 60 } 61 switch (random.nextInt(4)) { 62 case 0: 63 o_context += " + " + add1 + randomNumber(r) + add2; 64 break; 65 case 1: 66 o_context += " - " + add1 + randomNumber(r) + add2; 67 break; 68 case 2: 69 o_context += " × " + add1 + randomNumber(r) + add2; 70 break; 71 case 3: 72 o_context += " ÷ " + add1 + randomNumber(r) + add2; 73 break; 74 75 default: 76 break; 77 } 78 } 79 if (left == true && right == false) { 80 o_context += ")"; 81 } 82 a_context += ReversePolishNotation.evaluate(ReversePolishNotation.toReversePolishNotation(o_context)) 83 + "\r\n"; 84 o_context = (i+1)+". "+o_context; 85 o_context += " =\r\n"; 86 fos.write(o_context.getBytes()); 87 fos1.write(a_context.getBytes()); 88 } 89 fos.close(); 90 fos1.close(); 91 System.out.println("执行成功"); 92 } 93 94 // 任务二 95 public static void task2(String input) throws IOException { 96 97 // 题目文件名 98 String e = ""; 99 // 答案文件名 100 String a = ""; 101 // 目标文件 102 String o = ""; 103 104 List<Integer> Correct = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 105 List<Integer> Wrong = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 106 e = hasNum(‘e‘, ‘-‘, input); 107 a = hasNum(‘a‘, ‘-‘, input); 108 o = hasNum(‘o‘, ‘-‘, input); 109 110 System.out.println(e + "\n" + a + "\n" + o); 111 112 File file1 = new File(e); 113 File file2 = new File(a); 114 BufferedReader reader1 = null; 115 BufferedReader reader2 = null; 116 String temp1 = null; 117 String temp2 = null; 118 int line = 1; 119 reader1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file1)); 120 reader2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file2)); 121 while ((temp1 = reader1.readLine()) != null && (temp2 = reader2.readLine()) != null) { 122 temp1 = temp1.substring(temp1.indexOf(".")+2); 123 temp2 = temp2.substring(temp2.indexOf(".")+2); 124 temp1 = ReversePolishNotation.evaluate(ReversePolishNotation.toReversePolishNotation(temp1)); 125 if (temp1.equals(temp2)) { 126 Correct.add(line); 127 } else { 128 Wrong.add(line); 129 } 130 line++; 131 } 132 133 reader1.close(); 134 reader2.close(); 135 136 File file3 = new File(o); 137 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file3,true); 138 fos.write(("Correct:"+Correct.size()+Correct.toString()+ "\r\n").getBytes()); 139 fos.write(("Wrong:"+Wrong.size()+Wrong.toString()+ "\r\n").getBytes()); 140 fos.write("Repeat:\r\n".getBytes()); 141 fos.write("RepeatDetail:\r\n".getBytes()); 142 System.out.println("执行成功"); 143 }
ReversePolishNotation.class
1 package com.jmu.util; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.HashMap; 5 import java.util.Scanner; 6 import java.util.Stack; 7 8 /** 9 * 自然数分数四则运算 10 * @author csb 逆波兰表达式(后缀表达式) 11 * 是一种由波兰数学家扬·武卡谢维奇1920年引入的数学表达式方式,在逆波兰记法中,所有操作符置于操作数的后面,因此也被称为后缀表示法。 12 * 逆波兰记法不需要括号来标识操作符的优先级。 13 */ 14 public class ReversePolishNotation { 15 static HashMap<String, Integer> operatorLevel; 16 static { 17 operatorLevel = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 18 operatorLevel.put("(", 5); 19 operatorLevel.put(")", 5); 20 operatorLevel.put("×", 4); 21 operatorLevel.put("÷", 4); 22 operatorLevel.put("+", 3); 23 operatorLevel.put("-", 3); 24 } 25 26 public static String evaluate(String[] tokens) { 27 int x, y, z; 28 String s = ""; 29 int result = 0; 30 String operators = "+-×÷"; 31 Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); 32 for (String t : tokens) { 33 if (!operators.contains(t)) { 34 stack.push(t); 35 } else { 36 int a1, a2, b1, b2; 37 s = stack.pop(); 38 39 if (s.contains("‘")) { 40 x = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(0, s.indexOf("‘"))); 41 y = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(s.indexOf("‘") + 1, s.indexOf("/"))); 42 z = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(s.indexOf("/") + 1)); 43 a1 = x * z + y; 44 a2 = z; 45 } else if (s.contains("/")) { 46 y = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(0, s.indexOf("/"))); 47 z = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(s.indexOf("/") + 1)); 48 a1 = y; 49 a2 = z; 50 } else { 51 a1 = Integer.valueOf(s) * Integer.valueOf(s); 52 a2 = Integer.valueOf(s); 53 } 54 s = stack.pop(); 55 56 if (s.contains("‘")) { 57 x = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(0, s.indexOf("‘"))); 58 y = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(s.indexOf("‘") + 1, s.indexOf("/"))); 59 z = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(s.indexOf("/") + 1)); 60 b1 = x * z + y; 61 b2 = z; 62 } else if (s.contains("/")) { 63 y = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(0, s.indexOf("/"))); 64 z = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(s.indexOf("/") + 1)); 65 b1 = y; 66 b2 = z; 67 } else { 68 b1 = Integer.valueOf(s) * Integer.valueOf(s); 69 b2 = Integer.valueOf(s); 70 } 71 72 // int a = Integer.valueOf(stack.pop()); 73 // int b = Integer.valueOf(stack.pop()); 74 int index = operators.indexOf(t); 75 switch (index) { 76 case 0: 77 stack.push(TestFractory.fracAdd(a1, a2, b1, b2)); 78 break; 79 case 1: 80 stack.push(TestFractory.fracSub(b1, b2, a1, a2)); 81 break; 82 case 2: 83 stack.push(TestFractory.fracMul(a1, a2, b1, b2)); 84 break; 85 case 3: 86 stack.push(TestFractory.fracDiv(b1, b2, a1, a2)); 87 break; 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 String pp = stack.pop(); 92 //System.out.println(pp); 93 if (pp.contains("/")) { 94 if (pp.contains("-")) { 95 x=Integer.valueOf(pp.substring(1, pp.indexOf("/"))); 96 y=Integer.valueOf(pp.substring(pp.indexOf("/")+1)); 97 if (x%y==0) { 98 pp=x/y+""; 99 }else if(x<y){ 100 z = gcd(x,y); 101 pp=x/z+"/"+y/z; 102 }else { 103 z = gcd(x,y); 104 pp=(x/z)/(y/z)+"‘"+(x/z)%(y/z)+"/"+(y/z); 105 } 106 pp = "-"+pp; 107 }else{ 108 x=Integer.valueOf(pp.substring(0, pp.indexOf("/"))); 109 y=Integer.valueOf(pp.substring(pp.indexOf("/")+1)); 110 if (x%y==0) { 111 pp=x/y+""; 112 }else if(x<y){ 113 z = gcd(x,y); 114 pp=x/z+"/"+y/z; 115 }else { 116 z = gcd(x,y); 117 pp=(x/z)/(y/z)+"‘"+(x/z)%(y/z)+"/"+(y/z); 118 } 119 } 120 } 121 return pp; 122 } 123 124 public static String[] toReversePolishNotation(String input) { 125 input = input.replaceAll(" ", "").replaceAll("=", "");// 去除表达式中的空格和=号 126 String[] newArr = input.replaceAll("([\\+\\-\\×\\÷\\(\\)])", " $1 ").trim().replaceAll(" ", " ").split(" "); // 先把字符串中的操作符左右加空格,再去除最左和最后的空格,在把由于括号和运算符连在一起造成2个空格换成一个空格,最后根据空格分开 127 ArrayList<String> output = new ArrayList<String>(); 128 Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); 129 for (String t : newArr) { 130 switch (t) { 131 case "(": 132 stack.push(t); 133 break; 134 case "+": 135 if (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)) { 136 do { 137 if (stack.peek().equals("(")) { 138 break; 139 } 140 output.add(stack.pop()); 141 142 } while (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)); 143 stack.push(t); 144 } else { 145 stack.push(t); 146 } 147 break; 148 case "-": 149 if (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)) { 150 do { 151 if (stack.peek().equals("(")) { 152 break; 153 } 154 output.add(stack.pop()); 155 } while (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)); 156 stack.push(t); 157 } else { 158 stack.push(t); 159 } 160 break; 161 case "×": 162 if (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)) { 163 do { 164 if (stack.peek().equals("(")) { 165 break; 166 } 167 output.add(stack.pop()); 168 } while (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)); 169 stack.push(t); 170 } else { 171 stack.push(t); 172 } 173 break; 174 case "÷": 175 if (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)) { 176 do { 177 if (stack.peek().equals("(")) { 178 break; 179 } 180 output.add(stack.pop()); 181 } while (!stack.empty() && operatorLevel.get(stack.peek()) >= operatorLevel.get(t)); 182 stack.push(t); 183 } else { 184 stack.push(t); 185 } 186 break; 187 case ")": 188 while (!stack.isEmpty() && !stack.peek().equals("(")) { 189 output.add(stack.pop()); 190 } 191 stack.pop(); 192 break; 193 default: 194 output.add(t); 195 break; 196 } 197 // System.out.println(t); 198 // System.out.println("stack="+stack); 199 // System.out.println("output="+output); 200 } 201 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { 202 output.add(stack.pop()); 203 } 204 String[] result = new String[output.size()]; 205 output.toArray(result); 206 return result; 207 } 208 209 public static int gcd(int x, int y) { // 这个是运用辗转相除法求 两个数的 最大公约数 看不懂可以百度 // 下 210 if (y == 0) 211 return x; 212 else 213 return gcd(y, x % y); 214 } 215 216 }
TestFractory.class
1 package com.jmu.util; 2 3 public class TestFractory { 4 5 /** 6 * 一元运算符:分数四则运算 7 * @param args 8 */ 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 11 System.out.println(fracAdd(4,5,1,5)); 12 System.out.println(fracSub(1,5,-7,20)); 13 System.out.println(fracMul(-6,5,7,-5)); 14 System.out.println(fracDiv(0,5,0,20)); 15 } 16 //分数相加 17 static String fracAdd(int first_numerator,int first_denominator,int second_numrator,int second_denominator){ 18 //以下代码能够在控制台上显示结果 19 //需要调用求最大公约数的函数 20 //需要调用求最小公倍数的函数 21 if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator!=0) { 22 return second_numrator+"/"+second_denominator; 23 }else if (first_numerator!=0 && second_numrator==0) { 24 return first_numerator+"/"+first_denominator; 25 }else if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator==0) { 26 return "0"; 27 } 28 int a = lcm(first_denominator,second_denominator); 29 int numerator,denominator; 30 numerator = first_numerator * ( a / first_denominator) + second_numrator * (a / second_denominator); 31 denominator = a; 32 int b = gcd(numerator,denominator); 33 numerator = numerator / b; 34 denominator = denominator / b; 35 //System.out.println(numerator+"/"+denominator); 36 return numerator+"/"+denominator; 37 } 38 //分数相减 39 static String fracSub(int first_numerator,int first_denominator,int second_numrator,int second_denominator){ 40 if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator!=0) { 41 return second_numrator+"/"+second_denominator; 42 }else if (first_numerator!=0 && second_numrator==0) { 43 return first_numerator+"/"+first_denominator; 44 }else if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator==0) { 45 return "0"; 46 } 47 int a = lcm(first_denominator,second_denominator); 48 int numerator,denominator; 49 numerator = first_numerator * ( a / first_denominator) - second_numrator * (a / second_denominator); 50 denominator = a; 51 int b = gcd(numerator,denominator); 52 numerator = numerator / b; 53 denominator = denominator / b; 54 //System.out.println(numerator+"/"+denominator); 55 return numerator+"/"+denominator; 56 } 57 //分数相乘 58 static String fracMul(int first_numerator,int first_denominator,int second_numrator,int second_denominator){ 59 if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator!=0) { 60 return "0"; 61 }else if (first_numerator!=0 && second_numrator==0) { 62 return "0"; 63 }else if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator==0) { 64 return "0"; 65 } 66 int numerator,denominator; 67 numerator = first_numerator * second_numrator; 68 denominator = first_denominator * second_denominator; 69 int b = gcd(numerator,denominator); 70 numerator = numerator / b; 71 denominator = denominator / b; 72 if ((numerator>0&&denominator>0)||(numerator<0&&denominator<0)) { 73 return Math.abs(numerator)+"/"+Math.abs(denominator); 74 }else{ 75 return "-"+Math.abs(numerator)+"/"+Math.abs(denominator); 76 } 77 //return numerator+"/"+denominator; 78 } 79 //分数相除 80 static String fracDiv(int first_numerator,int first_denominator,int second_numrator,int second_denominator){ 81 if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator!=0) { 82 return "0"; 83 }else if (first_numerator!=0 && second_numrator==0) { 84 return "0"; 85 }else if (first_numerator==0 && second_numrator==0) { 86 return "0"; 87 } 88 int numerator,denominator; 89 numerator = first_numerator * second_denominator; 90 denominator = first_denominator * second_numrator; 91 int b = gcd(numerator,denominator); 92 numerator = numerator / b; 93 denominator = denominator / b; 94 //System.out.println(numerator+"/"+denominator); 95 if ((numerator>0&&denominator>0)||(numerator<0&&denominator<0)) { 96 return Math.abs(numerator)+"/"+Math.abs(denominator); 97 }else{ 98 return "-"+Math.abs(numerator)+"/"+Math.abs(denominator); 99 } 100 //return numerator+"/"+denominator; 101 } 102 //判断数的大小 103 static int min(int m,int n){ 104 if(m > n){ 105 return n; 106 } 107 else{ 108 return m; 109 } 110 } 111 //最大公约数 112 static int gcd(int m,int n){ 113 min(m,n); 114 int s = 1; 115 for(int i = 2;i <= min(m,n);i ++){ 116 for(int j = 2;j <= i;j++){ 117 if(m % j == 0 && n % j == 0){ 118 m = m / j; 119 n = n / j; 120 s = s * j; 121 } 122 } 123 } 124 return s; 125 126 } 127 //最小公倍数 128 static int lcm(int m,int n){ 129 int b = gcd(m,n) * (m / gcd(m,n)) * (n / gcd(m,n)); 130 return b; 131 132 } 133 }
测试运行
输入:-n 10 -r 10 -o Exercise.txt
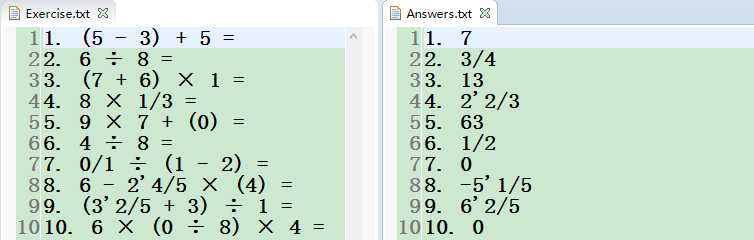
输出:Exercise.txt和Answers.txt文件
输入:-e Exercise.txt -a Answers.txt -o Grade.txt

输出:Grade.txt文件

展示PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | estimated time | Actual time |
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 10 |
| · Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 20 | 30 |
| · Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 100 |
| · Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 20 | 10 |
| · Design Review | 设计复审 | 10 | 20 |
| · Coding Standard | 代码规范 | 10 | 15 |
| · Design | 具体设计 | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding | 具体编码 | 300 | 420 |
| · Code Review | 代码复审 | 60 | 30 |
| · Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 10 | 20 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 120 |
| · | 测试报告 | 10 | 20 |
| · | 计算工作量 | ||
| · | 并提出过程改进计划 | ||
小结
带分数的四则运算程序实现起来还是挺麻烦的,首先要先生成四则运算的表达式另外可以在生成的过程中加入多个括号并且可以嵌套(目前只能实现一个括号)。计算过程中甲将表达式转换成逆波兰并进行运算,但是考虑到带有分数,所有在进行两个数的计算时,先转换成分数再进行加减乘除。后面的表达式的查重还没有什么好的方法,大家有想法的可以下面留言。
标签:gcd context 学习 ++ ring not round 1.5 一起
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/huangjinyong/p/7561067.html