标签:部分 共享内存 处理 idt ges 公司 day printf double
1.Cuda的编程模型
a. GPU(图形处理器)早期主要应用于图形渲染,使得应用程序能实现更强的视觉效果。(并行运算)
CUDA是由英伟达为他们公司GPU创立的一个并行计算平台和编程模型。CUDA包含三大组件,分别是NVIDIA驱动、toolkit和
samples.toolkit里面包含的nvcc编译器、调试工具和函数库。
开发人员可以通过调用CUDA函数库中的API,来使用GPU进行并行计算。NVIDIA公司为了吸引更多的开发人员,对CUDA进行了编程语言扩展,如CUDA C/C++语言
b. CUDA编程模型
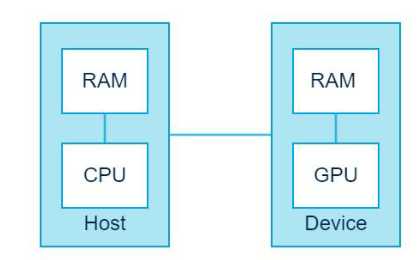
在CUDA的架构下,一个程序分为两个部分:host端和device端。Host端是指在CPU上执行的部分,而device端则在GPU上执行的部分。Device端的程序又称 为“KERNEL”。通常host端程序会将数据准备好后,复制到显卡的内存中,再由显示芯片执行device端程序,完成再由host端程序将结果从显卡的内存中取回。
2.Cuda编程技术
a.第一个Cuda程序
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <math.h> void function() { int i,j; double y; for(i=0;i<1000;i++); for(j=0;j<1000;j++); y = sin((double)i); } int main() { struct time val tpstart,tpend; float timeuse; // 获取该时刻的时间 gettimeofday(&start,NULL); function(); gettimeofday(&tpend,NULL); timeuse = 1000000*(tpend.tv_sec - tpend.tv_sec) + (tpend.tv_usec - tpstart.tv_usec); timeuse /= 1000000; pritnf("used time is: %f\n",timeuse); getchar(); return 0; }
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <math.h> void function() { int i,j; double y; for(i=0;i<1000;i++); for(j=0;j<1000;j++); y = sin((double)i); } int main() { struct time val tpstart,tpend; float timeuse; // 获取该时刻的时间 gettimeofday(&start,NULL); function(); gettimeofday(&tpend,NULL); timeuse = 1000000*(tpend.tv_sec - tpend.tv_sec) + (tpend.tv_usec - tpstart.tv_usec); timeuse /= 1000000; pritnf("used time is: %f\n",timeuse); getchar(); return 0; }
NVCC 编译选项 源文件.CU 源文件.cpp
1. 在GPU上执行的函数通常称为核函数。
2. 一般通过标识符__global__修饰,调用通过<<<参数1,参数2>>>,
参数1代表线程格里有多少线程块;参数2代表一个线程块里有多少线程。 #cudaMalloc( 1. 函数原型: cudaError_t cudaMalloc (void **devPtr, size_t size)。
2. 函数用处:与C语言中的malloc函数一样,只是此函数在GPU的内存你分配内存
3. 注意事项:
3.1. 可以将cudaMalloc()分配的指针传递给在设备上执行的函数;
3.2. 不可以在主机代码中使用cudaMalloc()分配的指针进行内存读写操作
# cudaMemcpy()
1. 函数原型:
cudaError_t cudaMemcpy (void *dst, const void *src, size_t count, cudaMemcpyK
2. 函数作用:与c语言中的memcpy函数一样,只是此函数可以在主机内存和GPU
内存之间互相拷贝数据。
3. 函数参数:cudaMemcpyKind kind表示数据拷贝方向,如果kind赋值为
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost表示数据从设备内存拷贝到主机内存。
#cudaFree()
1. 函数原型:cudaError_t cudaFree ( void* devPtr )。
2. 函数作用:与c语言中的free()函数一样,只是此函数释放的是cudaMalloc()分配的内存
b.Cuda线程
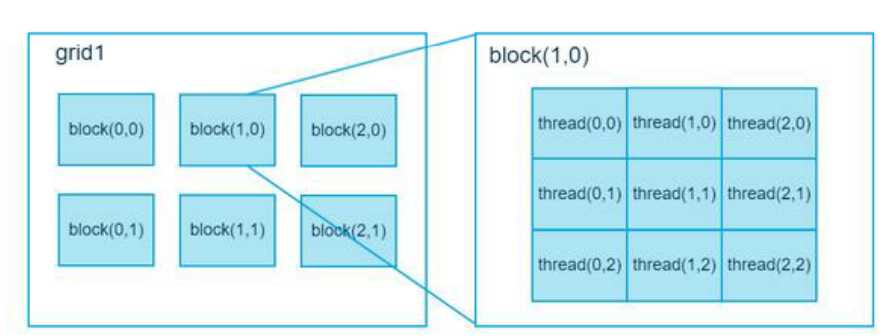
在CUDA中,显示芯片执行时的最小单位是thread,数个thread都可以组成一个block。数个block可以组成grid。每个thread都有自己的一份register 和local memory的空间。
同一个block中的每个thread则有共享的一份share memory
c.Cuda内存
GPU的内存中可读写的有:寄存器(regiesters)、Localmenory、共享内存(shared memory)和全局内存(global memory),只读的有:常量内存(constant memory)和 纹理内存(texture memroy)。
之前cudaMalloc 分配,复制的都是global memory。
共享内存则允许同一个block中的线程共享这一段内存。
#include <sys/time.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #define N 10 __global__ void vecAdd(int *a, int *b, int *c) { int tid = threadIdx.x; if (tid < N) { c[tid] = a[tid] + b[tid]; } } int main(void) { int a[N], b[N], c[N]; int *dev_a, *dev_b, *dev_c; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { a[i] = -i; b[i] = i * i; } cudaMalloc( (void **)&dev_a, N * sizeof(int) ); cudaMalloc( (void **)&dev_b, N * sizeof(int) ); cudaMalloc( (void **)&dev_c, N * sizeof(int) ); cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice ); cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice ); struct timeval tpstart,tpend; float timeuse; gettimeofday(&tpstart,NULL); vecAdd<<<1, N>>>(dev_a, dev_b, dev_c); gettimeofday(&tpend,NULL); timeuse=1000000*(tpend.tv_sec-tpstart.tv_sec)+ tpend.tv_usec-tpstart.tv_usec; timeuse/=1000000; printf("Used Time:%f\n",timeuse); cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost ); for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a[i], b[i], c[i]); } cudaFree(dev_a); cudaFree(dev_b); cudaFree(dev_c); return 0; }
标签:部分 共享内存 处理 idt ges 公司 day printf double
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lvxiaoning/p/7760975.html