标签:绑定 sse 16px void error 构造 index 异常 adl
上篇文章梳理了Struts2中的XWork的容器的实现,这篇文章,着重回顾XWork中的各个元素以及他们的作用和相互之间的关系。
首先,大体感受一下XWork中的各个主要元素。
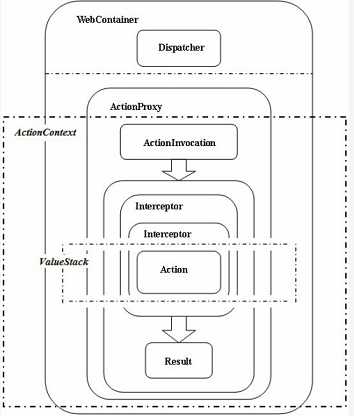
主要分为三个部分:
(1),核心分发器 Dispatcher : Dispatcher 不属于XWork框架的组成,但是是XWork框架的调用者和驱动执行者,在运行过程中起着重要的作用。
(2),控制流体系 (ActionProxy, ActionInvocation, Inteceptor, Action, Result), 其中,Interceptor和Action以及Result作为事件处理节点,是处理事件逻辑的主要地方,而ActionProxy和ActionInvocation负责对这些事件处理节点进行调用。
这里,ActionProxy主要是XWork框架和外部环境,为框架内部元素提供一个环境的同时也提供外部调用XWork内部元素的接口,即负责提供一个执行环境。而ActionInvocation作为核心调度器,主要负责的就是对事件处理节点进行调用。
(3),数据流体系 (ActionContext, ValueStack),其中ActionContext负责数据的储存和数据的共享,而ValueStack负责数据的操作。
以上就是对XWork框架内部元素的大致的认识,接下来的部分,通过从源码的方式,查看各个元素内部的组成。
一,XWork中的数据流体系
XWork中的数据流体系,包括了ActionContext和ValueStack两大部分,
1 public class ActionContext implements Serializable { 2 static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal(); 3 public static final String ACTION_NAME = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"; 4 public static final String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; 5 public static final String SESSION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"; 6 public static final String APPLICATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"; 7 public static final String PARAMETERS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"; 8 public static final String LOCALE = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"; 9 public static final String TYPE_CONVERTER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.typeConverter"; 10 public static final String ACTION_INVOCATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"; 11 public static final String CONVERSION_ERRORS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"; 12 public static final String CONTAINER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"; 13 private Map<String, Object> context; 14 15 public void setValueStack(ValueStack stack) { 16 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack", stack); 17 } 18 19 // 省略了许多其他对象的getter,setter 20 21 public ValueStack getValueStack() { 22 return (ValueStack)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"); 23 } 24 25 public Object get(String key) { 26 return this.context.get(key); 27 } 28 29 public void put(String key, Object value) { 30 this.context.put(key, value); 31 } 32 }
通过源码可以发现,其实ValueStack是ActionContext的内部对象。正如之前提到的,ActionContext在框架内部提供一个数据储存和数据共享的环境,而ValueStack则是在ActionContext的基础之上,增加对数据的操作的功能。
既然ValueStack是ActionContext的内部对象,让我们把重点放到ActionContext类中,查看源码看看内部的数据结构如何。
1 public class ActionContext implements Serializable { 2 static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal(); 3 public static final String ACTION_NAME = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"; 4 public static final String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; 5 public static final String SESSION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"; 6 public static final String APPLICATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"; 7 public static final String PARAMETERS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"; 8 public static final String LOCALE = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"; 9 public static final String TYPE_CONVERTER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.typeConverter"; 10 public static final String ACTION_INVOCATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"; 11 public static final String CONVERSION_ERRORS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"; 12 public static final String CONTAINER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"; 13 private Map<String, Object> context; 14 15 public ActionContext(Map<String, Object> context) { 16 this.context = context; 17 } 18 19 public void setActionInvocation(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) { 20 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation", actionInvocation); 21 } 22 23 public ActionInvocation getActionInvocation() { 24 return (ActionInvocation)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"); 25 } 26 27 public void setApplication(Map<String, Object> application) { 28 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application", application); 29 } 30 31 public Map<String, Object> getApplication() { 32 return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"); 33 } 34 35 public static void setContext(ActionContext context) { 36 actionContext.set(context); 37 } 38 39 public static ActionContext getContext() { 40 return (ActionContext)actionContext.get(); 41 } 42 43 public void setContextMap(Map<String, Object> contextMap) { 44 getContext().context = contextMap; 45 } 46 47 public Map<String, Object> getContextMap() { 48 return this.context; 49 } 50 51 public void