标签:struct init cal 它的 stat data turn 释放 任务
依稀记得第一次接触Hook的概念是在周伟民先生的书中-><<多任务下的数据结构与算法>>,当时觉得Hook很奇妙,有机会要学习到,正好近段日子找来了MiniHook,就一起分享一下。
本篇文章是在x64下测试与分析jmp+offset类型的Hook,并且逆推测出热补丁的简单用法,MinHook它的中心就是覆盖重写并且可以复原。知道大概的思路后后让我们先来具体的实现MinHook再去做测试。
首先是堆的申请(申请PAGE_SIZE大小自动生长的堆),以下是实现与卸载
1 NTSTATUS WINAPI Initialize(VOID)
2 {
3 NTSTATUS Status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
4
5 EnterSpinLock();
6
7 if (__HeapHandle == NULL)
8 {
9 __HeapHandle = HeapCreate(0,//申请堆栈
10 0, //提交 PAGE_SIZE
11 0); //If dwMaximumSize is 0, the heap can grow in size.自动增长
12 if (__HeapHandle != NULL)
13 {
14 //没有实现
15 }
16 else
17 {
18 Status = STATUS_MEMORY_NOT_ALLOCATED;
19 }
20 }
21 else
22 {
23 Status = STATUS_ADDRESS_ALREADY_EXISTS;
24 }
25
26 LeaveSpinLock();
27
28 return Status;
29 }
30
31 NTSTATUS WINAPI Uninitialize(VOID)
32 {
33 NTSTATUS Status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
34
35 return Status;
36 }
第一幕CreateHook
CreateHook 第一步:判断内存是否申请好了,是否可执行,判断是否已经Hook过了,如果已经Hook过,当让他返回其所在位置,因为此时他的地址位置已经可以用来启动Hoook,如下代码详解
1 UINT FindHookEntry(LPVOID FunctionAddress)
2 {
3 UINT i;
4 for (i = 0; i < __Hooks.Length; ++i)
5 {
6 if ((ULONG_PTR)FunctionAddress == (ULONG_PTR)__Hooks.Items[i].TargetFunctionAddress)
7 return i;
8 }
9 return STATUS_NOT_FOUND;
10 }
CreateHook 第二步:进行Hook,在这里用到TRAMPOLINE结构体,我称之为跳板结构体,作为数据的中间传输过渡,TRAMPOLINE中几个注意的成员是1.Relay:在x64下Fake函数到原函数的中转站(x86用不到),2.OldIPs:原函数地址的偏移字节的保存3.NewIPs: 已经写入FakeFunctionAddress函数的字节数 4.MemorySlot:32字节原函数地址的前7个字节和跳转指令后的字节 5.PachAbove:热补丁
