标签:map对象 object 获取 ash new 一个 线程 hashcode 有一个
在一般的网站开发中,基于Java的Web 框架都使用了ThreadLocal来存储一些全局的参数,在拦截器\Filter中设置变量,让变量可以在任意地方被获取。
一早就了解到里面有用到WeakReference(弱引用),但对弱引用仅限于一种懵懂的概念,并且认为只要GC,弱引用的对象就被回收掉了,实际情况呢?
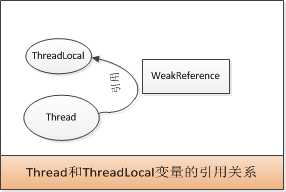
Thread对象有一个变量名为 threadLocals 的 ThreadLocalMap对象,这个类和Map类似,里面定义了一个Entry,不过这个Entry对象弱引用了ThreadLocal
/** * The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using * its main ref field as the key (which is always a * ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get() * == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the * entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to * as "stale entries" in the code that follows. */ static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) { super(k); //调用父类构造函数,设置Reference的referent属性 value = v; } } /** * Set the value associated with key. * * @param key the thread local object * @param value the value to be set */ private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) { // We don‘t use a fast path as with get() because it is at // least as common to use set() to create new entries as // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast // path would fail more often than not. Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { ThreadLocal k = e.get(); 获取Reference的referent属性 if (k == key) { e.value = value; return; } if (k == null) { replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return; } } tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); int sz = ++size; if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash(); }
一直以来,我把WeakReference理解成:弱引用的对象一定会在下次GC时回收掉,按此推断,ThreadLocal变量是不太安全的,因为用着用着就可能被GC掉了。
但是如果ThreadLocal有这么严重的问题,谁会去用呢!
实际上对象B弱引用了A,如果A除了B以外,没有其他引用(强、软引用)时,才会把A GC调,这也是为什么ThreadLocal实际上是一个安全的操作。
Thread.threadLocals 是一个Map,每个Entry都弱引用了ThreadLocal对象
因此Thread.threadLocals对每个ThreadLocal对象都是弱引用关系
调用ThreadLocal.get()方法
/** * Returns the value in the current thread‘s copy of this * thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the * current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned * by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method. * * @return the current thread‘s value of this thread-local */ public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); 可以看到get实际上是获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) return (T)e.value; } return setInitialValue(); } /** * Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in * InheritableThreadLocal. * * @param t the current thread * @return the map */ ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; }
可以理解为一个ThreadLocal实例,在多个线程都存在副本,并且在不同线程设置的值,都不会影响到其他线程,因为ThreadLocal实例是存储在当前Thread对象上的
ThreadLocal被设置为null时,由于Thread对象只是弱引用了ThreadLocal,除非ThreadLocal对象还被其他实例引用,他就会被回收掉
以下情况ThreadLocal遍历是永远不会回收的
public class FlagContext { /** * ThreadLocal变量 */ private final static ThreadLocal<Boolean> tbFlag = new ThreadLocal<Boolean>(); }
FlagContext的静态变量引用了ThreadLocal实例tbFlag,tbFlag永远不会为空,因此,这种情况下,tbFlag对应的值,只会在线程生命周期结束,或调用tbFlag.remove()才会被回收
标签:map对象 object 获取 ash new 一个 线程 hashcode 有一个
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/windliu/p/7623369.html