setConversionErrors(Map<String, Object> conversionErrors) { 52 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors", conversionErrors); 53 } 54 55 public Map<String, Object> getConversionErrors() { 56 Map<String, Object> errors = (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"); 57 if (errors == null) { 58 errors = new HashMap(); 59 this.setConversionErrors((Map)errors); 60 } 61 62 return (Map)errors; 63 } 64 65 public void setLocale(Locale locale) { 66 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale", locale); 67 } 68 69 public Locale getLocale() { 70 Locale locale = (Locale)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"); 71 if (locale == null) { 72 locale = Locale.getDefault(); 73 this.setLocale(locale); 74 } 75 76 return locale; 77 } 78 79 public void setName(String name) { 80 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name", name); 81 } 82 83 public String getName() { 84 return (String)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"); 85 } 86 87 public void setParameters(HttpParameters parameters) { 88 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters", parameters); 89 } 90 91 public HttpParameters getParameters() { 92 return (HttpParameters)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"); 93 } 94 95 public void setSession(Map<String, Object> session) { 96 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session", session); 97 } 98 99 public Map<String, Object> getSession() { 100 return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"); 101 } 102 103 public void setValueStack(ValueStack stack) { 104 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack", stack); 105 } 106 107 public ValueStack getValueStack() { 108 return (ValueStack)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"); 109 } 110 111 public void setContainer(Container cont) { 112 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container", cont); 113 } 114 115 public Container getContainer() { 116 return (Container)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"); 117 } 118 119 public <T> T getInstance(Class<T> type) { 120 Container cont = this.getContainer(); 121 if (cont != null) { 122 return cont.getInstance(type); 123 } else { 124 throw new XWorkException("Cannot find an initialized container for this request."); 125 } 126 } 127 128 public Object get(String key) { 129 return this.context.get(key); 130 } 131 132 public void put(String key, Object value) { 133 this.context.put(key, value); 134 } 135 }
通过源码可以发现,在最后的get方法和put方法中,其实是对ActionContext中存放的Map对象进行操作,其中还存放这框架内部其他的元素,如Session, Application等,
在ActionContext类中,我们还需要注意的地方,就是在Web环境中,对并发中对共享数据的线程安全的处理,在ActionContext中,使用一个ThreadLocal对ActionContext中的Map对象进行封装。
1 public class ActionContext implements Serializable { 2 static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal(); 3 4 // 省略其他代码。。。 5 6 public void setActionInvocation(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) { 7 this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation", actionInvocation); 8 } 9 10 public static void setContext(ActionContext context) { 11 actionContext.set(context); 12 } 13 }
ActionContext中封装了许多对框架内部对象的访问接口,主要分成两种:
(1),对XWork框架对象的访问,getContainer,getValueStack,getActionInvocation;
(2),对数据对象的访问, getSession,getApplication,getParameters等;
1 ActionContext内部对访问数据对象的封装都是以Map形式返回,这体现了XWork与Web容器解耦的思想,XWrok本身并不是一个Web容器框架。
XWork实现访问真正的web容器对象实在ActionContext的子类ServletActionContext中,查看源码
1 public class ServletActionContext extends ActionContext implements StrutsStatics { 2 private static final long serialVersionUID = -666854718275106687L; 3 public static final String STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY = "struts.valueStack"; 4 public static final String ACTION_MAPPING = "struts.actionMapping"; 5 6 private ServletActionContext(Map context) { 7 super(context); 8 } 9 10 public static ActionContext getActionContext(HttpServletRequest req) { 11 ValueStack vs = getValueStack(req); 12 return vs != null ? new ActionContext(vs.getContext()) : null; 13 } 14 15 public static ValueStack getValueStack(HttpServletRequest req) { 16 return (ValueStack)req.getAttribute("struts.valueStack"); 17 } 18 19 public static ActionMapping getActionMapping() { 20 return (ActionMapping)ActionContext.getContext().get("struts.actionMapping"); 21 } 22 23 public static PageContext getPageContext() { 24 return (PageContext)ActionContext.getContext().get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.PageContext"); 25 } 26 27 public static void setRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { 28 ActionContext.getContext().put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletRequest", request); 29 } 30 31 public static HttpServletRequest getRequest() { 32 return (HttpServletRequest)ActionContext.getContext().get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletRequest"); 33 } 34 35 public static void setResponse(HttpServletResponse response) { 36 ActionContext.getContext().put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletResponse", response); 37 } 38 39 public static HttpServletResponse getResponse() { 40 return (HttpServletResponse)ActionContext.getContext().get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletResponse"); 41 } 42 43 public static ServletContext getServletContext() { 44 return (ServletContext)ActionContext.getContext().get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.ServletContext"); 45 } 46 47 public static void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) { 48 ActionContext.getContext().put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.ServletContext", servletContext); 49 } 50 }
以上是对数据流体系中的ActionContext的内部实现进行的了解,接下来我们将进入数据流中的另一个对象——ValueStack;
XWork中的ValueStack其实是对OGNL(Object Graph Navigation Language)进行的扩展,让ValueStack再进行OGNL计算时,可以将一组对象作为Root对象。
1 public interface ValueStack { 2 String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; 3 String REPORT_ERRORS_ON_NO_PROP = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ReportErrorsOnNoProp"; 4 5 Map<String, Object> getContext(); 6 7 void setDefaultType(Class var1); 8 9 void setExprOverrides(Map<Object, Object> var1); 10 11 Map<Object, Object> getExprOverrides(); 12 13 // 获取包含栈内所有元素的容器结构 14 CompoundRoot getRoot(); 15 // 根据传入的表达式和对象进行写值计算 16 void setValue(String var1, Object var2); 17 18 void setParameter(String var1, Object var2); 19 20 void setValue(String var1, Object var2, boolean var3); 21 22 String findString(String var1); 23 24 String findString(String var1, boolean var2); 25 // 根据传入的表达式进行求值计算 26 Object findValue(String var1); 27 28 Object findValue(String var1, boolean var2); 29 30 Object findValue(String var1, Class var2); 31 32 Object findValue(String var1, Class var2, boolean var3); 33 34 // 得到栈顶元素 35 Object peek(); 36 37 // 弹出栈顶 38 Object pop(); 39 40 // 压栈 41 void push(Object var1); 42 43 void set(String var1, Object var2); 44 45 int size(); 46 }
ValueStack作为一个接口,提供了一些我们所熟知的栈的操作方法。通过查看其子类,我们可以了解ValueStack的使用方法。
1 public class OgnlValueStack implements Serializable, ValueStack, ClearableValueStack, MemberAccessValueStack { 2 public static final String THROW_EXCEPTION_ON_FAILURE = OgnlValueStack.class.getName() + ".throwExceptionOnFailure"; 3 private static final Logger LOG = LogManager.getLogger(OgnlValueStack.class); 4 private static final long serialVersionUID = 370737852934925530L; 5 private static final String MAP_IDENTIFIER_KEY = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.OgnlValueStack.MAP_IDENTIFIER_KEY"; 6 protected CompoundRoot root; // 这里使用了装饰模式, 后面的源码分析中会说到,对这个对象的操作内部其实是对对象的迭代遍历操作 7 protected transient Map<String, Object> context; 8 protected Class defaultType; 9 protected Map<Object, Object> overrides; 10 protected transient OgnlUtil ognlUtil; 11 protected transient SecurityMemberAccess securityMemberAccess; 12 private transient XWorkConverter converter; 13 private boolean devMode; 14 private boolean logMissingProperties; 15 // 省略了许多代码。。。。 16 protected OgnlValueStack(XWorkConverter xworkConverter, CompoundRootAccessor accessor, TextProvider prov, boolean allowStaticAccess) { 17 this.setRoot(xworkConverter, accessor, new CompoundRoot(), allowStaticAccess); 18 this.push(prov); 19 } 20 21 protected OgnlValueStack(ValueStack vs, XWorkConverter xworkConverter, CompoundRootAccessor accessor, boolean allowStaticAccess) { 22 this.setRoot(xworkConverter, accessor, new CompoundRoot(vs.getRoot()), allowStaticAccess); 23 } 24 25 protected void setRoot(XWorkConverter xworkConverter, CompoundRootAccessor accessor, CompoundRoot compoundRoot, boolean allowStaticMethodAccess) { 26 this.root = compoundRoot; 27 this.securityMemberAccess = new SecurityMemberAccess(allowStaticMethodAccess); 28 this.context = Ognl.createDefaultContext(this.root, accessor, new OgnlTypeConverterWrapper(xworkConverter), this.securityMemberAccess); 29 this.context.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack", this); 30 Ognl.setClassResolver(this.context, accessor); 31 ((OgnlContext)this.context).setTraceEvaluations(false); 32 ((OgnlContext)this.context).setKeepLastEvaluation(false); 33 } 34 35 36 public Map<String, Object> getContext() { 37 return this.context; 38 } 39 40 public void setDefaultType(Class defaultType) { 41 this.defaultType = defaultType; 42 } 43 44 public void setExprOverrides(Map<Object, Object> overrides) { 45 if (this.overrides == null) { 46 this.overrides = overrides; 47 } else { 48 this.overrides.putAll(overrides); 49 } 50 51 } 52 53 public Map<Object, Object> getExprOverrides() { 54 return this.overrides; 55 } 56 57 public CompoundRoot