标签:机器学习 bsp online log const printf 自己 += ++
吴恩达老师的机器学习公开课的第二课主要讲了随机梯度下降算法,我记录了一些要点并写了一点自己的想法于此。

以上便是第二节课的核心内容。
另外的内容还有随机梯度下降法。思想是很平凡的,当数据较多的时候随机选择数据进行梯度下降,以精度换速度。
梯度下降法似乎并不能处理局部最优的问题。吴恩达老师在课上给的解释是实际中大部分函数都是碗状的,无需考虑局部最优问题。
梯度下降很容易让人联想到模拟退火算法。
这里有模拟退火算法的一道典型例题:bzoj3580 http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3680
题意抽象后为给n个点的坐标(x,y)与权值w,找点ans使得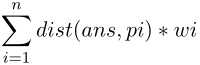 最小。
最小。
模拟退火算法用“醉鬼”思想尝试跳出局部最优问题。
#include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<cstdlib> #define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;++i) using namespace std; const double eps=1e-8; const double T_min=1e-8; const double PI=acos(-1.0); const double step=0.99; const int MAXN=10010; double tot; int n; struct Point { double x,y,w; Point() {} Point(double xx,double yy) {x=xx;y=yy;} Point operator -(const Point &b)const { return Point(x-b.x,y-b.y); } Point operator +(const Point &b)const { return Point(x+b.x,y+b.y); } double operator *(const Point &b)const { return x*b.x+y*b.y; } }p[MAXN]; Point now,ans; double dist(Point a,Point b) { return sqrt((a-b)*(a-b)); } double random01() { return (rand()%1000+1)/1000.0; } double fx(Point x) { double res=0.0; rep(i,1,n) res+=dist(x,p[i])*p[i].w; if(res<tot) {tot=res;ans=x;} return res; } int main() { srand(2333); //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); int a,b,w,dif; tot=1e18; scanf("%d",&n); rep(i,1,n) { scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y,&p[i].w); now=now+p[i]; } now.x/=n;now.y/=n; double T=100000.0,alpha; while(T>T_min) { alpha=2.0*PI*random01(); Point tmp(now.x+T*cos(alpha),now.y+T*sin(alpha)); dif=fx(now)-fx(tmp); if(dif>=0||exp(dif/T)>random01()) now=tmp; T*=step; } T=0.001; rep(i,1,1000) { alpha=2.0*PI*random01(); Point tmp(ans.x+ T*cos(alpha)*random01(),ans.y+T*sin(alpha)*random01()); fx(tmp); } printf("%.3f %.3f\n",ans.x,ans.y); return 0; }
标签:机器学习 bsp online log const printf 自己 += ++
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhixingr/p/7815736.html