标签:style blog class code java tar
一、概述
1、调用STM32库函数配置与直接配置寄存器
① 直接配置寄存器
使用过51单片机的朋友都知道为了将IO口配置成某种特殊功能或者配置中断控制,我们先将需要如下步骤:
根据需要配置功能计算值---->直接写入寄存器
② 调用STM32库函数配置
定义一个配置结构体变量---->根据配置功能依次给这个结构体变量的成员赋值----->将结构体变量的地址传入库函数,并调用STM32库函数实现配置
其中最后一个步骤的"调用STM32库函数",实际上就是将配置结果写入寄存器。
前两个步骤是以一种高级的形式(将结构体变量的成员和它的值以利于人理解的方式定义)将我们希望的配置参数写入结构体变量(内存)中。然后再将将结构体变量的地址传入库函数(这些参数就传给STM32库函数),STM32库函数根据设置参数计算出要写入寄存器的值,最后写入到寄存器中,完成整个配置。
③ 调用STM32库函数配置与直接配置寄存器的对比
直接配置寄存器需要计算写入值(人做的),然后直接写入。代码量要小,执行时间少,效率高,但是辛苦了人。
调用STM32库函数配置,计算写入值以及写入寄存器都是库函数完成的,而人就像一个领导通过结构体告诉库函数我要怎样配置。可见人的工作量大大减小了,显然辛苦了机器,不过CPU速度很高,咱们不用担心。
2、STM32库函数实现的组成
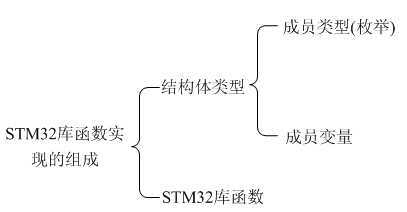
STM32定义了配置需要的结构体,结构体变量都是见名知意的,而且用枚举定义了许多新的类型。枚举方法适合变量值比较少的情况,分别给每个值一个名字,便于用户识别和赋值。
3、声明
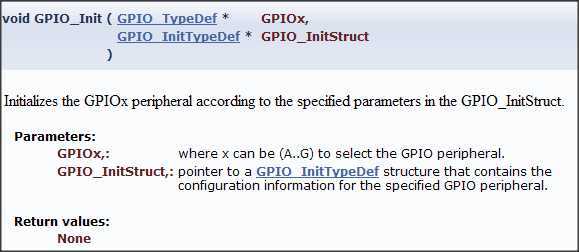
以下阐述以配置GPIO实现流水灯程序为例进行说明,测试库函数是GPIO_Init(),
硬件电路如下:
二、结构体
GPIO_Init库函数目的就是对GPIOx设置成我们需要的参数值,参数值保存在GPIO_InitStruct。其中涉及到两个结构体,来看一下。
1、GPIO_TypeDef
定义是在stm32f10x.h中
typedef struct { __IO uint32_t CRL; __IO uint32_t CRH; __IO uint32_t IDR; __IO uint32_t ODR; __IO uint32_t BSRR; __IO uint32_t BRR; __IO uint32_t LCKR; } GPIO_TypeDef;
看一下怎么利用这个结构体类型是怎么访问寄存器CRL、CRH?
#define PERIPH_BASE ((uint32_t)0x40000000) /*!< Peripheral base address in the alias region */ #define APB2PERIPH_BASE (PERIPH_BASE + 0x10000) #define GPIOC_BASE (APB2PERIPH_BASE + 0x1000) #define GPIOC ((GPIO_TypeDef *) GPIOC_BASE)
GPIOC最终的值是0x40000000+0x10000+0x1000,也就是0x4001100,而且注意这个值不是int类型,而是一个指向GPIO_TypeDef结构体类型的常量指针。通过定义和GPIOC值一样的指针变量,我们就可以访问到端口GPIOC的每一个寄存器。
GPIO_TypeDef * GPIOx = GPIOC; GPIOx->CRL = 0xffffffff;
2、GPIO_InitTypeDef
定义在stm32f10x_gpio.h中
typedef struct { uint16_t GPIO_Pin; /*!< Specifies the GPIO pins to be configured. This parameter can be any value of @ref GPIO_pins_define */ GPIOSpeed_TypeDef GPIO_Speed; /*!< Specifies the speed for the selected pins. This parameter can be a value of @ref GPIOSpeed_TypeDef */ GPIOMode_TypeDef GPIO_Mode; /*!< Specifies the operating mode for the selected pins. This parameter can be a value of @ref GPIOMode_TypeDef */ }GPIO_InitTypeDef;
初始化GPIO的结构体类型--GPIO_InitTypeDef有三个成员,需要设置的引脚GPIO_Pin,需要设置的引脚速度GPIO_Speed,需要设置的引脚工作模式GPIO_Mode。这三个成员包含了配置GPIO的所有信息,而且这三个成员都是见名知意。当然不可能直接将这三个成员写入到配置寄存器中,需要转化成对应的寄存器值才能写入,这就是GPIO_Init所要干的活。
① GPIO_Pin
GPIO_Pin的类型是uint16_t,那么它的取值表含义是什么呢?