getRoot() { 58 return this.root; 59 } 60 61 public void setParameter(String expr, Object value) { 62 this.setValue(expr, value, this.devMode); 63 } 64 65 public void setValue(String expr, Object value) { 66 this.setValue(expr, value, this.devMode); 67 } 68 69 public void setValue(String expr, Object value, boolean throwExceptionOnFailure) { 70 Map context = this.getContext(); 71 72 try { 73 this.trySetValue(expr, value, throwExceptionOnFailure, context); 74 } catch (OgnlException var10) { 75 this.handleOgnlException(expr, value, throwExceptionOnFailure, var10); 76 } catch (RuntimeException var11) { 77 this.handleRuntimeException(expr, value, throwExceptionOnFailure, var11); 78 } finally { 79 this.cleanUpContext(context); 80 } 81 82 } 83 84 private void cleanUpContext(Map<String, Object> context) { 85 ReflectionContextState.clear(context); 86 context.remove("conversion.property.fullName"); 87 context.remove("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ReportErrorsOnNoProp"); 88 } 89 90 public String findString(String expr) { 91 return (String)this.findValue(expr, String.class); 92 } 93 94 public String findString(String expr, boolean throwExceptionOnFailure) { 95 return (String)this.findValue(expr, String.class, throwExceptionOnFailure); 96 } 97 98 public Object findValue(String expr, boolean throwExceptionOnFailure) { 99 Object var4; 100 try { 101 this.setupExceptionOnFailure(throwExceptionOnFailure); 102 Object var3 = this.tryFindValueWhenExpressionIsNotNull(expr); 103 return var3; 104 } catch (OgnlException var9) { 105 var4 = this.handleOgnlException(expr, throwExceptionOnFailure, var9); 106 return var4; 107 } catch (Exception var10) { 108 var4 = this.handleOtherException(expr, throwExceptionOnFailure, var10); 109 } finally { 110 ReflectionContextState.clear(this.context); 111 } 112 113 return var4; 114 } 115 116 protected void setupExceptionOnFailure(boolean throwExceptionOnFailure) { 117 if (throwExceptionOnFailure) { 118 this.context.put(THROW_EXCEPTION_ON_FAILURE, true); 119 } 120 121 } 122 123 private Object tryFindValueWhenExpressionIsNotNull(String expr) throws OgnlException { 124 return expr == null ? null : this.tryFindValue(expr); 125 } 126 127 protected Object handleOtherException(String expr, boolean throwExceptionOnFailure, Exception e) { 128 this.logLookupFailure(expr, e); 129 if (throwExceptionOnFailure) { 130 throw new XWorkException(e); 131 } else { 132 return this.findInContext(expr); 133 } 134 } 135 136 private Object tryFindValue(String expr) throws OgnlException { 137 expr = this.lookupForOverrides(expr); 138 Object value; 139 if (this.defaultType != null) { 140 value = this.findValue(expr, this.defaultType); 141 } else { 142 value = this.getValueUsingOgnl(expr); 143 if (value == null) { 144 value = this.findInContext(expr); 145 } 146 } 147 148 return value; 149 } 150 151 private String lookupForOverrides(String expr) { 152 if (this.overrides != null && this.overrides.containsKey(expr)) { 153 expr = (String)this.overrides.get(expr); 154 } 155 156 return expr; 157 } 158 159 public Object findValue(String expr, Class asType, boolean throwExceptionOnFailure) { 160 Object var6; 161 try { 162 Object value; 163 try { 164 this.setupExceptionOnFailure(throwExceptionOnFailure); 165 Object var4 = this.tryFindValueWhenExpressionIsNotNull(expr, asType); 166 return var4; 167 } catch (OgnlException var11) { 168 value = this.handleOgnlException(expr, throwExceptionOnFailure, var11); 169 var6 = this.converter.convertValue(this.getContext(), value, asType); 170 return var6; 171 } catch (Exception var12) { 172 value = this.handleOtherException(expr, throwExceptionOnFailure, var12); 173 var6 = this.converter.convertValue(this.getContext(), value, asType); 174 } 175 } finally { 176 ReflectionContextState.clear(this.context); 177 } 178 179 return var6; 180 } 181 182 private Object getValue(String expr, Class asType) throws OgnlException { 183 return this.ognlUtil.getValue(expr, this.context, this.root, asType); 184 } 185 186 protected Object findInContext(String name) { 187 return this.getContext().get(name); 188 } 189 190 public Object findValue(String expr, Class asType) { 191 return this.findValue(expr, asType, false); 192 } 193 194 public Object peek() { 195 return this.root.peek(); 196 } 197 198 public Object pop() { 199 return this.root.pop(); 200 } 201 202 public void push(Object o) { 203 this.root.push(o); 204 } 205 206 public void set(String key, Object o) { 207 Map setMap = this.retrieveSetMap(); 208 setMap.put(key, o); 209 } 210 211 212 public int size() { 213 return this.root.size(); 214 } 215 216 public void clearContextValues() { 217 ((OgnlContext)this.context).getValues().clear(); 218 } 219 220 }
可以看到子类对ActionContext接口中的方法的实现,而其中主要起作用的是ServletActionContext中的CompoundRoot类型的root对象,
