标签:情况 name 使用 context ret 允许 todo http strong
1.描述
允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变他的行为,对象看起来似乎修改了他的类。
2.模式的使用
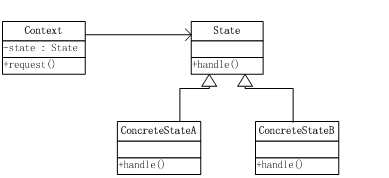
·环境(Context):环境是一个类,该类含有抽象状态(State)的声明,可以引用任何具体状态类的实例。用户对该环境(Context)类的实例在某种状态下的行为感兴趣。
·抽象状态(State):抽象状态是一个接口或抽象类。抽象状态中定义了与环境(Context)的一个特定状态相关的若干个方法。
·具体状态(Concrete State):具体状态是实现(扩展)抽象状态的类。
3.使用情景
·一个对象的行为依赖他的状态,并且他必须在运行时根据状态改变他的行为。
·需要编写大量的条件分支语句来决定一个操作的行为,并且这些条件恰好表示对象的一种状态。
4.优点
·容易增加新的状态。
·环境(Context)中不必出现大量条件语句。
·可以让用户方便的切换环境(Context)实例的状态。
·避免环境(Context)实例出现内部状态不一致的情况。
·当状态对象没有实例变量时,环境(Context)的各个实例可以共享一个状态对象。
5.UML图
6案例
案例一
一个温度计(环境),在不同温度(状态)时显示不同信息。
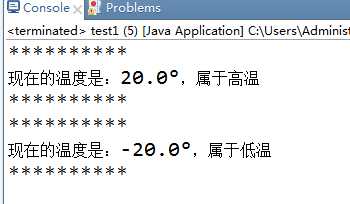
1 package 状态模式; 2 3 public class test1 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Thermometer t = new Thermometer(); 7 HeightState h = new HeightState(20); 8 LowState l = new LowState(-20); 9 t.setState(h); 10 t.show(); 11 t.setState(l); 12 t.show(); 13 } 14 15 } 16 17 /* 18 * 环境 19 */ 20 class Thermometer { 21 TemperatureState state; 22 public void setState(TemperatureState temperatureState){ 23 this.state = temperatureState; 24 } 25 public void show(){ 26 System.out.println("**********"); 27 state.showTemperature(); 28 System.out.println("**********"); 29 } 30 } 31 32 /* 33 * 抽象状态 34 */ 35 interface TemperatureState { 36 public void showTemperature(); 37 } 38 39 /* 40 * 具体状态 41 */ 42 class LowState implements TemperatureState { 43 double n = 0; 44 LowState(double n){ 45 if(n <= 0) 46 this.n = n; 47 } 48 public void showTemperature() { 49 System.out.println("现在的温度是:" + n + "°,属于低温"); 50 } 51 52 } 53 54 /* 55 * 具体状态 56 */ 57 class HeightState implements TemperatureState { 58 double n = 0; 59 HeightState(double n){ 60 if(n > 0) 61 this.n = n; 62 } 63 public void showTemperature() { 64 System.out.println("现在的温度是:" + n + "°,属于高温"); 65 } 66 67 }
案例二:状态切换(环境实例在某种状态下执行一个方法后,可能导致该实例的状态发生变化)
一把枪(环境),有2颗子弹、一颗子弹、无子弹三种状态,有开枪和装弹两种操作。在有子弹时才能开枪,在无子弹时才能装弹。
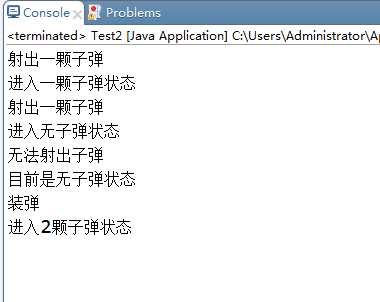
1 package 状态模式; 2 3 public class test2 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Gun gun = new Gun(); 7 gun.fire(); 8 gun.fire(); 9 gun.fire(); 10 gun.load(); 11 } 12 13 } 14 15 /* 16 * 环境 17 */ 18 class Gun { 19 State state1, state2, state3; 20 State state; 21 Gun(){ 22 this.state1 = new State1(this); 23 this.state2 = new State2(this); 24 this.state3 = new State3(this); 25 state = state1; 26 } 27 28 public void setState(State state){ 29 this.state = state; 30 } 31 32 public State getState1() { 33 return state1; 34 } 35 36 public State getState2() { 37 return state2; 38 } 39 40 public State getState3() { 41 return state3; 42 } 43 44 public State getState() { 45 return state; 46 } 47 48 public void fire(){ 49 state.fire(); 50 } 51 52 public void load(){ 53 state.loadBullet(); 54 } 55 } 56 57 /* 58 * 抽象状态 59 */ 60 interface State { 61 public void fire(); 62 public void loadBullet(); 63 public String showStateMess(); 64 } 65 66 /* 67 * 具体状态 68 */ 69 class State1 implements State { 70 Gun gun; 71 State1(Gun gun){ 72 this.gun = gun; 73 } 74 public void fire() { 75 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 76 System.out.println("射出一颗子弹"); 77 gun.setState(gun.getState2()); 78 System.out.println("进入" + gun.getState2().showStateMess()); 79 } 80 81 public void loadBullet() { 82 