标签:i+1 question another direct ber pos complete rem ssi
树在数据结构中占有非常重要的地位。本文从树的基本概念入手,给出完美(Perfect)二叉树,完全(Complete)二叉树和完满(Full)二叉树的区别。如果学习过二叉树,但是对这三种二叉树并没有深入的理解,或者完全被国产数据结构教科书所误导(只听说过满二叉树和完全二叉树)的朋友不妨花点时间耐着性子将本文仔细阅读N(>=1)遍。
1. 树(Tree)的基本概念
1.1 树的定义
A tree is a (possibly non-linear) data structure made up of nodes or vertices and edges without having any cycle. The tree with no nodes is called the null or empty tree. A tree that is not empty consists of a root node and potentially many levels of additional nodes that form a hierarchy.
树是由结点或顶点和边组成的(可能是非线性的)且不存在着任何环的一种数据结构。没有结点的树称为空(null或empty)树。一棵非空的树包括一个根结点,还(很可能)有多个附加结点,所有结点构成一个多级分层结构。
[注:本文将node一律译为"结点"(而不是"节点"),因为joint或connection是节点,而node是结点。关于"结点"与"节点"请自行搜索浙江大学陈水福教授的文章--"360度"解读如何正确应用"结点"与"节点"]
例如:

A simple unordered tree; in this diagram, the node labeled 7 has two children, labeled 2 and 6, and one parent, labeled 2. The root node, at the top, has no parent. 上图是一棵无序的树示例。在上图中,标号为7的结点有两个孩子,分别是标号为2和6的结点。
根结点,在最顶端,它没有双亲。
1.2 树的基本术语
| Root | The top node in a tree. | 根 | 树的顶端结点 |
| Child | A node directly connected to another node when moving away from the Root. | 孩子 | 当远离根(Root)的时候,直接连接到另外一个结点的结点被称之为孩子(Child); |
| Parent | The converse notion of a child. | 双亲 | 相应地,另外一个结点称为孩子(child)的双亲(parent)。 |
| Siblings | A group of nodes with the same parent. | 兄弟 | 具有同一个双亲(Parent)的孩子(Child)之间互称为兄弟(Sibling)。 |
| Ancestor | A node reachable by repeated proceeding from child to parent. | 祖先 | 结点的祖先(Ancestor)是从根(Root)到该结点所经分支(Branch)上的所有结点。 |
| Descendant | A node reachable by repeated proceeding from parent to child. | 子孙 | 反之,以某结点为根的子树中的任一结点都称为该结点的子孙(Ancestor)。 |
| Leaf | A node with no children. | 叶子(终端结点) | 没有孩子的结点(也就是度为0的结点)称为叶子(Leaf)或终端结点。 |
| Branch | A node with at least one child. | 分支(非终端结点) | 至少有一个孩子的结点称为分支(Branch)或非终端结点。 |
| Degree | The number of sub trees of a node. | 度 | 结点所拥有的子树个数称为结点的度(Degree)。 |
| Edge | The connection between one node and another. | 边 | 一个结点和另一个结点之间的连接被称之为边(Edge)。 |
| Path | A sequence of nodes and edges connecting a node with a descendant. | 路径 | 连接结点和其后代的结点之间的(结点,边)的序列。 |
| Level | The level of a node is defined by 0 + (the number of connections between the node and the root). | 层次 | 结点的层次(Level)从根(Root)开始定义起,根为第0层,根的孩子为第1层。以此类推,若某结点在第i层,那么其子树的根就在第i+1层。 |
| Height of node | The height of a node is the number of edges on the longest path between that node and a leaf. | 结点的高度 | 结点的高度是该结点和某个叶子之间存在的最长路径上的边的个数。 |
| Height of tree | The height of a tree is the height of its root node. | 树的高度 | 树的高度是其根结点的高度。 |
| Depth of node |
The depth of a node is the number of edges from the tree‘s root node to the node. | 结点的深度 | 结点的深度是从树的根结点到该结点的边的个数。(注:树的深度指的是树中结点的最大层次。) |
| Forest | A forest is a set of n ≥ 0 disjoint trees. | 森林 | 森林是n(>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合。 |
2 二叉树(Binary Tree)
2.1 什么是二叉树(Binary Tree)
每个结点至多拥有两棵子树(即二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点),并且,二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒。
2.2 二叉树的性质
(1)若二叉树的层次从0开始,则在二叉树的第i层至多有2^i个结点(i>=0)。
(2)高度为k的二叉树最多有2^(k+1) - 1个结点(k>=-1)。 (空树的高度为-1)
(3)对任何一棵二叉树,如果其叶子结点(度为0)数为m, 度为2的结点数为n, 则m = n + 1。
2.3 完美二叉树(Perfect Binary Tree)
A Perfect Binary Tree(PBT) is a tree with all leaf nodes at the same depth.