1 public class CompoundRoot extends CopyOnWriteArrayList<Object> { 2 private static final long serialVersionUID = 8563229069192473995L; 3 4 public CompoundRoot() { 5 } 6 7 public CompoundRoot(List<?> list) { 8 super(list); 9 } 10 11 public CompoundRoot cutStack(int index) { 12 return new CompoundRoot(this.subList(index, this.size())); 13 } 14 15 public Object peek() { 16 return this.get(0); 17 } 18 19 public Object pop() { 20 return this.remove(0); 21 } 22 23 public void push(Object o) { 24 this.add(0, o); 25 } 26 }
这里使用的CompoundRoot使用了装饰模式,封装了一个CopyOnWriteArrayList,就在这个ArrayList实现的栈中,对数据进行从栈顶到栈底的匹配和进行数据计算的功能。
这里,我们深入OgnlValueStack的原理,了解到OgnlValueStack是从OgnlValueStack创建出来的,并在该类中指定了许多OGNL计算的默认实现方式。
1 public class OgnlValueStackFactory implements ValueStackFactory { 2 protected XWorkConverter xworkConverter; 3 protected CompoundRootAccessor compoundRootAccessor; 4 protected TextProvider textProvider; 5 protected Container container; 6 protected boolean allowStaticMethodAccess; 7 8 public OgnlValueStackFactory() { 9 } 10 11 @Inject 12 public void setXWorkConverter(XWorkConverter converter) { 13 this.xworkConverter = converter; 14 } 15 16 @Inject("system") 17 public void setTextProvider(TextProvider textProvider) { 18 this.textProvider = textProvider; 19 } 20 21 @Inject( 22 value = "allowStaticMethodAccess", 23 required = false 24 ) 25 public void setAllowStaticMethodAccess(String allowStaticMethodAccess) { 26 this.allowStaticMethodAccess = BooleanUtils.toBoolean(allowStaticMethodAccess); 27 } 28 29 public ValueStack createValueStack() { 30 ValueStack stack = new OgnlValueStack(this.xworkConverter, this.compoundRootAccessor, this.textProvider, this.allowStaticMethodAccess); 31 this.container.inject(stack); 32 stack.getContext().put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container", this.container); 33 return stack; 34 } 35 36 // 创建OgnlValueStack 37 public ValueStack createValueStack(ValueStack stack) { 38 // 设置OGNL计算时需要的参数 39 ValueStack result = new OgnlValueStack(stack, this.xworkConverter, this.compoundRootAccessor, this.allowStaticMethodAccess); 40 // 对OgnlValueStack进行参数注入, XWork容器的inject方法 41 this.container.inject(result); 42 stack.getContext().put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container", this.container); 43 return result; 44 } 45 46 47 // 初始化 OGNL 的相关设置 PropertyAcessor, MethodAccessor, NullHandler 48 @Inject 49 public void setContainer(Container container) throws ClassNotFoundException { 50 // 从XWork容器container中获取所有PropertyAccessor的实现类 51 Set<String> names = container.getInstanceNames(PropertyAccessor.class); 52 Iterator i$ = names.iterator(); 53 54 String name; 55 Class cls; 56 while(i$.hasNext()) { 57 name = (String)i$.next(); 58 cls = Class.forName(name); 59 if (cls != null) { 60 if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(cls)) { 61 PropertyAccessor var6 = (PropertyAccessor)container.getInstance(PropertyAccessor.class, name); 62 } 63 // 根据不同的类名, 为OGNL分配对应的PropertyAccessor实现类 64 OgnlRuntime.setPropertyAccessor(cls, (PropertyAccessor)container.getInstance(PropertyAccessor.class, name)); 65 // 找到CompoundRootAccessor的实现,并初始化 66 if (this.compoundRootAccessor == null && CompoundRoot.class.isAssignableFrom(cls)) { 67 this.compoundRootAccessor = (CompoundRootAccessor)container.getInstance(PropertyAccessor.class, name); 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 72 // 从容器中获取 MethodAccessor的实现类 73 names = container.getInstanceNames(MethodAccessor.class); 74 i$ = names.iterator(); 75 76 while(i$.hasNext()) { 77 name = (String)i$.next(); 78 cls = Class.forName(name); 79 if (cls != null) { 80 // 根据不同类名,为OGNL分配对应的MethodAccessor实现 81 OgnlRuntime.setMethodAccessor(cls, (MethodAccessor)container.getInstance(MethodAccessor.class, name)); 82 } 83 } 84 85 // 从容器中获取NullHandler的实现类 86 names = container.getInstanceNames(NullHandler.class); 87 i$ = names.iterator(); 88 89 while(i$.hasNext()) { 90 name = (String)i$.next(); 91 cls = Class.forName(name); 92 if (cls != null) { 93 // 根据不同类名,为OGNL分配对应的NullHandler实现 94 OgnlRuntime.setNullHandler(cls, new OgnlNullHandlerWrapper((NullHandler)container.getInstance(NullHandler.class, name))); 95 } 96 } 97 98 if (this.compoundRootAccessor == null) { 99 throw new IllegalStateException("Couldn‘t find the compound root accessor"); 100 } else { 101 this.container = container; 102 } 103 } 104 }
至此,我们梳理一下ValueStack对OGNL的扩展的操作, ValueStack作为一个接口,被OgnlValueStack所实现,封装了进行OGNL计算的操作方法,而OgnlValueStack又是在OgnlValueStackFactory创建,在其setContainer方法中完成OGNL的运行参数的实现方式的选择和设置(PropertyAccessor, MethodAccessor, NullHandler),最后的调用OgnlUtil,就剩下对OGNL原始API的调用了。
这里,我们还需要注意一下其中的一个类CompoundRootAccessor,这个类是ClassResolver和PropertyAccessor和MethodAccessor的默认实现类,这三个,都是OGNL计算时所需要指定的默认行为规则。
