/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don‘t change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//如果table为空,或者length=0,即没有数据,要resize()扩容
//Map刚创建完成时会走这段逻辑
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//如果算出的table对应位置没有数,就将其放到该位置上
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//如果冲突,要在这个节点上构造平衡树,并将数据存储到这棵树上
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果当前节点的hash值相同,key也相同,则将该节点替换
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//如果当前节点为平衡树节点,遍历平衡树,并将该值挂到树上
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//遍历类似链表的结构,如果找到链表的尾部,且没有超过最大长度放到链表上
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
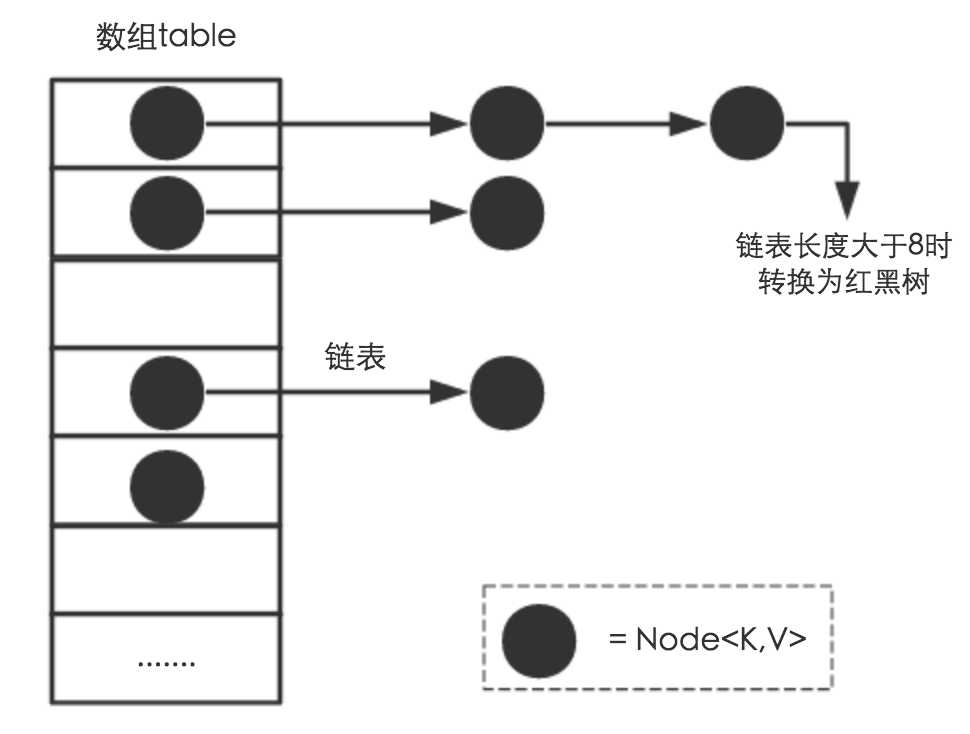
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
//如果超过最大长度,则放到treeify(红黑树)结构上
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
HashMap不是线程安全的,但是在读HashMap中的值时,其结构发生了变化,则会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException
她是通过自身的私有变量modCount控制的,modCount很像HashMap的版本号,如果其结构发生变化modCount的值肯定发生变化,代表一个新版本的HashMap产生了。
HashMap中有一个函数,用来计算比给定值大的第一个2的幂次方数
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
int数值占用4个字节,32bit。该算法的思路是,用给定值的最高位的1,将其最高位右边的位都填充为1。然后在加上1。
例如 cap = 20
n = cap - 1 = 19 0001 0011
n>>>1 = 0000 1001
n|=n>>>1 = 0001 1011
n>>>2 = 0000 0110
n|=n>>>2 = 0001 1111
n>>>4 = 0000 0001
n|=n>>>4= 0001 1111
n>>>8 与 n >>>16 都为0 所以最后的结果为 31(0001 1111) + 1 =32
table的size要是2的幂级数,是为了在resize()的时,对于某个node,要么不移动,要么移动到其位置*2的地方。
在resize()函数中有这样一段代码:
next = e.next;
// 如果e.hash 小于 oldCap 不移动存储的位置
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
// 如果 e.hash >= oldCap 要移动存储的位置
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
可以看出上面代码中设计到两个链表(loHead,loTail)和(hiHead,hiTail)。每一次循环都是往某个链表中添加一个元素。重点是为什么要弄两个链表。这是因为table中前半部分的element是不用移动的。
假设原来的capacity = 16 在往table中放数据时。都是e.hash&(capacity-1) ,数据都存放到0至15的位置。假设原来有一个element.hash < 16 则 e.hash&capacity == 0 。这里我们就明白了,原来table前部中的元素是不需要移动的。如果原来链表中存储着e.hash >= 16 的,这是在 e.hash & capacity != 0 这时就将其存储到table的后半部分。因为在resize()时调用的时oldCap == 16 当table.length = 32 时,我们假设原来有一个元素 e.hash ==18
e.hash & oldCap == 2,当再次分配时,会走(hiHead,hiTail)这段逻辑,放在角标为16+2 的位置。当扩容完成,我们用新的容量取余时,会计算的到18。证明在扩容时放数据的位置没有问题。
当节点为TreeNode时,调用TreeNode的split方法。在处理树节点时,也是先按链表处理,然后在重构成树。
TreeNode与Node之间的继承关系:
而且TreeNode中有一个变量prev
//bit 当前table长度
//e 当前树节点
for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next;
e.next = null;
//如果e.hash小于当前table的长度,
if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {
// 如果loTail为空,说明当前链表中没有数据
if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)
//数据头即为e
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
// 每次添加一个节点就将loTail指向当前节点
loTail = e;
// 计数器 +1 为了根据这个数值的大小决定存储成树形,还是链表
++lc;
}
else {
// 如果 e.hash >= 当前table的长度
// 如果当前链表中没有数据
if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)
// 将数据头指向当前节点
hiHead = e;
else
// 如果当前链表不为空,则在链表的尾部加上一个节点
hiTail.next = e;
// 尾部永远指向最后添加的节点
hiTail = e;
++hc;
}
}