All internal nodes have degree 2.
一个深度为k(>=-1)且有2^(k+1) - 1个结点的二叉树称为完美二叉树。 (注: 国内的数据结构教材大多翻译为"满二叉树")
例如:
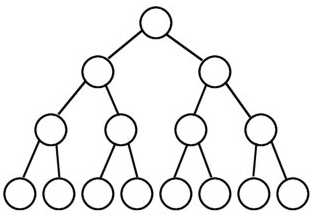
2.4 完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)
A Complete Binary Tree (CBT) is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
换句话说,完全二叉树从根结点到倒数第二层满足完美二叉树,最后一层可以不完全填充,其叶子结点都靠左对齐。
例如:
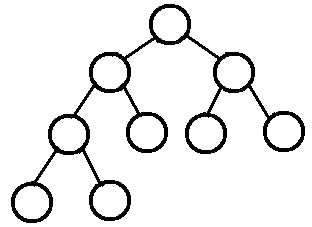
2.5 完满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)
A Full Binary Tree (FBT) is a tree in which every node other than the leaves has two children.
换句话说,所有非叶子结点的度都是2。(只要你有孩子,你就必然是有两个孩子。)
注:Full Binary Tree又叫做Strictly Binary Tree。
例如:
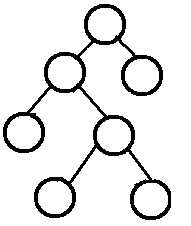
2.6 完美(Perfect)二叉树 v.s. 完全(Complete)二叉树
(1) 一棵完美(Perfect)二叉树看起来是这个样儿的, 【图2.6.1】
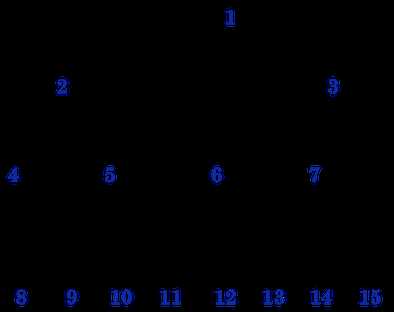
(2) 那么,将编号为15, 14, ..., 9的叶子结点从右到左依次拿掉或者拿掉部分,则是一棵完全(Complete)二叉树,
例如,将上图中的编号为15, 14, 13, 12, 11叶子结点都拿掉(从右到左的顺序), 【图2.6.2】
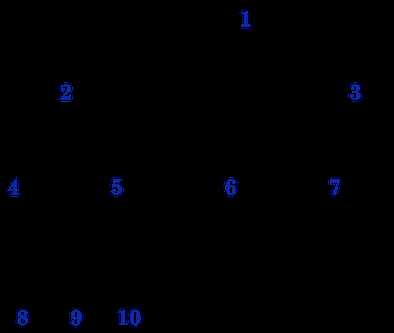
(3) 下图就不是一棵完全(Complete)二叉树,【图2.6.3】,
如果将编号11(K)结点从编号6(E)的左儿子位置移动到编号5(E)的右儿子位置,则变成一棵完全(Complete)二叉树。
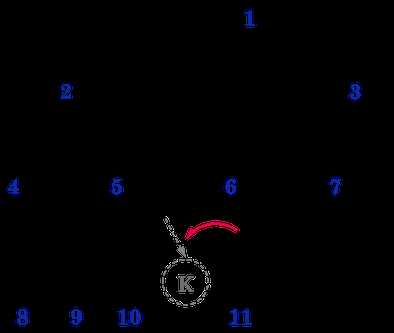
注: 图2.6.1, 2.6.2和2.6.3均来自:http://alrightchiu.github.io/SecondRound/binary-tree-introjian-jie.html, 但是,其将Full Binary Tree当做就是Perfect Binary Tree, 我认为是不正确的,特此说明。