1 public class CompoundRootAccessor implements PropertyAccessor, MethodAccessor, ClassResolver { 2 3 public void setProperty(Map context, Object target, Object name, Object value) throws OgnlException { 4 // 得到OGNL 的Root对象和上下文context 5 CompoundRoot root = (CompoundRoot)target; 6 OgnlContext ognlContext = (OgnlContext)context; 7 8 // 迭代 CompoundRoot对象中的元素 9 Iterator i$ = root.iterator(); 10 11 while(true) { 12 Object o; 13 do { 14 if (!i$.hasNext()) { 15 boolean reportError = BooleanUtils.toBoolean((Boolean)context.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ReportErrorsOnNoProp")); 16 if (reportError || this.devMode) { 17 String msg = String.format("No object in the CompoundRoot has a publicly accessible property named ‘%s‘ (no setter could be found).", name); 18 if (reportError) { 19 throw new XWorkException(msg); 20 } 21 22 LOG.warn(msg); 23 } 24 25 return; 26 } 27 28 o = i$.next(); 29 } while(o == null); 30 31 try { 32 // 判断当前元素是否能被写值 33 if (OgnlRuntime.hasSetProperty(ognlContext, o, name)) { 34 OgnlRuntime.setProperty(ognlContext, o, name, value); 35 // 若匹配成功,则不再继续往下匹配,直接返回 36 return; 37 } 38 // 直接往Map中写值 39 if (o instanceof Map) { 40 Map map = (Map)o; 41 42 try { 43 map.put(name, value); 44 return; 45 } catch (UnsupportedOperationException var11) { 46 ; 47 } 48 } 49 } catch (IntrospectionException var12) { 50 ; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 public Object getProperty(Map context, Object target, Object name) throws OgnlException { 56 // 得到OGNL 的Root对象和上下文context 57 CompoundRoot root = (CompoundRoot)target; 58 OgnlContext ognlContext = (OgnlContext)context; 59 60 // 根据不同的类型获取值 61 if (name instanceof Integer) { 62 Integer index = (Integer)name; 63 return root.cutStack(index.intValue()); 64 } else if (!(name instanceof String)) { 65 return null; 66 } else if ("top".equals(name)) { 67 return root.size() > 0 ? root.get(0) : null; 68 } else { 69 // 对于普通属性, 迭代CompoundRoot对象进行匹配,匹配到第一个值进行返回 70 Iterator i$ = root.iterator(); 71 72 while(true) { 73 Object o; 74 do { 75 if (!i$.hasNext()) { 76 if (context.containsKey(OgnlValueStack.THROW_EXCEPTION_ON_FAILURE)) { 77 throw new NoSuchPropertyException(target, name); 78 } 79 80 return null; 81 } 82 83 o = i$.next(); 84 } while(o == null); 85 86 try { 87 if (OgnlRuntime.hasGetProperty(ognlContext, o, name) || o instanceof Map && ((Map)o).containsKey(name)) { 88 return OgnlRuntime.getProperty(ognlContext, o, name); 89 } 90 } catch (OgnlException var10) { 91 if (var10.getReason() != null) { 92 String msg = "Caught an Ognl exception while getting property " + name; 93 throw new XWorkException(msg, var10); 94 } 95 } catch (IntrospectionException var11) { 96 ; 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 } 101 102 // 。。。。省略其他代码 103 104 }
至此,我们可以看出,ValueStack作为XWork框架的核心元素之一,是框架进行OGNL计算的场所,以及是XWork数据访问的基础。
最后,我们看下在PrepareOperations中的构造函数中,初始化ActionContext和ValueStack的构造函数,从源码的层面了解ActionContext和ValueStack的关系,
1 public class PrepareOperations {
2 public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
3 Integer counter = Integer.valueOf(1);
4 Integer oldCounter = (Integer)request.getAttribute("__cleanup_recursion_counter");
5 if (oldCounter != null) {
6 counter = oldCounter.intValue() + 1;
7 }
8
9 ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext();
10 ActionContext ctx;
11 if (oldContext != null) {
12 ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap(oldContext.getContextMap()));
13 } else {
14 ValueStack stack = ((ValueStackFactory)this.dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class)).createValueStack();
15 stack.getContext().putAll(this.dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, (ActionMapping)null));
16 ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
17 }
18
19 request.setAttribute("__cleanup_recursion_counter", counter);
20 ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
21 return ctx;
22 }
23 }
从源码的角度可以看出, ActionContext的创建伴随ValueStack的创建,从红体的这段代码可以看出ValueStack和ActionContext的上下文环境其实是相同的。
二,XWork的控制流体系
还记得之前提到过的XWork中的控制流体系的组成元素吗,ActionProxy, ActionInvocation, Interceptor,Action,Result。其中,ActionProxy和ActionInvocation归类于事件调度节点,Interceptor,Action和Result归类于事件处理节点。
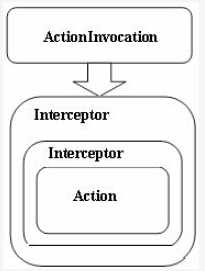
其中,Action和Interceptor主要负责对请求进行逻辑处理的,并在Action执行之后返回一个Result对象。在这里不做过多的说明,贴一下源码就算过了。
1 public interface Action {
2 String SUCCESS = "success";
3 String NONE = "none";
4 String ERROR = "error";
5 String INPUT = "input";
6 String LOGIN = "login";
7
8 String execute() throws Exception;
9 }
1 public interface Interceptor extends Serializable {
2 void destroy();
3
4 void init();
5
6 String intercept(ActionInvocation var1) throws Exception;
7 }
1 public interface Result extends Serializable {
2 void execute(ActionInvocation var1) throws Exception;
3 }
然后主要看的是两个事件调度节点的作用。
首先是核心调度——ActionInvocation:
