标签:void union end src 内存 情况 排序 null 替换
1.//输入一个字符串,然后逆序输出
#include<string> int main() { char a[100]; cin>>a; int len=strlen(a); for(;len>=0;len--) { cout<<a[len-1]; } cout<<endl; return 0; }
2.windows的内存管理方式
union X { class S{ public: char s1; char s2; char s3; }s; static const char c=‘e‘; }x; int main() { x.s.s1=‘a‘; x.s.s2=‘b‘; x.s.s3=‘c‘; x.s.s1=x.c; cout<<x.s.s1<<endl; cout<<sizeof(x)<<endl; return 0; }
4.指针与引用的区别
指针是一个实体,引用是个别名
引用使用时无需解引用(*),指针需要解引用
引用只能在定义时被初始化一次,之后不可改变,指针可变
引用没有const,指针有const
引用不能为NULL,指针可以为NULL
sizeof引用,得到的是所指变量(对象)的大小,而sizeof指针,得到的是指针本身(所指的变量或对象的地址)的大小
和引用的自增(++)运算意义不一样
在内存分配上,程序为指针变量分配内存区域,而引用不需要分配内存区域
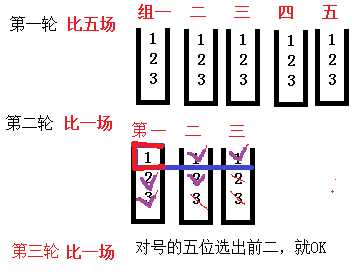
5.25个人5个赛道,至少比赛几场可以得到前三名?
七场
#include<assert.h> char* Strcpy(char*dest,const char*src) { assert(dest!=NULL && src!=NULL); char* ret=dest; while((*dest++ = *src++)!=‘\0‘); return ret; }
8.冒泡排序及其优化
//int* BubbleSort(int a[],int size) //{ // int i=size; // while(i) // { // for(int j=0;j<i-1;j++) // { // if(a[j]>a[j+1]) // swap(a[j],a[j+1]); // } // i--; // } // return a; //} int* BubbleSort1(int a[],int size) { int i=size; bool isExchange=true; while(i && isExchange) { isExchange=false; for(int j=0;j<i-1;j++) { if(a[j]>a[j+1]) { swap(a[j],a[j+1]); isExchange=true; } } i--; } return a; } void Test() { int ar[]={1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0}; int*p=BubbleSort1(ar,10); for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { cout<<p[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } int main() { Test(); return 0; }
标签:void union end src 内存 情况 排序 null 替换
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/JN-PDD/p/7700407.html