标签:log group ble front fqdn 语法 min depends nan
上一篇大概介绍了怎么用Terraform在Azure上创建一个虚拟机,接下来,我们会用Terraform来做一些更复杂的工作。
在开始工作前,我们还是要先解释下会用到的几个命令。
因为我用的是Win10系统,所以下载的Terraform下载后就是一个执行文件,可以放在任何一个目录下执行。在最开始的时候,记得先要执行以下命令:
terraform init
这条命令会初始化terraform的执行目录。如果查看隐藏目录的话,会看见这条命令创建一了一个隐藏目录”.terraform”,并在这个目录里下载了两个插件。
Terraform可以使用不同的工作区域来区分不同的执行环境。命令是:
terraform workspace
可以在后面再加上new,delete,show,list,select参数来创建删除和管理工作区域。
还有两个很重要的命令是terraform plan和terraform apply
terraform plan会解析配置脚本,并比较现有资源和配置脚本之间的差异。如果用了 -out 参数,可以输出一个执行脚本。如果配置脚本的语法或参数错误,plan命令会返回相应的错误信息。换句话说,plan没有报错,说明至少脚本的语法是正确的。
terraform apply,当plan没有报错后,就可以执行apply命令,它会真正在Azure上创建脚本所指定的资源。这个阶段也可能会报错,例如,资源已经存在,或者资源不足,护着指定的资源不存在。
要注意的是,在没有特殊指定时,plan和apply会执行当前目录下的所有配置脚本。所以为什么会有workspace的设置,这就可以理解了。不过按我的理解,多建几个目录会是更简单和可靠的方法。
如果要删除资源,也是有命令可以用的。。。。。。
terraform plan -destroy 和 terraform destroy
大概了解了terraform的主要命令后,要开始做一些更复杂的事情了。这次我打算建的一个简单的应用环境,负载均衡后带两台虚拟机,对外开放80端口,包括健康检查,独立的网络。依然放在上一篇文档所建立的资源组lyq-testterraform-rg里。
配置脚本如下:经过上一篇文档,我就不介绍每一段是干什么的了。脚本还是很容易读懂的。
provider "azurerm" {
subscription_id = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
client_id = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
client_secret = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
tenant_id = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
environment = "china"
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
name = "${var.resource_group}"
location = "${var.location}"
}
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "stor" {
name = "${var.dns_name}stor"
location = "${var.location}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
account_type = "Standard_GRS"
}
resource "azurerm_availability_set" "avset" {
name = "${var.dns_name}avset"
location = "${var.location}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
platform_fault_domain_count = 2
platform_update_domain_count = 2
managed = true
}
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "lbpip" {
name = "${var.rg_prefix}-ip"
location = "${var.location}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
public_ip_address_allocation = "dynamic"
domain_name_label = "${var.lb_ip_dns_name}"
}
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" {
name = "${var.virtual_network_name}"
location = "${var.location}"
address_space = ["${var.address_space}"]
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
}
resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet" {
name = "${var.rg_prefix}subnet"
virtual_network_name = "${azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.name}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
address_prefix = "${var.subnet_prefix}"
}
resource "azurerm_lb" "lb" {
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
name = "${var.rg_prefix}lb"
location = "${var.location}"
frontend_ip_configuration {
name = "LoadBalancerFrontEnd"
public_ip_address_id = "${azurerm_public_ip.lbpip.id}"
}
}
resource "azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool" "backend_pool" {
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
loadbalancer_id = "${azurerm_lb.lb.id}"
name = "BackendPool1"
}
resource "azurerm_lb_nat_rule" "tcp" {
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
loadbalancer_id = "${azurerm_lb.lb.id}"
name = "RDP-VM-${count.index}"
protocol = "tcp"
frontend_port = "5000${count.index + 1}"
backend_port = 3389
frontend_ip_configuration_name = "LoadBalancerFrontEnd"
count = 2
}
resource "azurerm_lb_rule" "lb_rule" {
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
loadbalancer_id = "${azurerm_lb.lb.id}"
name = "LBRule"
protocol = "tcp"
frontend_port = 80
backend_port = 80