核心调度ActionInvocation的作用主要是对Interceptor和Action共同构成的执行栈进行调度,查看其源码,
1 public interface ActionInvocation extends Serializable { 2 // 获取和 ActionInvocation 绑定的Action 3 Object getAction(); 4 5 // 是否完成对Action个Result对象的调用 6 boolean isExecuted(); 7 8 // 获取和 ActionInvocation 绑定的ActionContext 9 ActionContext getInvocationContext(); 10 11 // 获取和 ActionInvocation 绑定的ActionProxy 12 ActionProxy getProxy(); 13 14 Result getResult() throws Exception; 15 16 // 获取调度结果代码 17 String getResultCode(); 18 19 // 设置调度结果代码 20 void setResultCode(String var1); 21 22 // 获取和 ActionInvocation 绑定的ValueStack 23 ValueStack getStack(); 24 25 // 注册 PreResultListener,作用于Action执行完后,Result执行前 26 void addPreResultListener(PreResultListener var1); 27 28 String invoke() throws Exception; 29 30 String invokeActionOnly() throws Exception; 31 32 void setActionEventListener(ActionEventListener var1); 33 34 void init(ActionProxy var1); 35 36 ActionInvocation serialize(); 37 38 ActionInvocation deserialize(ActionContext var1); 39 }
可以看出ActionInvocation 中,主要包含三种方法:
(1),对控制流和数据流元素的访问,getStack, getActionProxy, getAction
(2),对执行调用的扩展的方法, addPreListener, setActionEventListener
(3),对执行栈进行调用的接口, invoke , invokeActionOnly
这些方法,保证了ActionInvocation在对执行栈进行调用的过程中,也能访问XWrok框架中的任何其他元素。
ActionInvocation的核心的方法在于invoke方法中,通过查看默认的实现DefaultActionInvocation了解invoke方法的原理,
1 public class DefaultActionInvocation implements ActionInvocation { 2 public String invoke() throws Exception { 3 String profileKey = "invoke: "; 4 5 String var21; 6 try { 7 UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey); 8 // 若已经执行过,则抛出异常 9 if (this.executed) { 10 throw new IllegalStateException("Action has already executed"); 11 } 12 // 遍历Interceptor的迭代器,调用所有的Interceptor 13 if (this.interceptors.hasNext()) { 14 InterceptorMapping interceptorMapping = (InterceptorMapping)this.interceptors.next(); 15 String interceptorMsg = "interceptorMapping: " + interceptorMapping.getName(); 16 UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg); 17 18 try { 19 Interceptor interceptor = interceptorMapping.getInterceptor(); 20 if (interceptor instanceof WithLazyParams) { 21 interceptor = this.lazyParamInjector.injectParams(interceptor, interceptorMapping.getParams(), this.invocationContext); 22 } 23 // ActionInvocation的调度核心, 将ActionInvocation的实现类作为参数传入Interceptor执行,这里会递归调用Interceptor 24 this.resultCode = interceptor.intercept(this); 25 } finally { 26 UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg); 27 } 28 } else { 29 // 若没有Interceptor 对象,直接调用Action返回resultCode 30 this.resultCode = this.invokeActionOnly(); 31 } 32 33 if (!this.executed) { 34 if (this.preResultListeners != null) { 35 LOG.trace("Executing PreResultListeners for result [{}]", this.result); 36 Iterator i$ = this.preResultListeners.iterator(); 37 38 // 执行完Action和Result之后,调用PreResultListener对象 39 while(i$.hasNext()) { 40 Object preResultListener = i$.next(); 41 PreResultListener listener = (PreResultListener)preResultListener; 42 String _profileKey = "preResultListener: "; 43 44 try { 45 UtilTimerStack.push(_profileKey); 46 listener.beforeResult(this, this.resultCode); 47 } finally { 48 UtilTimerStack.pop(_profileKey); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 53 // 最后执行Result 54 if (this.proxy.getExecuteResult()) { 55 this.executeResult(); 56 } 57 58 this.executed = true; 59 } 60 61 var21 = this.resultCode; 62 } finally { 63 UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey); 64 } 65 66 return var21; 67 } 68 }
结合源码可以看出invoke方法的调度顺序,若执行栈的下个元素是Interceptor,则执行Interceptor,若下一个是Action,则执行Action,若没有下一个元素,则返回执行代码ResultCode,之后调用PreResultListener和Result对象。
然后是执行窗口——ActionProxy
之前提到过,ActionProxy为XWork内部元素提供一个执行环境,并且为外部元素的调用提供了接口。
1 public interface ActionProxy { 2 3 // 获取ActionProxy代理的Action对象 4 Object getAction(); 5 6 String getActionName(); 7 8 // 获取 A抽屉onProxy的配置对象 9 ActionConfig getConfig(); 10 11 //设置在执行Action之后执行指定Result的标志 12 void setExecuteResult(boolean var1); 13 //获取在执行Action之后执行指定Result的标志 14 boolean getExecuteResult(); 15 16 // 获取ActionProxy绑定的ActionInvocation 17 ActionInvocation getInvocation(); 18 19 String getNamespace(); 20 21 // 执行接口 22 String execute() throws Exception; 23 24 // 获取逻辑处理的方法名称 25 String getMethod(); 26 27 boolean isMethodSpecified(); 28 }
从接口定义中我们可以对ActionProxy产生更深入的理解,ActionProxy负责处理XWork内部对象(如Action,Interceptor)和web请求对象之间的关系。
ActionProxy的初始化是在DefaultActionProxyFactory类中,源码:
