标签:glin col import a标签 http mac sep ted roo
本书使用的文件、代码:https://github.com/huangtao36/data_wrangling
第三章使用的数据文件:
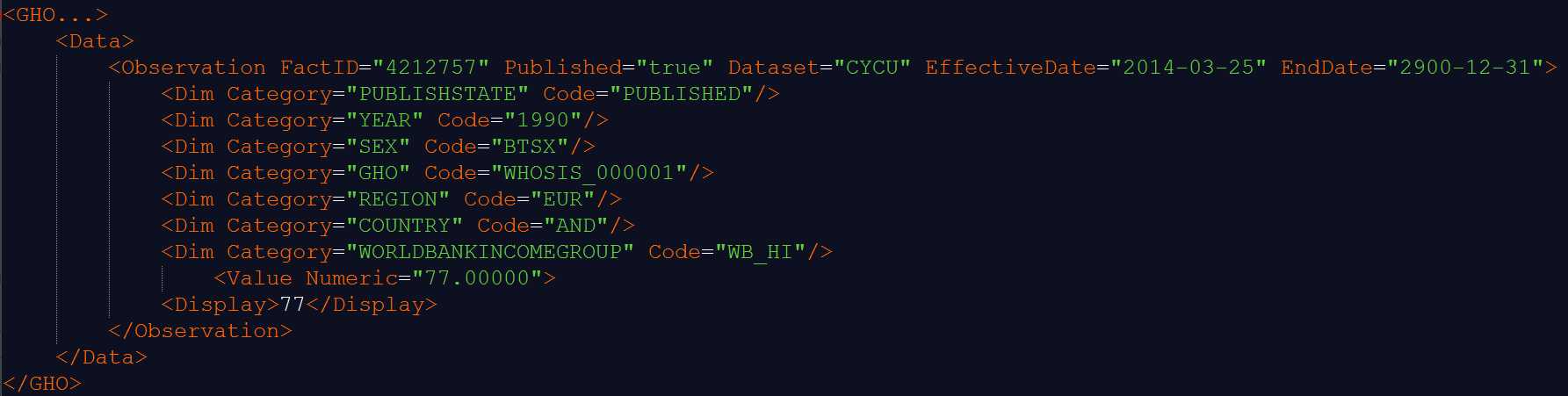
XML中有两个位置可以保存数据:
1、两个标签之间:<Display>71</Display>
2、标签的属性:<Dim Category="SEX" Code="BTSX"/>——其中Category的属性值是“SEX”,Code的属性值是"BTSX"。
XML的属性可以保存特定标签的额外信息,这些标签又嵌套在另一个标签中。
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse(‘data-text.xml‘)
root = tree.getroot() #获取树的根元素
data = root.find(‘Data‘)
all_data = []
for observation in data:
record = {}
for item in observation:
lookup_key_List = list(item.attrib.keys())
lookup_key = lookup_key_List[0]
if lookup_key == ‘Numeric‘:
rec_key = ‘NUMERIC‘
rec_value = item.attrib[‘Numeric‘]
else:
rec_key = item.attrib[lookup_key]
rec_value = item.attrib[‘Code‘]
record[rec_key] = rec_value
all_data.append(record)
print (all_data)
输出(部分):
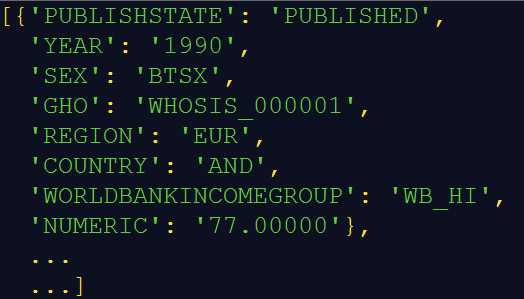
(输出的是单行数据,为了直观,这里进行了处理。)
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
本例中使用的是ElementTree、还可以使用lxml、minidom这两种库来解析XML文件,在此不做说明
获取Data元素中的内容
由上面的样本可知,我们使用的数据是包含在一个<Data>...</Data>中的,这里使用根元素的find方法可以利用标签名来搜索子元素。
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse(‘data-text.xml‘) root = tree.getroot() #获取树的根元素 data = root.find(‘Data‘)
print (list(data))
输出:
标签:glin col import a标签 http mac sep ted roo
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/huangtao36/p/7745445.html