标签:env choices upload col /usr 一句话 elf func direct
混合搜索在各大网站如京东、淘宝都有应用,他们的原理都是什么呢?本博文将为你介绍它们的实现过程。
混合搜索的原理,用一句话来说就是:关键字id进行拼接。
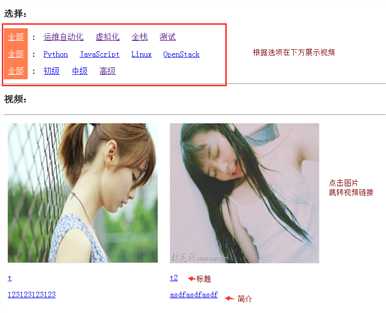
视频方向:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Direction(models.Model): weight = models.IntegerField(verbose_name=‘权重(按从大到小排列)‘, default=0) name = models.CharField(verbose_name=‘名称‘, max_length=32) classification = models.ManyToManyField(‘Classification‘) class Meta: db_table = ‘Direction‘ verbose_name_plural = u‘方向(视频方向)‘ def __str__(self): return self.name |
视频分类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Classification(models.Model): weight = models.IntegerField(verbose_name=‘权重(按从大到小排列)‘, default=0) name = models.CharField(verbose_name=‘名称‘, max_length=32) class Meta: db_table = ‘Classification‘ verbose_name_plural = u‘分类(视频分类)‘ def __str__(self): return self.name |
视频:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
class Video(models.Model): status_choice = ( (0, u‘下线‘), (1, u‘上线‘), ) level_choice = ( (1, u‘初级‘), (2, u‘中级‘), (3, u‘高级‘), ) status = models.IntegerField(verbose_name=‘状态‘, choices=status_choice, default=1)#可用于管理员的审核 level = models.IntegerField(verbose_name=‘级别‘, choices=level_choice, default=1) classification = models.ForeignKey(‘Classification‘, null=True, blank=True) weight = models.IntegerField(verbose_name=‘权重(按从大到小排列)‘, default=0) title = models.CharField(verbose_name=‘标题‘, max_length=32) summary = models.CharField(verbose_name=‘简介‘, max_length=32) img = models.ImageField(verbose_name=‘图片‘, upload_to=‘./static/images/Video/‘) href = models.CharField(verbose_name=‘视频地址‘, max_length=256) create_date = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True) class Meta: db_table = ‘Video‘ verbose_name_plural = u‘视频‘ def __str__(self): return self.title |
备注:
默认url:
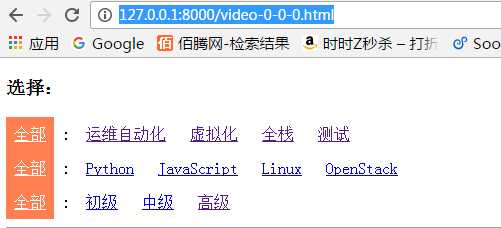
http://127.0.0.1:8000/video-0-0-0.html,其中第一个数字代表视频方向,默认0代表全部方向;第二个数字代表视频分类,默认0代表全部分类;第三个数字代表视频等级,默认0代表全部等级。
每一个a标签默认的url:
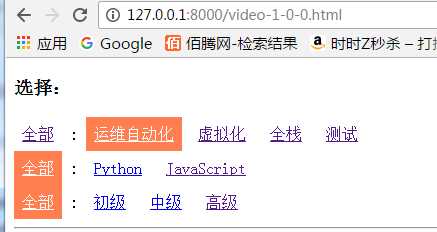
例如运维自动化:<a href="/video-1-0-0.html">运维自动化</a>,即视频方向的对应数字为1,视频分类和视频等级都为0,这样做的目的是为了将此url和用户当前url进行拼接,并跳转到新的url。
选择运维自动化后的url:
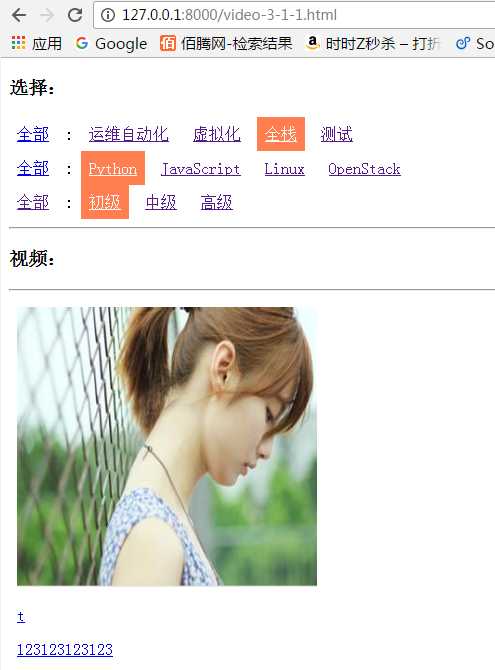
多选情况下的url:
|
1
|
{% load xx %} |
注:
关于自定义simple_tag的更多信息,详见下文。
 css代码
css代码设置css目的,当用户选择视频方向、视频分类、视频等级时,加深对应a标签。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