1 public class DefaultActionProxyFactory implements ActionProxyFactory { 2 3 @Inject 4 public void setContainer(Container container) { 5 this.container = container; 6 } 7 8 public ActionProxy createActionProxy(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, Map<String, Object> extraContext, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) { 9 // 创建 ActionProxy关联的ActionInvocation对象,并实施依赖注入 10 ActionInvocation inv = this.createActionInvocation(extraContext, true); 11 this.container.inject(inv); 12 return this.createActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext); 13 } 14 15 public ActionProxy createActionProxy(ActionInvocation inv, String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) { 16 // 创建默认实现类 , 实施依赖注入 17 DefaultActionProxy proxy = new DefaultActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext); 18 this.container.inject(proxy); 19 // 完成自身初始化 20 proxy.prepare(); 21 return proxy; 22 } 23 24 // 省略其他代码。。。 25 }
至此,我们从源码层面大致了解XWork中的数据流和控制流的构成。数据流的相互访问是ActionContext和ValueStack的包含关系,而控制流则是ActionInvocation对Action和Interceptor的调用关系, 但是,控制流和数据流是如何实现彼此之间的相互访问的呢。
实际上,数据流和控制流的相互访问的重点就是控制流体系中的事件处理节点——Action。而使用的方法就是我们在使用Struts2框架时经常看到的方法——实现一系列的Aware接口。
我们在Struts2中已经很熟悉各种各样的Aware接口了,举个栗子( ̄▽ ̄)/
1 public interface ServletRequestAware {2 void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest var1); 3 }
实现对应的Aware接口后,Action类就会获取对应的接口对象,也就是在控制流中(Action)访问到数据流中的元素了(封装成Map对象的HttpServlet, HttpServletResponse等)。其实现是在ServletConfigInterceptor类中,
1 public class ServletConfigInterceptor extends AbstractInterceptor implements StrutsStatics { 2 private static final long serialVersionUID = 605261777858676638L; 3 4 public ServletConfigInterceptor() { 5 } 6 7 public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { 8 Object action = invocation.getAction(); 9 ActionContext context = invocation.getInvocationContext(); 10 HttpServletRequest request; 11 if (action instanceof ServletRequestAware) { 12 request = (HttpServletRequest)context.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletRequest"); 13 ((ServletRequestAware)action).setServletRequest(request); 14 } 15 16 if (action instanceof ServletResponseAware) { 17 HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)context.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletResponse"); 18 ((ServletResponseAware)action).setServletResponse(response); 19 } 20 21 if (action instanceof ParameterAware) { 22 context.getParameters().applyParameters((ParameterAware)action); 23 } 24 25 if (action instanceof HttpParametersAware) { 26 ((HttpParametersAware)action).setParameters(context.getParameters()); 27 } 28 29 if (action instanceof ApplicationAware) { 30 ((ApplicationAware)action).setApplication(context.getApplication()); 31 } 32 33 if (action instanceof SessionAware) { 34 ((SessionAware)action).setSession(context.getSession()); 35 } 36 37 if (action instanceof RequestAware) { 38 ((RequestAware)action).setRequest((Map)context.get("request")); 39 } 40 41 if (action instanceof PrincipalAware) { 42 request = (HttpServletRequest)context.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletRequest"); 43 if (request != null) { 44 ((PrincipalAware)action).setPrincipalProxy(new ServletPrincipalProxy(request)); 45 } 46 } 47 48 if (action instanceof ServletContextAware) { 49 ServletContext servletContext = (ServletContext)context.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.ServletContext"); 50 ((ServletContextAware)action).setServletContext(servletContext); 51 } 52 53 return invocation.invoke(); 54 } 55 }
就是实现对应的接口获取对应的对象,代码简单易懂。
最后的最后提一下Struts2是如何从请求对象的值赋给Action对象中的属性的,过程在ParametersInterceptor中,
1 public class ParametersInterceptor extends MethodFilterInterceptor { 2 3 public String doIntercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { 4 Object action = invocation.getAction(); 5 if (!(action instanceof NoParameters)) { 6 ActionContext ac = invocation.getInvocationContext(); 7 HttpParameters parameters = this.retrieveParameters(ac); 8 if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { 9 LOG.debug("Setting params {}", this.getParameterLogMap(parameters)); 10 } 11 12 if (parameters != null) { 13 Map contextMap = ac.getContextMap(); 14 15 try { 16 ReflectionContextState.setCreatingNullObjects(contextMap, true); 17 ReflectionContextState.setDenyMethodExecution(contextMap, true); 18 ReflectionContextState.setReportingConversionErrors(contextMap, true); 19 ValueStack stack = ac.getValueStack(); 20 this.setParameters(action, stack, parameters); 21 } finally { 22 ReflectionContextState.setCreatingNullObjects(contextMap, false); 23 ReflectionContextState.setDenyMethodExecution(contextMap, false); 24 ReflectionContextState.setReportingConversionErrors(contextMap, false); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 return invocation.invoke(); 30 } 31 // 省略了其他代码 ...... 32 }
代码的内容就不说了,因为我自己也看不懂。。。大概就是通过retrieveParameters方法获取请求的数据,然后从ActionContext中获取ValueStack,使用ValueStack的OGNL操作对属性进行最终的赋值,贴上最后一幅图,
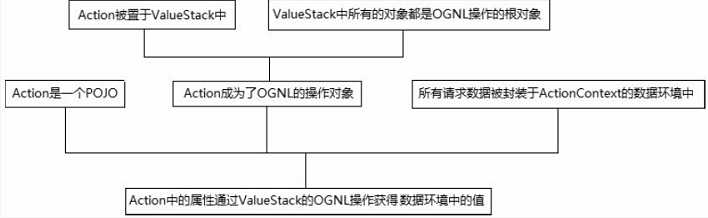
这最后一张图片,这是我第三次看这本书,才发现其中每一句话中所包含的内容。
一天又过去了,写完了篇文章,秋招溜了溜了,苦逼们好好学习,加油( ? ?ω?? )?
标签:绑定 sse 16px void error 构造 index 异常 adl
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/forwrader/p/7691174.html