标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar strong
参考:http://student.zjzk.cn/course_ware/data_structure/web/chazhao/chazhao9.3.1.1.htm
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 typedef int InfoType; //其它数据域,自定义 5 typedef int KeyType; //假定关键字类型为整数 6 typedef struct node //结点类型 7 { 8 KeyType key; //关键字项 9 InfoType otherinfo; //其它数据域,InfoType视应用情况而定,下面不处理它 10 node *lchild, *rchild; //左右孩子指针 11 }BSTNode; 12 typedef BSTNode *BSTree; //BSTree是二叉排序树的类型 13 14 //非递归 15 void InsertBSTNode(BSTree *Tptr, KeyType key) 16 {//若二叉排序树 *Tptr中没有关键字为key,则插入,否则直接返回 17 BSTNode *f, *p = *Tptr; //p的初值指向根结点 18 while(p) 19 { 20 if(p->key==key) //树中已有key,无须插入 21 return; 22 f = p; //记录 23 p = key < p->key ? p->lchild : p->rchild; 24 } 25 p = new BSTNode; 26 p->key = key; 27 p->lchild = NULL; 28 p->rchild = NULL; 29 if(NULL == *Tptr) 30 *Tptr = p; 31 else 32 { 33 if (key < f->key) 34 f->lchild = p; 35 else 36 f->rchild = p; 37 } 38 } 39 40 BSTree CreateBSTree(KeyType *array, int size) 41 { 42 BSTNode *root = NULL; 43 for (int i=0;i<size;++i) 44 InsertBSTNode(&root, array[i]); 45 return root; 46 } 47 48 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) 49 { 50 int array[] = {5,3,7,2,4,8}; 51 int size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(int); 52 BSTree tree = CreateBSTree(array, size); 53 system("pause"); 54 return 0; 55 }
使用调试模式查看构建的二叉查找树如下图
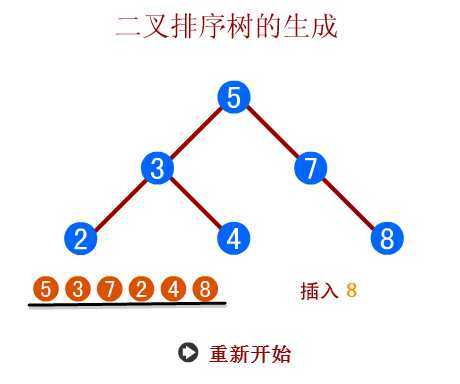
(1) 二叉排序树的插入和生成
①二叉排序树插入新结点的过程
在二叉排序树中插入新结点,要保证插入后仍满足BST性质。其插入过程是:
(a)若二叉排序树T为空,则为待插入的关键字key申请一个新结点,并令其为根;
(b)若二叉排序树T不为空,则将key和根的关键字比较:
(i)若二者相等,则说明树中已有此关键字key,无须插入。
(ii)若key<T→key,则将key插入根的左子树中。
(iii)若key>T→key,则将它插入根的右子树中。
子树中的插入过程与上述的树中插入过程相同。如此进行下去,直到将key作为一个新的叶结点的关键字插入到二叉排序树中,或者直到发现树中已有此关键字为止。
②二叉排序树插入新结点的递归算法
【参见参考书目】
③二叉排序树插入新结点的非递归算法
void InsertBST(BSTree *Tptr,KeyType key)
{ //若二叉排序树 *Tptr中没有关键字为key,则插入,否则直接返回
BSTNode *f,*p=*TPtr; //p的初值指向根结点
while(p){ //查找插入位置
if(p->key==key) return;//树中已有key,无须插入
f=p; //f保存当前查找的结点
p=(key<p->key)?p->lchild:p->rchild;
//若key<p->key,则在左子树中查找,否则在右子树中查找
} //endwhile
p=(BSTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
p->key=key; p->lchild=p->rchild=NULL; //生成新结点
if(*TPtr==NULL) //原树为空
*Tptr=p; //新插入的结点为新的根
else //原树非空时将新结点关p作为关f的左孩子或右孩子插入
if(key<f->key)
f->lchild=p;
else f->rchild=p;
} //InsertBST
④二叉排序树的生成
二叉排序树的生成,是从空的二叉排序树开始,每输入一个结点数据,就调用一次插入算法将它插入到当前已生成的二叉排序树中。生成二叉排序树的算法如下:
BSTree CreateBST(void)
{ //输入一个结点序列,建立一棵二叉排序树,将根结点指针返回
BSTree T=NULL; //初始时T为空树
KeyType key;
scanf("%d",&key); //读人一个关键字
while(key){ //假设key=0是输人结束标志
InsertBST(&T,key); //将key插入二叉排序树T
scanf("%d",&key);//读人下一关键字
}
return T; //返回建立的二叉排序树的根指针
} //BSTree
⑤二叉排序树的生成过程
由输入实例(5,3,7,2,4,8),根据生成二叉排序树算法生成二叉排序树的过程【参见动画演示】
注意:
输入序列决定了二叉排序树的形态。
二叉排序树的中序序列是一个有序序列。所以对于一个任意的关键字序列构造一棵二叉排序树,其实质是对此关键字序列进行排序,使其变为有序序列。"排序树"的名称也由此而来。通常将这种排序称为树排序(Tree Sort),可以证明这种排序的平均执行时间亦为O(nlgn)。
对相同的输入实例,树排序的执行时间约为堆排序的2至3倍。因此在一般情况下,构造二叉排序树的目的并非为了排序,而是用它来加速查找,这是因为在一个有序的集合上查找通常比在无序集合上查找更快。因此,人们又常常将二叉排序树称为二叉查找树。
标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar strong
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kira2will/p/3965915.html