frontend_ip_configuration_name = "LoadBalancerFrontEnd"
enable_floating_ip = false
backend_address_pool_id = "${azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backend_pool.id}"
idle_timeout_in_minutes = 5
probe_id = "${azurerm_lb_probe.lb_probe.id}"
depends_on = ["azurerm_lb_probe.lb_probe"]
}
resource "azurerm_lb_probe" "lb_probe" {
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
loadbalancer_id = "${azurerm_lb.lb.id}"
name = "tcpProbe"
protocol = "tcp"
port = 80
interval_in_seconds = 5
number_of_probes = 2
}
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "nic" {
name = "nic${count.index}"
location = "${var.location}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
count = 2
ip_configuration {
name = "ipconfig${count.index}"
subnet_id = "${azurerm_subnet.subnet.id}"
private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"
load_balancer_backend_address_pools_ids = ["${azurerm_lb_backend_address_pool.backend_pool.id}"]
load_balancer_inbound_nat_rules_ids = ["${element(azurerm_lb_nat_rule.tcp.*.id, count.index)}"]
}
}
resource "azurerm_virtual_machine" "vm" {
name = "vm${count.index}"
location = "${var.location}"
resource_group_name = "${azurerm_resource_group.rg.name}"
availability_set_id = "${azurerm_availability_set.avset.id}"
vm_size = "${var.vm_size}"
network_interface_ids = ["${element(azurerm_network_interface.nic.*.id, count.index)}"]
count = 2
storage_image_reference {
publisher = "${var.image_publisher}"
offer = "${var.image_offer}"
sku = "${var.image_sku}"
version = "${var.image_version}"
}
storage_os_disk {
name = "osdisk${count.index}"
create_option = "FromImage"
}
os_profile {
computer_name = "${var.hostname}"
admin_username = "${var.admin_username}"
admin_password = "${var.admin_password}"
}
}
看完上面脚本,大家是不是觉得上面每个参数都是$的引用,到底引用了什么?Terraform的这个特性是非常好的,可以很简单定义不同的参数引用。上面这个脚本对应的所有参数引用在下面这个脚本里定义:
variable "resource_group" {
description = "The name of the resource group in which to create the virtual network."
default = "lyq-testterraform-rg"
}
variable "rg_prefix" {
description = "The shortened abbreviation to represent your resource group that will go on the front of some resources."
default = "rg"
}
variable "hostname" {
description = "VM name referenced also in storage-related names."
default = "lyqterravm"
}
variable "dns_name" {
description = " Label for the Domain Name. Will be used to make up the FQDN. If a domain name label is specified, an A DNS record is created for the public IP in the Microsoft Azure DNS system."
default = "lyqterraform"
}
variable "lb_ip_dns_name" {
description = "DNS for Load Balancer IP"
default = "lyqtestterralb"
}
variable "location" {
description = "The location/region where the virtual network is created. Changing this forces a new resource to be created."
default = "chinanorth"
}
variable "virtual_network_name" {
description = "The name for the virtual network."
default = "lyq-test-vnet"
}
variable "address_space" {
description = "The address space that is used by the virtual network. You can supply more than one address space. Changing this forces a new resource to be created."
default = "10.0.0.0/16"
}
variable "subnet_prefix" {
description = "The address prefix to use for the subnet."
default = "10.0.10.0/24"
}
variable "storage_account_tier" {
description = "Defines the Tier of storage account to be created. Valid options are Standard and Premium."
default = "Premium"
}
variable "storage_replication_type" {
description = "Defines the Replication Type to use for this storage account. Valid options include LRS, GRS etc."
default = "LRS"
}
variable "vm_size" {
description = "Specifies the size of the virtual machine."