<h3>选择:</h3><div> {% action_all current_url 1 %} : {% for item in direction_list %} {% action current_url item 1 %} {% endfor %}</div><div> {% action_all current_url 2 %} : {% for item in class_list %} {% action current_url item 2 %} {% endfor %}</div><div> {% action_all current_url 3 %} : {% for item in level_list %} {% action current_url item 3 %} {% endfor %}</div><hr /> |
该区域全部基于自定义simple_tag实现,详见下文。
视频显示区域html:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<h3>视频:</h3> <hr /> {% for item in video_list %} <a class="item" href="{{ item.href }}"> <img src="/{{ item.img }}"> <p>{{ item.title }}</p> <p>{{ item.summary }}</p> </a> {% endfor %} |
循环显示符合条件的全部视频。
我们希望,当用户选择全部标签时,url对应位置为0,即当用户三个选择都是全部时,url为:/video-0-0-0.html
以视频方向为例介绍:
对应位置html:
|
1
|
{% action_all current_url 1 %} : |
从上述html可看出,action_all为对应的函数,它接收两个参数:当前url(current_url)、当前位置(视频方向、视频分类、视频等级)。其中current_url是后台传入html的,详见下文后台views函数介绍。
action_all函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-from django import template from django.utils.safestring import mark_safe@register.simple_tag #注册simple_tagdef action_all(current_url,index): #接收当前url和对应的位置参数 """ 获取当前url,video-1-1-2.html :param current_url: :param item: :return: """ url_part_list = current_url.split(‘-‘) #根据“-”进行分割 if index == 3: #如果是视频等级 if url_part_list[index] == "0.html": #如果选择的是全部 temp = "<a href=‘%s‘ class=‘active‘>全部</a>" #添加 “active”属性 else: temp = "<a href=‘%s‘>全部</a>" url_part_list[index] = "0.html" else: if url_part_list[index] == "0": temp = "<a href=‘%s‘ class=‘active‘>全部</a>" else: temp = "<a href=‘%s‘>全部</a>" url_part_list[index] = "0" href = ‘-‘.join(url_part_list) #处理后的列表再拼接成url字符串 temp = temp % (href,) #生成对应的a标签 return mark_safe(temp) #返回原生html |
以视频方向为例介绍:
对应位置html:
|
1
|
{% action current_url item 1 %} |
从上述html可看出:action函数接收三个参数 当前url、当前标签对象、当前位置。
action函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
@register.simple_tagdef action(current_url, item,index): # videos-0-0-1.html # item: id name # video- 2 -0-0.html url_part_list = current_url.split(‘-‘) if index == 3: if str(item[‘id‘]) == url_part_list[3].split(‘.‘)[0]: #如果当前标签被选中 temp = "<a href=‘%s‘ class=‘active‘>%s</a>" else: temp = "<a href=‘%s‘>%s</a>" url_part_list[index] = str(item[‘id‘]) + ‘.html‘ #拼接对应位置的部分url else: if str(item[‘id‘]) == url_part_list[index]: temp = "<a href=‘%s‘ class=‘active‘>%s</a>" else: temp = "<a href=‘%s‘>%s</a>" url_part_list[index] = str(item[‘id‘]) ur_str = ‘-‘.join(url_part_list) #拼接整体url temp = temp %(ur_str, item[‘name‘]) #生成对应的a标签 return mark_safe(temp) #返回安全的html |
至此,所有选择标签生成完毕,能够根据用户选择动态生成url。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