1 typedef struct _TRAMPOLINE
2 {
3 LPVOID TargetFunctionAddress; // [In] Address of the target function.
4 LPVOID FakeFunctionAddress; // [In] Address of the detour function.
5 LPVOID MemorySlot; // MemorySlot 32字节原函数地址的前五个字节和跳转指令后的字节
6
7 #if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
8 LPVOID Relay; // [Out] Address of the relay function.
9 #endif
10 BOOL PatchAbove; // [Out] Should use the hot patch area? //Patch --->热补丁哦 //0xA 0xB
11 UINT IP; // [Out] Number of the instruction boundaries.
12 UINT8 OldIPs[8]; // [Out] Instruction boundaries of the target function.
13 UINT8 NewIPs[8]; // [Out] Instruction boundaries of the trampoline function.
14 } TRAMPOLINE, *PTRAMPOLINE;
CreateHook 第三步: 分配一块内存用来保存Trampoline里的MemorySlot数据 ,以下是MemorySlot结构体定义(MemorySlot内存构建放到最后的代码链接中):
1 #define MEMORY_BLOCK_SIZE 0x1000
2 #if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
3 #define MEMORY_SLOT_SIZE 64
4 #else
5 #define MEMORY_SLOT_SIZE 32
6 #endif
7
8 // Max range for seeking a memory block. (= 1024MB)
9 #define MAX_MEMORY_RANGE 0x40000000
10
11 typedef struct _MEMORY_SLOT
12 {
13 union
14 {
15 struct _MEMORY_SLOT *Flink;//下一指针
16 UINT8 BufferData[MEMORY_SLOT_SIZE];
17 };
18 } MEMORY_SLOT, *PMEMORY_SLOT; //32字节
19
20 typedef struct _MEMORY_BLOCK
21 {
22 _MEMORY_BLOCK* Flink;
23 PMEMORY_SLOT FreeMeorySlotHead; // First element of the free slot list.空闲插槽列表的第一个元素。
24 UINT UsedCount;
25 } MEMORY_BLOCK, *PMEMORY_BLOCK; //12字节
CreateHook 第四步:CreateTrampoline
Hook的Target我们这里先使用MessageBoxW,作为一个详细的jmp跳转流程解释,然后我写了几个汇编程序去进行其他E8,Call等指令的跳转实现,不过它是怎么跳转的我会在下面跳转的时候贴出来,首先来玩X64下的MessageBoxW,
64位 MessageBox 00007FF97B4485A0 48 83 EC 38 sub rsp,38h 00007FF97B4485A4 45 33 DB xor r11d,r11d 00007FF97B4485A7 44 39 1D 7A 33 03 00 cmp dword ptr [gfEMIEnable (07FF97B47B928h)],r11d 00007FF97B4485AE 74 2E je MessageBoxW+3Eh (07FF97B4485DEh) 00007FF97B4485B0 65 48 8B 04 25 30 00 00 00 mov rax,qword ptr gs:[30h] 00007FF97B4485B9 4C 8B 50 48 mov r10,qword ptr [rax+48h] 00007FF97B4485BD 33 C0 xor eax,eax 00007FF97B4485BF F0 4C 0F B1 15 98 44 03 00 lock cmpxchg qword ptr [gdwEMIThreadID (07FF97B47CA60h)],r10 00007FF97B4485C8 4C 8B 15 99 44 03 00 mov r10,qword ptr [gpReturnAddr (07FF97B47CA68h)] 00007FF97B4485CF 41 8D 43 01 lea eax,[r11+1] 00007FF97B4485D3 4C 0F 44 D0 cmove r10,rax 00007FF97B4485D7 4C 89 15 8A 44 03 00 mov qword ptr [gpReturnAddr (07FF97B47CA68h)],r10 00007FF97B4485DE 83 4C 24 28 FF or dword ptr [rsp+28h],0FFFFFFFFh 00007FF97B4485E3 66 44 89 5C 24 20 mov word ptr [rsp+20h],r11w 00007FF97B4485E9 E8 A2 FE FF FF call MessageBoxTimeoutW (07FF97B448490h) 00007FF97B4485EE 48 83 C4 38 add rsp,38h
前面讲过我们是通过跳转加指令形式跳转到我们需要到的地址处,上面代码注释中我们了解到OldPos与NewPos是在MemorySlot创建过程对原函数地址的偏移字节的保存和已经写入FakeFunctionAddress函数的字节数,如下
1 ULONG_PTR OldInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress + OldPos; 2 ULONG_PTR NewInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos; 3 //数据 4 //OldPos是指的指令的偏移字节 即5个字节中的第2345位.OldInstance地址 5 //指令长度
了解到一些后,我们就应该去真正的对MemorySlot去构建,他的构建用了一个超级大的do-While()循坏(因为实践了好几种跳转指令,心累),x86下的MessageBoxW跳转在5字节处,所以为了之后的恢复,我们需要把7字节的内容做一个保存,这就是所谓的OriginalDataBackup数组的作用->用来恢复也就是解除Hook,后面会逐步解析他的作用和位置,我们这里先记住即可
MemorySlot开始申请32字节的长度,,我们利用反汇编引擎HDE计算出MessageBoxW函数基地址,从上面给出的MessageBoxW的地址内容中,我们可以看到到达5字节的加法是先加4个字节到下一地址,然后加3到跳转位置,记录在OldPos,NewPos中
CopyCodeLength = HDE_DISASM((LPVOID)OldInstance, &hde);
if (hde.flags & F_ERROR)
{
return FALSE;
}
CopyCodeData = (LPVOID)OldInstance;
.....