default = "Standard_D1"
}
variable "image_publisher" {
description = "name of the publisher of the image (az vm image list)"
default = "MicrosoftWindowsServer"
}
variable "image_offer" {
description = "the name of the offer (az vm image list)"
default = "WindowsServer"
}
variable "image_sku" {
description = "image sku to apply (az vm image list)"
default = "2012-R2-Datacenter"
}
variable "image_version" {
description = "version of the image to apply (az vm image list)"
default = "latest"
}
variable "admin_username" {
description = "administrator user name"
default = "lyqadmin"
}
variable "admin_password" {
description = "administrator password (recommended to disable password auth)"
default = "P@ssw0rd1234"
}
如果我们不给参数定义default值,那么在执行plan时,就会要求输入相应的参数,这样就可以实现自定义配置。
把这两个脚本分别保存为tf文件,例如2VMLB.tf和variables.tf。然后执行terraform plan和 apply,不出意外的话,我们就可以在azure.cn界面里看到创建出来的这些资源了。
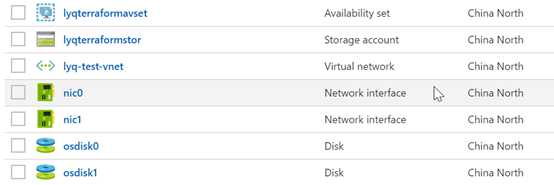
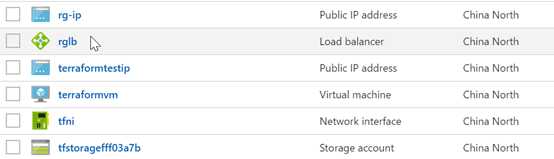

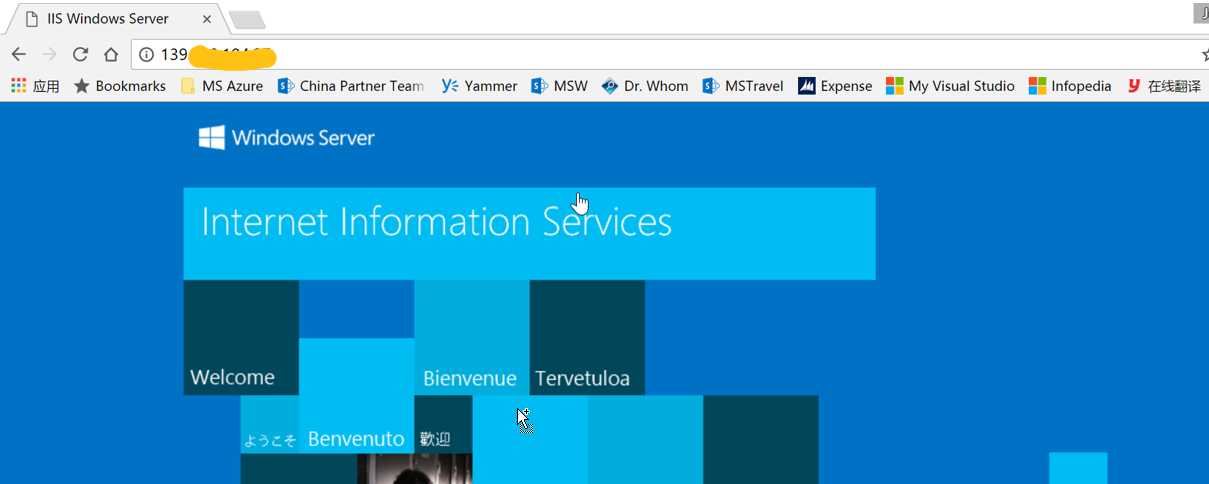
因为指定的虚拟机用了win2012R2模板,所以需要进虚拟机去开启IIS,完成后,就可以通过负载均衡的公网IP访问了。

Code as IaaS for Azure : Terraform 做多一点事情
标签:log group ble front fqdn 语法 min depends nan
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lujohn/p/7631727.html