{% for item in video_list %} <a class="item" href="{{ item.href }}"> <img src="/{{ item.img }}"> <p>{{ item.title }}</p> <p>{{ item.summary }}</p> </a> {% endfor %} |
循环显示所有符合条件的视频。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
def video(request,*args,**kwargs): print(kwargs) print(request.path) request_path = request.path #当前请求的路径 q = {} #从数据库获取视频时的filter条件字典 q[‘status‘] = 1 #状态为审核通过的 class_id = int(kwargs.get(‘classification_id‘)) #获取url中的视频分类id direction_list = models.Direction.objects.all().values(‘id‘,‘name‘) #从数据库中获取所有的视频方向(包括视频方向的id和name) if kwargs.get(‘direction_id‘) == ‘0‘: # 方向选择全部 print(‘方向等于0‘) class_list = models.Classification.objects.all().values(‘id‘, ‘name‘) #方向id=0,即获取所有的视频分类(包括视频分类的id和name) if kwargs.get(‘classification_id‘) == ‘0‘: #如果视频分类id也为0,即全部分类 pass else: # 如果视频分类不是全部,过滤条件为视频分类id in [url中的视频分类id] q[‘classification_id__in‘] = [class_id,] else: print(‘方向不为0‘) # 方向选择某一个方向, # 如果分类是0 if kwargs.get(‘classification_id‘) == ‘0‘: print(‘分类为0‘) obj = models.Direction.objects.get(id=int(kwargs.get(‘direction_id‘))) #获取已选择的视频方向 class_list = obj.classification.all().values(‘id‘, ‘name‘) #获取该方向的所有视频分类 id_list = list(map(lambda x: x[‘id‘], class_list)) #获取所有视频分类对应的视频分类id q[‘classification_id__in‘] = id_list #过滤条件为视频分类id in [该方向下的所有视频分类id] else:#方向不为0,分类也不为0 obj = models.Direction.objects.get(id=int(kwargs.get(‘direction_id‘))) class_list = obj.classification.all().values(‘id‘, ‘name‘) id_list = list(map(lambda x:x[‘id‘], class_list)) q[‘classification_id__in‘] = [class_id,] #过滤条件为视频分类id in [已经选择的视频分类id] print(‘分类不为0‘) # 当前分类如果在获取的所有分类中,则方向下的所有相关分类显示 # 当前分类如果不在获取的所有分类中, if int(kwargs.get(‘classification_id‘)) in id_list: pass else: print(‘不再,获取指定方向下的所有分类:选中的回到全部‘) url_part_list = request_path.split(‘-‘) url_part_list[2] = ‘0‘ request_path = ‘-‘.join(url_part_list) level_id = int(kwargs.get(‘level_id‘)) #视频等级id if level_id == 0: pass else: q[‘level‘] = level_id #过滤条件增加视频等级 # models.Video.objects.filter(status=1) video_list = models.Video.objects.filter(**q).values(‘title‘,‘summary‘, ‘img‘, ‘href‘) # level_list = models.Video.level_choice ret = map(lambda x:{"id": x[0], ‘name‘: x[1]}, models.Video.level_choice)#把视频等级转化为单个标签是字典格式,整体是列表格式 level_list = list(ret) return render(request, ‘video.html‘, {‘direction_list‘: direction_list, ‘class_list‘: class_list, ‘level_list‘: level_list, ‘current_url‘: request_path, "video_list": video_list}) |
:以上就是混合搜索的前后端全过程
标签:env choices upload col /usr 一句话 elf func direct
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/pyxiaomangshe/p/7753390.html