Trampoline->OldIPs[Trampoline->IP] = OldPos;
Trampoline->NewIPs[Trampoline->IP] = NewPos;
Trampoline->IP++;
到达7字节了,我们就可以去做跳回MessageBoxW基地址加5字节偏移跳转指令了
1if (OldPos >= sizeof(JMP_REL))
{
// The trampoline function is long enough.
#if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
//OldInstance = 00007FF97B4485A7;
jmp.Address = OldInstance;
#else
//OldInstance = 74CA8B85
//目标 = 源 + Offset + 5
//Offset = 目标 - (源 + 5)
jmp.Operand = (UINT32)(OldInstance - (NewInstance + sizeof(jmp))); //计算跳转到目标的偏移
#endif
CopyData = &jmp;
CopyDataLength = sizeof(jmp);
IsLoop = TRUE;
}
1 //这里是热补丁的判断 是否有足够的位置长跳转
2 if (OldPos < sizeof(JMP_REL)
3 && !IsCodePadding((LPBYTE)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress + OldPos, sizeof(JMP_REL) - OldPos))
4 {
5
6 // Is there enough place for a short jump?
7 //没有有足够的位置长跳转,那是否有足够的位置短跳转?
8 if (OldPos < sizeof(JMP_REL_SHORT)
9 && !IsCodePadding((LPBYTE)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress + OldPos, sizeof(JMP_REL_SHORT) - OldPos))
10 {
11 return FALSE;
12 }
13 //只能写短跳转,使用热补丁
14 // Can we place the long jump above the function?
15 //热补丁:目标地址之前地址是否可执行?
16 if (!SeIsExecutableAddress((LPBYTE)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress - sizeof(JMP_REL)))
17 return FALSE;
18 //目标地址之前是否是可被覆盖的空白
19 if (!IsCodePadding((LPBYTE)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress - sizeof(JMP_REL), sizeof(JMP_REL)))
20 return FALSE;
21 //标志可以热补丁
22 Trampoline->PatchAbove = TRUE;
做了这么多工作,无非是为了MemorySlot里有数据前7个字节和跳转回MessageBoxW基地址+5字节的的偏移,构造好后,我们的TRAPOLINE结构也就完成
CreateHook第五步:添加Hook信息了(TRAMPLIONE结构体过渡),我们需要再去创建一个HookEntry的结构体去完成接收信息
1 // Hook information.
