标签:one 理解 put 目的 else 有序 set 上下文 硬件
一、实验目的
1.理解不同体系结构风格的具体内涵。
2.学习体系结构风格的具体实践。
二、实验环境
硬件: (依据具体情况填写)
软件:Java或任何一种自己熟悉的语言
三、实验内容
“上下文关键字”KWIC(Key Word in Context,文本中的关键字)检索系统接受有序的行集合:每一行是单词的有序集合;每一个单词又是字母的有序集合。通过重复地删除航中第一个单词,并把它插入行尾,每一行可以被“循环地移动”。KWIC检索系统以字母表的顺序输出一个所有行循环移动的列表。
尝试用不同的策略实现这个系统。选择2-3种体系结构风格来实现。
四、实验步骤:
采用主/子程序的风格
1、体系结构图:
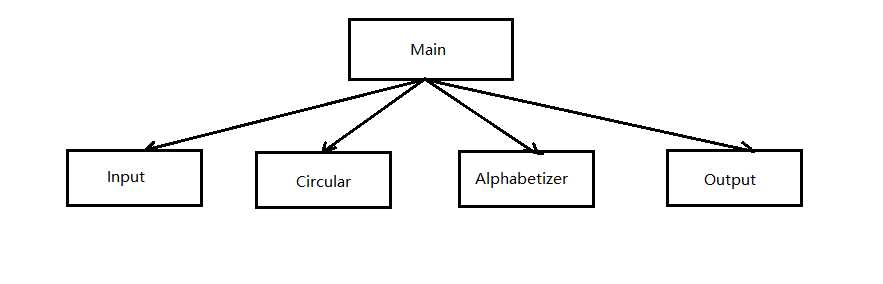
2、简述体系结构各部件的主要功能,实现思想。
上述的主程序/子程序的方法,将问题分解为输入(Input)、循环移动(Circular Shifter)、按字母表排序(Alphabetizer)、输出(Output)。
Input: 将读取到的每行的数据保存到inList
Circular Shifter:主函数调用该方法,该方法对characters中的每行的数据进行循环移位,并将移位得到的新行保存到outList
alphabetizer: 对circularShift中得到的行数据outList进行按字母顺序排序
Output:output方法遍历输出经过alphabetizer方法处理后的outList
3、写出主要的代码
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 /** 6 * KWIC(Key Word in Context,文本中的关键字) 7 * 采用主/子程序风格 8 * @author L 9 * 10 */ 11 public class KWIC { 12 13 private List<String[]> inList = new ArrayList<String[]>(); 14 private List<String[]> outList = new ArrayList<String[]>(); 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 KWIC test = new KWIC(); 17 test.input(); 18 test.CircularShifter(); 19 test.Alphabetizer(); 20 test.output(); 21 } 22 /** 23 * 输入 24 */ 25 private void input() { 26 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 27 System.out.println("========input========"); 28 while (true) { 29 String temp; 30 temp = scanner.nextLine(); 31 if (!temp.equals("!q")) { 32 inList.add(temp.split(" ")); 33 } 34 else{ 35 break; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 /** 40 * 循环位移 41 */ 42 private void CircularShifter() { 43 ArrayList<String[]> tempList = new ArrayList<String[]>(); 44 tempList.addAll(inList); 45 String temp; 46 for (int i = 0; i < tempList.size(); i++) { 47 for (int j = 0;j < tempList.get(i).length; j++) { 48 outList.add(tempList.get(i).clone()); 49 temp = tempList.get(i)[0]; 50 for (int k = 0;k < tempList.get(i).length-1; k++) { 51 tempList.get(i)[k] = tempList.get(i)[k+1]; 52 if(k == tempList.get(i).length-2){ 53 54 tempList.get(i)[tempList.get(i).length-1]=temp; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 /** 61 * 按字母表顺序排序 62 */ 63 private void Alphabetizer(){ 64 String[] temp; 65 for(int i = 0;i<outList.size();i++){ 66 for(int j = i;j<outList.size()-1;j++){ 67 if(outList.get(i)[0].toLowerCase().charAt(0)>outList.get(j+1)[0].toLowerCase().charAt(0)){ 68 temp = outList.get(i); 69 outList.set(i, outList.get(j+1)); 70 outList.set(j+1, temp); 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 /** 76 * 输出 77 */ 78 private void output(){ 79 System.out.println("========onput========"); 80 for(int i = 0;i<outList.size();i++){ 81 for (int j = 0;j<outList.get(i).length;j++){ 82 System.out.print(outList.get(i)[j]+" "); 83 } 84 System.out.println(""); 85 } 86 } 87 }