#define GPIO_Pin_0 ((uint16_t)0x0001) /*!< Pin 0 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_1 ((uint16_t)0x0002) /*!< Pin 1 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_2 ((uint16_t)0x0004) /*!< Pin 2 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_3 ((uint16_t)0x0008) /*!< Pin 3 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_4 ((uint16_t)0x0010) /*!< Pin 4 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_5 ((uint16_t)0x0020) /*!< Pin 5 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_6 ((uint16_t)0x0040) /*!< Pin 6 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_7 ((uint16_t)0x0080) /*!< Pin 7 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_8 ((uint16_t)0x0100) /*!< Pin 8 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_9 ((uint16_t)0x0200) /*!< Pin 9 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_10 ((uint16_t)0x0400) /*!< Pin 10 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_11 ((uint16_t)0x0800) /*!< Pin 11 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_12 ((uint16_t)0x1000) /*!< Pin 12 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_13 ((uint16_t)0x2000) /*!< Pin 13 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_14 ((uint16_t)0x4000) /*!< Pin 14 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_15 ((uint16_t)0x8000) /*!< Pin 15 selected */ #define GPIO_Pin_All ((uint16_t)0xFFFF) /*!< All pins selected */
选中某一位(置1),就意味着要配置这一位。
② GPIO_Speed
它的类型是一个枚举类型--GPIOSpeed_TypeDef
typedef enum { GPIO_Speed_10MHz = 1, GPIO_Speed_2MHz, GPIO_Speed_50MHz }GPIOSpeed_TypeDef;
可见GPIO_Speed只有三种取值,这三种取值无疑是见名知意的。GPIO_Speed_10MHz = 1,编译器自动的会为剩余两种取值以合适的数字值取代:GPIO_Speed_2MHz=2,GPIO_Speed_50MHz=3。
用枚举类型定义取值较少的类型带来的好处:
③ GPIO_Mode
它的类型也是一个枚举类型-- GPIOMode_TypeDef
typedef enum { GPIO_Mode_AIN = 0x0, GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING = 0x04, GPIO_Mode_IPD = 0x28, GPIO_Mode_IPU = 0x48, GPIO_Mode_Out_OD = 0x14, GPIO_Mode_Out_PP = 0x10, GPIO_Mode_AF_OD = 0x1C, GPIO_Mode_AF_PP = 0x18 }GPIOMode_TypeDef;
这里人为的给每一种类型值都设置了数字值,其目的肯定是为了以后根据这些数字值便于得到写入寄存器的值,也就是便于GPIO_Init函数根据这些值得到对应配置寄存器的值。
三、库函数
GPIO_Init函数的功能是配置GPIOx,实际上就是配置GPIOx的六个寄存器。
__IO uint32_t CRL;
__IO uint32_t CRH;
__IO uint32_t IDR;
__IO uint32_t ODR;
__IO uint32_t BSRR;
__IO uint32_t BRR;
__IO uint32_t LCKR;
函数代码如下:

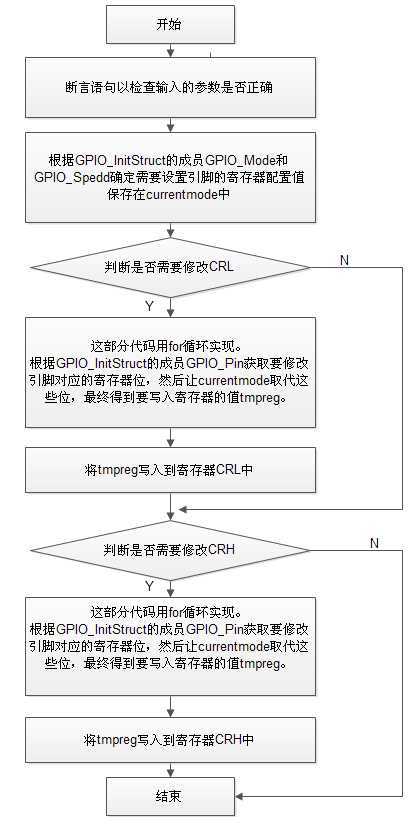
/** * @brief Initializes the GPIOx peripheral according to the specified * parameters in the GPIO_InitStruct. * @param GPIOx: where x can be (A..G) to select the GPIO peripheral. * @param GPIO_InitStruct: pointer to a GPIO_InitTypeDef structure that * contains the configuration information for the specified GPIO peripheral. * @retval None */ void GPIO_Init(GPIO_TypeDef* GPIOx, GPIO_InitTypeDef* GPIO_InitStruct) { uint32_t currentmode = 0x00, currentpin = 0x00, pinpos = 0x00, pos = 0x00; uint32_t tmpreg = 0x00, pinmask = 0x00; /* Check the parameters */ assert_param(IS_GPIO_ALL_PERIPH(GPIOx)); assert_param(IS_GPIO_MODE(GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Mode)); assert_param(IS_GPIO_PIN(GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Pin)); /*---------------------------- GPIO