2 typedef struct _HOOK_ENTRY
3 {
4 LPVOID TargetFunctionAddress; //目标地址
5 LPVOID FakeFunctionAddress; //Fake地址即覆盖地址
6 LPVOID TrampolineMemorySlot; // Address of the trampoline function.
7 UINT8 OriginalDataBackup[8]; // Original prologue of the target function.目标功能的原始序幕- //恢复Hook使用的存放原先数据
8
9 UINT8 PatchAbove : 1; // Uses the hot patch area. 备份原函数的5字节,重要!!!
10 UINT8 IsEnabled : 1; // Enabled.启用或者关闭
11 UINT8 queueEnable : 1; // Queued for enabling/disabling when != isEnabled.
12
13 UINT IP : 4; // Count of the instruction boundaries.索引 想到汇编的IP就很明白了
14 UINT8 OldIPs[8]; // Instruction boundaries of the target function.原地址的字节变化就靠它了
15 UINT8 NewIPs[8]; // Instruction boundaries of the trampoline function 用在后续解释的MemorySlot中
16 } HOOK_ENTRY, *PHOOK_ENTRY; //44字节
17
18
19 typedef struct _HOOK_INFORMATION_
20 {
21 PHOOK_ENTRY Items; // Data heap
22 UINT MaximumLength; // Size of allocated data heap, items
23 UINT Length; // Actual number of data items
24 }HOOK_INFORMATION,*PHOOK_INFORMATION;
当有了这个结构体后就可以去CreateHook了,下面是构建过程:
1 if (CreateTrampoline(&Tl))
2 {
3 PHOOK_ENTRY HookEntry = AddHookEntry(); //填充一个HookInfo信息
4 if (HookEntry != NULL)
5 {
6 HookEntry->TargetFunctionAddress = Tl.TargetFunctionAddress;
7 #if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
8 HookEntry->FakeFunctionAddress = Tl.pRelay;//跳转在trampoline
9 #else
10 HookEntry->FakeFunctionAddress = Tl.FakeFunctionAddress;
11 #endif
12 HookEntry->TrampolineMemorySlot = Tl.MemorySlot;
13 HookEntry->PatchAbove = Tl.PatchAbove
14 HookEntry->IsEnabled = FALSE;
15 //HookEntry->QueueEnable = FALSE;
16 HookEntry->IP = Tl.IP;
17
18 memcpy(HookEntry->OldIPs, Tl.OldIPs, ARRAYSIZE(Tl.OldIPs));
19 memcpy(HookEntry->NewIPs, Tl.NewIPs, ARRAYSIZE(Tl.NewIPs));
20
21 // Back up the target function.
22
23 if (Tl.PatchAbove)//这就是热补丁
24 {
25 memcpy(
26 HookEntry->OriginalDataBackup,
27 (LPBYTE)TargetFunctionAddress - sizeof(JMP_REL),
28 sizeof(JMP_REL) + sizeof(JMP_REL_SHORT));
29 }
30 else
31 { //存储源函数的数据内容
32 memcpy(HookEntry->OriginalDataBackup, TargetFunctionAddress, sizeof(JMP_REL));
33 }
34 if (OriginalWhitelist != NULL)//白名单,用来恢复
35 {
36 *OriginalWhitelist = HookEntry->TrampolineMemorySlot;
37 }
到这里为止终于是创建了Hook
第二幕 EnableHook
顾名思义就是启动Hook,显而易见得知它的作用无非就是覆盖原函数我们记录的那7字节,如下:
1 //SHELLCODE 2 PJMP_REL jmp = (PJMP_REL)PatchData; 3 jmp->Opcode = 0xE9;//跳转 4 jmp->Operand = (UINT32)((LPBYTE)HookEntry->FakeFunctionAddress - (PatchData + sizeof(JMP_REL))); 5
当需要解除Hook时候我们就可以用到在前面说过的OriginalDataBackup去恢复原函数,或者直接调用MemorySlot中记录下的原始序幕
1 else
2 {
3 memcpy(PatchData, HookEntry->OriginalDataBackup, sizeof(JMP_REL));
4 }
第三幕 MessageBoxW测试
1 if (CreateHook(&MessageBoxW, &FakeMessageBox,
2 reinterpret_cast<LPVOID*>(&__OriginalMessageBoxW)) != STATUS_SUCCESS)//告知要hook成什么样子
3 {
4 return;
5 }
6