采用管道过滤器风格
1、体系结构图:
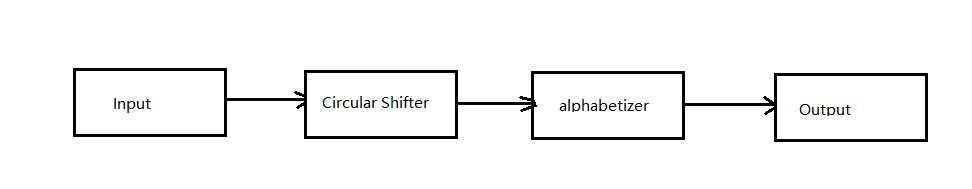
2、简述体系结构各部件的主要功能,实现思想。
上述的管道过滤器的方法,将问题分解为输入(Input)、循环移动(Circular Shifter)、按字母表排序(Alphabetizer)、输出(Output)。
Input: 将读取到的每行的数据保存到inList,调用Circular Shifter方法
Circular Shifter:主函数调用该方法,该方法对characters中的每行的数据进行循环移位,并将移位得到的新行保存到outList,调用alphabetizer方法
alphabetizer: 对circularShift中得到的行数据outList进行按字母顺序排序,调用Output方法
Output:output方法遍历输出经过alphabetizer方法处理后的outList
3、写出主要的代码
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 /** 6 * KWIC(Key Word in Context,文本中的关键字) 7 * 采用管道过滤器风格 8 * @author L 9 * 10 */ 11 public class KWIC2 { 12 13 private List<String[]> inList = new ArrayList<String[]>(); 14 private List<String[]> outList = new ArrayList<String[]>(); 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 KWIC2 test = new KWIC2(); 17 test.input(); 18 } 19 private void input() { 20 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 21 System.out.println("========input========"); 22 while (true) { 23 String temp; 24 temp = scanner.nextLine(); 25 if (!temp.equals("!q")) { 26 inList.add(temp.split(" ")); 27 } 28 else{ 29 break; 30 } 31 } 32 CircularShifter(); 33 } 34 35 private void CircularShifter() { 36 ArrayList<String[]> tempList = new ArrayList<String[]>(); 37 tempList.addAll(inList); 38 String temp; 39 for (int i = 0; i < tempList.size(); i++) { 40 for (int j = 0;j < tempList.get(i).length; j++) { 41 outList.add(tempList.get(i).clone()); 42 temp = tempList.get(i)[0]; 43 for (int k = 0;k < tempList.get(i).length-1; k++) { 44 tempList.get(i)[k] = tempList.get(i)[k+1]; 45 if(k == tempList.get(i).length-2){ 46 47 tempList.get(i)[tempList.get(i).length-1]=temp; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 Alphabetizer(); 53 } 54 private void Alphabetizer(){ 55 String[] temp; 56 for(int i = 0;i<outList.size();i++){ 57 for(int j = i;j<outList.size()-1;j++){ 58 if(outList.get(i)[0].toLowerCase().charAt(0)>outList.get(j+1)[0].toLowerCase().charAt(0)){ 59 temp = outList.get(i); 60 outList.set(i, outList.get(j+1)); 61 outList.set(j+1, temp); 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 output(); 66 } 67 private void output(){ 68 System.out.println("========onput========"); 69 for(int i = 0;i<outList.size();i++){ 70 for (int j = 0;j<outList.get(i).length;j++){ 71 System.out.print(outList.get(i)[j]+" "); 72 } 73 System.out.println(""); 74 } 75 } 76 }
显示结果:

标签:one 理解 put 目的 else 有序 set 上下文 硬件
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/DarrenFly/p/7857871.html