Mode Configuration -----------------------*/ currentmode = ((uint32_t)GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Mode) & ((uint32_t)0x0F); if ((((uint32_t)GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Mode) & ((uint32_t)0x10)) != 0x00) { /* Check the parameters */ assert_param(IS_GPIO_SPEED(GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Speed)); /* Output mode */ currentmode |= (uint32_t)GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Speed; } /*---------------------------- GPIO CRL Configuration ------------------------*/ /* Configure the eight low port pins */ if (((uint32_t)GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Pin & ((uint32_t)0x00FF)) != 0x00) { tmpreg = GPIOx->CRL; for (pinpos = 0x00; pinpos < 0x08; pinpos++) { pos = ((uint32_t)0x01) << pinpos; /* Get the port pins position */ currentpin = (GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Pin) & pos; if (currentpin == pos) { pos = pinpos << 2; /* Clear the corresponding low control register bits */ pinmask = ((uint32_t)0x0F) << pos; tmpreg &= ~pinmask; /* Write the mode configuration in the corresponding bits */ tmpreg |= (currentmode << pos); /* Reset the corresponding ODR bit */ if (GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Mode == GPIO_Mode_IPD) { GPIOx->BRR = (((uint32_t)0x01) << pinpos); } else { /* Set the corresponding ODR bit */ if (GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Mode == GPIO_Mode_IPU) { GPIOx->BSRR = (((uint32_t)0x01) << pinpos); } } } } GPIOx->CRL = tmpreg; } /*---------------------------- GPIO CRH Configuration ------------------------*/ /* Configure the eight high port pins */ if (GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Pin > 0x00FF) { tmpreg = GPIOx->CRH; for (pinpos = 0x00; pinpos < 0x08; pinpos++) { pos = (((uint32_t)0x01) << (pinpos + 0x08)); /* Get the port pins position */ currentpin = ((GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Pin) & pos); if (currentpin == pos) { pos = pinpos << 2; /* Clear the corresponding high control register bits */ pinmask = ((uint32_t)0x0F) << pos; tmpreg &= ~pinmask; /* Write the mode configuration in the corresponding bits */ tmpreg |= (currentmode << pos); /* Reset the corresponding ODR bit */ if (GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Mode == GPIO_Mode_IPD) { GPIOx->BRR = (((uint32_t)0x01) << (pinpos + 0x08)); } /* Set the corresponding ODR bit */ if (GPIO_InitStruct->GPIO_Mode == GPIO_Mode_IPU) { GPIOx->BSRR = (((uint32_t)0x01) << (pinpos + 0x08)); } } } GPIOx->CRH = tmpreg; } }
其中的英文注释已经写的非常清晰,不在多余的注释了,主要的是列出它的流程图:
四、总结库函数的实现
STM32定义了许多结构体、宏、枚举类型,给用户提供了见名知意的设置参数方法。
STM32库函数根据这些设置参数计算出要写入寄存器的值,最后写入到寄存器中,完成配置。
五、使用库函数
向各种结构体的成员写入适当的控制参数,填充结构体,最后调用STM库函数实现配置。
参考资料:《STM32库开发实战指南》
STM32库函数实现方法及使用,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style blog class code java tar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/amanlikethis/p/3720303.html