7 MessageBoxW(0, L"MessageBoxW", L"MessageBoxW", 0);//没有Hook还是原先,不要也行
8 if (EnableHook(MessageBoxW) != STATUS_SUCCESS)
9 {
10 printf("EnableHook is wrong\r\n");
11 return;
12 }
13 MessageBoxW(NULL, L"CreateHook()", L"CreateHook()", 0);//启动Hook后,现在是FakeHOOK
14
15 printf("Input AnyKey To Exit\r\n");
16 getchar();
17
18 Uninitialize();//返回释放
19 }
20
21 int WINAPI FakeMessageBox(
22 _In_opt_ HWND DialogHwnd,
23 _In_opt_ WCHAR* DialogText,
24 _In_opt_ WCHAR* DialogCaption,
25 _In_ UINT Type
26 )
27 {
28 __OriginalMessageBoxW(DialogHwnd, L"FakeMessageBox", L"FakeMessageBox", Type);
29 return 0;
30 }
编译运行后出结果啦,先是原先的MessageBoxW:
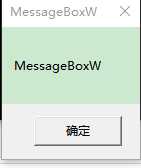
这是成功Hook后的:
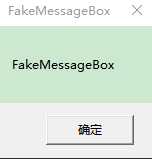
一切顺利,没有白费功夫,下面是我对EB,call,热补丁的汇编源码,我们仿照MessageBoxW的形式在test.cpp中定义函数指针,与Fake函数的输出形式。
在这里花费了功夫探索出了热补丁的简单定义是申请5字节空的内存然后 mov edi,edi,能应用正确,汇编代码如下
.DATA
MessageBoxW dq 0
.CODE
Asm_OnInitMember PROC
mov qword ptr[rsp+8h],rcx
push rbp
push rdi
sub rsp,28h
mov rax,qword ptr[rsp+28h+8h+8h+8h]
mov MessageBoxW,rax
add rsp,28h
pop rdi
pop rbp
ret
Asm_OnInitMember ENDP
Asm_1 PROC
mov qword ptr[rsp+8h],rcx
push rbp
push rdi
sub rsp,28h
xor rbx,rbx
;00007FF77A8012BC E9 7A 0B 00 00 jmp Asm_4 (07FF77A801E3Bh)
mov rax,qword ptr[rsp+28h+8h+8h+8h]
mov ebx,dword ptr[rax+1]
add rax,rbx
add rax,5
add rsp,28h
pop rdi
pop rbp
ret
Asm_1 ENDP
Asm_3 PROC
jmp Label1
Label1:
jmp Label2
Label2:
mov eax,-3
ret
Asm_3 ENDP
Asm_4 PROC
call Label0
jmp Exit;
Label0:
mov rcx,0;
call Label1; //Call
db ‘H‘
db 0
db ‘e‘
db 0
db ‘l‘
db 0
db ‘l‘
db 0
db ‘o‘
db 0
db ‘S‘
db 0
db ‘u‘
db 0
db ‘b‘
db 0
db ‘_‘
db 0
db ‘4‘
db 0
db 0
db 0
Label1:
pop rdx
call Label2;
db ‘H‘
db 0
db ‘e‘
db 0
db ‘l‘
db 0
db ‘l‘
db 0
db ‘o‘
db 0
db ‘S‘
db 0
db ‘u‘
db 0
db ‘b‘
db 0
db ‘_‘
db 0
db ‘4‘
db 0
db 0
db 0
Label2:
pop r8
mov r9,0
call MessageBoxW
ret
Exit:
ret
Asm_4 ENDP
Asm_10 PROC
db 0CCh
db 0CCh
db 0CCh
db 0CCh
db 0CCh
mov edi,edi
ret
Asm_10 ENDP
END
1 //热补丁测试
typedef void(*LPFN_SUB_10)();
void FakeSub_10(); //热补丁
LPFN_SUB_10 __OriginalSub_10 = NULL;
2
PVOID v10 = Asm_1(Asm_10);
3
4 if (SeCreateHook((PVOID)((ULONG_PTR)v10 + 5), &FakeSub_10,
5 reinterpret_cast<LPVOID*>(&__OriginalSub_10)) != STATUS_SUCCESS)
6 {
7 return;
8 }
9 //对于热补丁函数调用
10 ((LPFN_SUB_10)(((ULONG_PTR)v10 + 5)))();
11 if (SeEnableHook(ALL_HOOKS) != STATUS_SUCCESS)
12 {
13 printf("SeEnableHook() Error\r\n");
14 return;
15 }
16 ((LPFN_SUB_10)(((ULONG_PTR)v10 + 5)))();
E9的测试只需要自写一个函数调用测试调用即可,如下面这样就行了然后在仿照上面自行测试即可
1 1 //E9指令,这样就行了
2 2
3 3 void Sub_2()
4 4 {
5 5 printf("Sub_2\n\r");
6 6 }
下面是所有的正确输出结果:

好了,x86下的MiniHook终于是测试完了,写了一遍后又是更懂了,如果有什么差错,望大家纠正
[原创]MinHook测试与分析(x64下 E9,EB,CALL指令测试,且逆推测试微软热补丁)
标签:struct init cal 它的 stat data turn 释放 任务
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/L-Sunny/p/7588202.html