特别说明: 其实,理解完全(Complete)二叉树可以借助于栈(stack)的思想。 例如,把图2.6.1中的完美(Perfect)二叉树的所有结点按照编号1, 2, 3, ..., 15依次入栈(push)。 那么,对栈的每一次出栈(pop)操作后,栈里保存的结点集对应到图2.6.1上去都是一棵完全(Complete)二叉树。
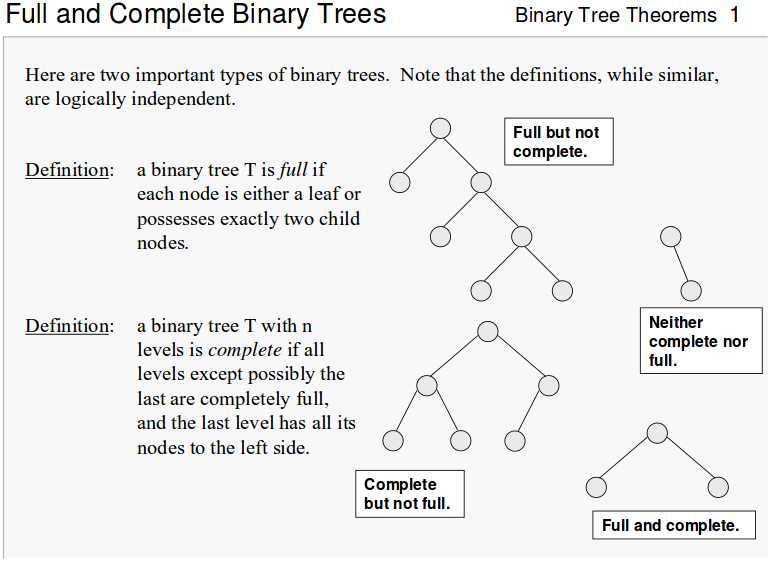
2.7 完全(Complete)二叉树 v.s. 完满(Full)二叉树
【截图来源:http://courses.cs.vt.edu/~cs3114/Fall09/wmcquain/Notes/T03a.BinaryTreeTheorems.pdf】
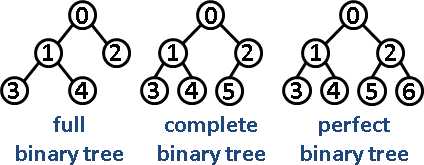
2.8 完满(Full)二叉树 v.s. 完全(Complete)二叉树 v.s. 完美(Perfect)二叉树
【图片来源: http://www.csie.ntnu.edu.tw/~u91029/BinaryTree2.png】
3. 总结 (下表参考来源)
| 完美二叉树 | Perfect Binary Tree |
Every node except the leaf nodes have two children and every level (last level too) is completely filled. 除了叶子结点之外的每一个结点都有两个孩子,每一层(当然包含最后一层)都被完全填充。 |
| 完全二叉树 | Complete Binary Tree | Every level except the last level is completely filled and all the nodes are left justified. 除了最后一层之外的其他每一层都被完全填充,并且所有结点都保持向左对齐。 |
| 完满二叉树 | Full/Strictly Binary Tree | Every node except the leaf nodes have two children. 除了叶子结点之外的每一个结点都有两个孩子结点。 |
标签:i+1 question another direct ber pos complete rem ssi
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/joyZzzzz/p/7588984.html