// 当前链表遍历完成后,根据计数器决定其存成什么样子。
if (loHead != null) {
if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index] = loHead;
if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified)
loHead.treeify(tab);
}
}
if (hiHead != null) {
if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index + bit] = hiHead;
if (loHead != null)
hiHead.treeify(tab);
}
下面就应该看treeify(tab)的实现了,这个实现就是将单向链表转换为红黑树的过程。
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
//当前节点为x
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
// next为下一个节点
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
// 当前节点的左右子节点清空
x.left = x.right = null;
// 第一次进入时,根为空,这是给根赋值,且将根节点标记为黑色
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
// 如果不是第一次进入
else {
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
// 如果根节点的hash比当前节点的hash大
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1; //存到左边
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1; // 存到右边
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
// 如果dir < 0 且 p 指向根节点的左子节点,如果dir > 0 p 指向根节点的右子节点
// 如果 p 指向的子节点为空,则要存入树中的节点存入子节点,否则,p指向其某个子节点,然后重复for循环
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
// 当前节点的父节点为根节点
x.parent = xp;
// 根据dir 将x存入根节点的子节点中
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
// 保证树的平衡
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}
HashMap为什么使用红黑树而不使用平衡树呢?
1. 如果插入一个node引起了树的不平衡,AVL和RB-Tree都是最多只需要2次旋转操作,即两者都是O(1);但是在删除node引起树的不平衡时,最坏情况下,AVL需要维护从被删node到root这条路径上所有node的平衡性,因此需要旋转的量级O(logN),而RB-Tree最多只需3次旋转,只需要O(1)的复杂度。
2. 其次,AVL的结构相较RB-Tree来说更为平衡,在插入和删除node更容易引起Tree的unbalance,因此在大量数据需要插入或者删除时,AVL需要rebalance的频率会更高。因此,RB-Tree在需要大量插入和删除node的场景下,效率更高。自然,由于AVL高度平衡,因此AVL的search效率更高。
3. map的实现只是折衷了两者在search、insert以及delete下的效率。总体来说,RB-tree的统计性能是高于AVL的。
作者:知乎用户
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
红黑树为满足如下条件的二叉搜索树:
1. 每个结点或者为黑色或者为红色。
2. 根结点为黑色。
3. 每个叶结点(实际上就是NULL指针)都是黑色的。
4. 如果一个结点是红色的,那么它的两个子节点都是黑色的(也就是说,不能有两个相邻的红色结点)。
5. 对于每个结点,从该结点到其所有子孙叶结点的路径中所包含的黑色结点数量必须相同。
下面是关于删除元素的代码解释:
/**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
// 如果table为空,或没有数据,或者某有节点的给定hash没有对应的元素,则直接返回空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
// 如果找到这样一个节点的hash,key 都和给定的值相等,则将其记录到node中
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
// 否则 如果其有下一个节点
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 如果当前节点存的是树,则直接从树种找
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 否则即为链表,从链表中查找
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e; // p一直指向e的前一个节点
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
// node != null 表示找到了对应的节点,如果要值相等,这值相等,否则值不等于空,且值也要相等
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
// 如果当前节点为树,则要从树种移除
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
// 如果是链表中的第一个节点,tab[index]存链表头的地方指向其下一个节点
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
// 否则 将找到的节点从链表中删除
p.next = node.next; // p一直指向e的前一个节点
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
关于红黑树的旋转建议百度