标签:show usr png min .so sum lin ini on()
TensorFlow本身是分布式机器学习框架,所以是基于深度学习的,前一篇TensorFlow简易学习[2]:实现线性回归对只一般算法的举例只是为说明TensorFlow的广泛性。本文将通过示例TensorFlow如何创建、训练一个神经网络。
主要包括以下内容:
神经网络基础
基本激励函数
创建神经网络
关于神经网络资源很多,这里推荐吴恩达的一个Tutorial。
关于激励函数的作用,常有解释:不使用激励函数的话,神经网络的每层都只是做线性变换,多层输入叠加后也还是线性变换。因为线性模型的表达能力不够,激励函数可以引入非线性因素(ref1)。 关于如何选择激励函数,激励函数的优缺点等可参考已标识ref1, ref2。
常用激励函数有(ref2): tanh, relu, sigmod, softplus
激励函数在TensorFlow代码实现:
#!/usr/bin/python ‘‘‘ Show the most used activation functions in Network ‘‘‘ import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 200) #1. struct #following are popular activation functions y_relu = tf.nn.relu(x) y_sigmod = tf.nn.sigmoid(x) y_tanh = tf.nn.tanh(x) y_softplus = tf.nn.softplus(x) #2. session sess = tf.Session() y_relu, y_sigmod, y_tanh, y_softplus =sess.run([y_relu, y_sigmod, y_tanh, y_softplus]) # plot these activation functions plt.figure(1, figsize=(8,6)) plt.subplot(221) plt.plot(x, y_relu, c =‘red‘, label = ‘y_relu‘) plt.ylim((-1, 5)) plt.legend(loc = ‘best‘) plt.subplot(222) plt.plot(x, y_sigmod, c =‘b‘, label = ‘y_sigmod‘) plt.ylim((-1, 5)) plt.legend(loc = ‘best‘) plt.subplot(223) plt.plot(x, y_tanh, c =‘b‘, label = ‘y_tanh‘) plt.ylim((-1, 5)) plt.legend(loc = ‘best‘) plt.subplot(224) plt.plot(x, y_softplus, c =‘c‘, label = ‘y_softplus‘) plt.ylim((-1, 5)) plt.legend(loc = ‘best‘) plt.show()
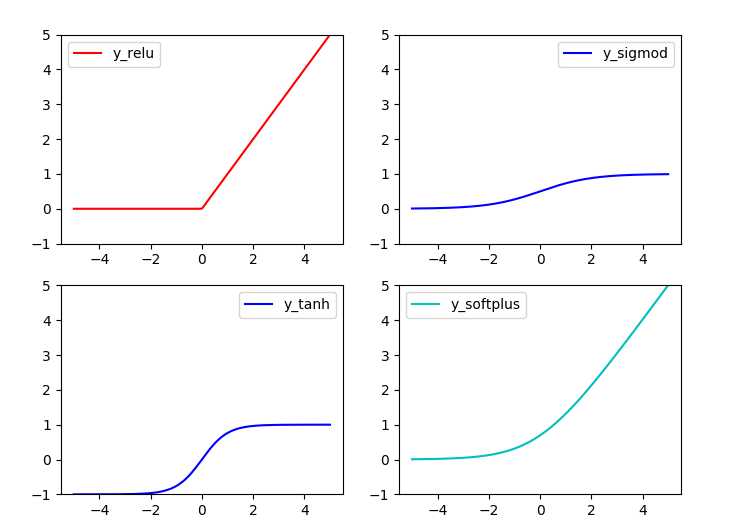
定义函数用于创建隐藏层/输出层:
#add a layer and return outputs of the layer def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None): #1. initial weights[in_size, out_size] Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size])) #2. bias: (+0.1) biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size]) + 0.1) #3. input*Weight + bias Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases #4. activation if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs
此处定义一个三层网络,即:输入-单层隐藏层-输出层。可通过以上函数添加层数。网络为全连接网络。
# add hidden layer l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) # add output layer prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
利用梯度下降,训练1000次。
loss function: suqare error loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) GD = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1) train_step = GD.minimize(loss)
#!/usr/bin/python ‘‘‘ Build a simple network ‘‘‘ import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np #1. add_layer def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None): #1. initial weights[in_size, out_size] Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size])) #2. bias: (+0.1) biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size]) + 0.1) #3. input*Weight + bias Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases #4. activation ## when activation_function is None then outlayer if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs ##begin build network struct## ##network: 1 * 10 * 1 #2. create data x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis] noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise #3. placehoder: waiting for the training data xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) #4. add hidden layer h1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) h2 = add_layer(h1, 10, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) #5. add output layer prediction = add_layer(h2, 10, 1, activation_function=None) #6. loss function: suqare error loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) GD = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1) train_step = GD.minimize(loss) ## End build network struct ### ## Initial the variables if int((tf.__version__).split(‘.‘)[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split(‘.‘)[0]) < 1: init = tf.initialize_all_variables() else: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() ## Session sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) # called in the visual ## Traing for step in range(1000): #当运算要用到placeholder时,就需要feed_dict这个字典来指定输入 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs:x_data, ys:y_data}) if i % 50 == 0: # to visualize the result and improvement try: ax.lines.remove(lines[0]) except Exception: pass prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data}) # plot the prediction lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, ‘r-‘, lw=5) plt.pause(1) sess.close()
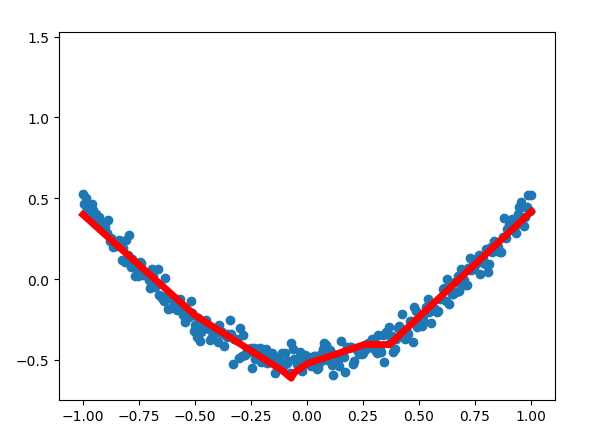
至此TensorFlow简易学习完结。
--------------------------------------
说明:本列为前期学习时记录,为基本概念和操作,不涉及深入部分。文字部分参考在文中注明,代码参考莫凡
标签:show usr png min .so sum lin ini on()
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/space-place/p/7891496.html