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 83 84 } 85 86 public String showStateMess() { 87 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 88 return "2颗子弹状态"; 89 } 90 91 } 92 93 /* 94 * 具体状态 95 */ 96 class State2 implements State { 97 Gun gun; 98 State2(Gun gun){ 99 this.gun = gun; 100 } 101 public void fire() { 102 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 103 System.out.println("射出一颗子弹"); 104 gun.setState(gun.getState3()); 105 System.out.println("进入" + gun.getState3().showStateMess()); 106 } 107 108 public void loadBullet() { 109 System.out.println("无法装弹"); 110 111 } 112 113 public String showStateMess() { 114 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 115 return "一颗子弹状态"; 116 } 117 118 } 119 120 /* 121 * 具体状态,空弹夹 122 */ 123 class State3 implements State { 124 Gun gun; 125 State3(Gun gun){ 126 this.gun = gun; 127 } 128 public void fire() { 129 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 130 System.out.println("无法射出子弹"); 131 System.out.println("目前是" + showStateMess() + ""); 132 } 133 134 public void loadBullet() { 135 System.out.println("装弹"); 136 gun.setState(gun.getState1()); 137 System.out.println("进入" + gun.getState1().showStateMess()); 138 } 139 140 public String showStateMess() { 141 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 142 return "无子弹状态"; 143 } 144 145 }
案例三:共享状态(多个实例共享同一个状态)
一列火车的各个车厢同时处于运动状态或静止状态,为了实现这个目的需要将状态设置为静态变量。
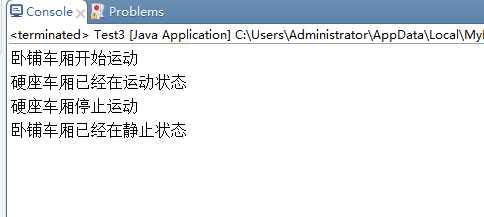
1 package 状态模式; 2 3 public class test3 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Vehicle car1 = new Vehicle("卧铺车厢"); 7 Vehicle car2 = new Vehicle("硬座车厢"); 8 car1.startUp(); 9 car2.startUp(); 10 car2.stop(); 11 car1.stop(); 12 } 13 14 } 15 16 /* 17 * 环境 18 */ 19 class Vehicle { 20 static StateOne moveState, stopState; 21 static StateOne state; 22 String name; 23 Vehicle(String name){ 24 this.name = name; 25 this.moveState = new VehicleMoveState(); 26 this.stopState = new VehicleStopState(); 27 state = stopState; 28 } 29 30 public void startUp(){ 31 state.startUp(this); 32 } 33 34 public void stop(){ 35 state.stop(this); 36 } 37 38 public void setState(StateOne state){ 39 this.state = state; 40 } 41 42 public static StateOne getMoveState() { 43 return moveState; 44 } 45 46 public static StateOne getStopState() { 47 return stopState; 48 } 49 50 public static StateOne getState() { 51 return state; 52 } 53 54 public String getName() { 55 return name; 56 } 57 } 58 59 /* 60 * 抽象状态 61 */ 62 interface StateOne { 63 public void startUp(Vehicle vehicle); 64 public void stop(Vehicle vehicle); 65 } 66 67 class VehicleMoveState implements StateOne{ 68 69 public void startUp(Vehicle vehicle) { 70 System.out.println(vehicle.getName() + "已经在运动状态"); 71 } 72 73 public void stop(Vehicle vehicle) { 74 System.out.println(vehicle.getName() + "停止运动"); 75 vehicle.setState(vehicle.getStopState()); 76 } 77 78 } 79 80 class VehicleStopState implements StateOne{ 81 82 public void startUp(Vehicle vehicle) { 83 System.out.println(vehicle.getName() + "开始运动"); 84 vehicle.setState(vehicle.getMoveState()); 85 } 86 87 public void stop(Vehicle vehicle) { 88 System.out.println(vehicle.getName() + "已经在静止状态"); 89 } 90 91 }
标签:情况 name 使用 context ret 允许 todo http strong
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/cxy2016/p/7670363.html