装系统相信大家都不陌生,对于运维攻城狮可以说是家常便饭,老大说:小刘今天装一下系统,明天把那几台机器系统重装一下。就这样一上午,一天就这么过去了。耗时费力不说,重点是没有效率,没错这就是我的痛点。一个好的运维工作时间清闲才说明你的工作做到位了。万一某天说小刘把100个新机器装一下系统。。。该如何彻底解放双手呢?
今天我们介绍一款无人值守自动化部署系统的软件Cobbler,真正是实现从机器上架,插上网线一切都交给Cobbler来完成
简介:
先介绍下Cobbler(补鞋匠),根据其名称可想而知。Cobbler是红帽(Red Hat)2008年推出的网络安装服务器套件 ,它大大降低 Linux 网络安装的技术门槛降,对于自动化运维可以必须要学的基础服务套件。
Cobbler是一款自动化操作系统部署的实现工具,由Python语言开发,是对PXE的二次封装。融合多种特性,提供了CLI和Web的管理形式。同时,Cobbler也提供了API接口,方便二次开发使用。它不仅可以安装物理机,同时也支持kvm、xen虚拟化、的安装。另外,它还能结合Puppet等集中化管理软件,实现自动化管理,同时还可以管理DHCP,DNS,以及yum包镜像。
Cobbler各个组件的关系(如下图)

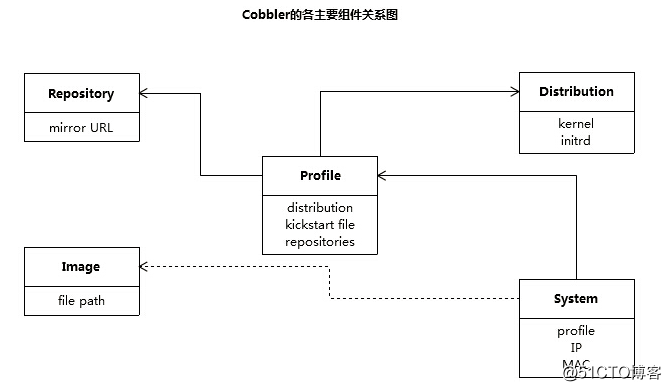
通过 cobbler,可以轻松实现对RedHat/Centos/Fedora系统的快速部署,同时也支持Suse 和Debian(Ubuntu)系统。Cobbler集成的服务:
PXE服务支持
DHCP服务管理
DNS服务管理(可选bind,dnsmasq)
电源管理
Kickstart服务支持
YUM仓库管理
TFTP(PXE启动时需要)
Apache(提供kickstart的安装源,并提供定制化的kickstart配置)
结合这些集成服务,Cobbler工作流程:

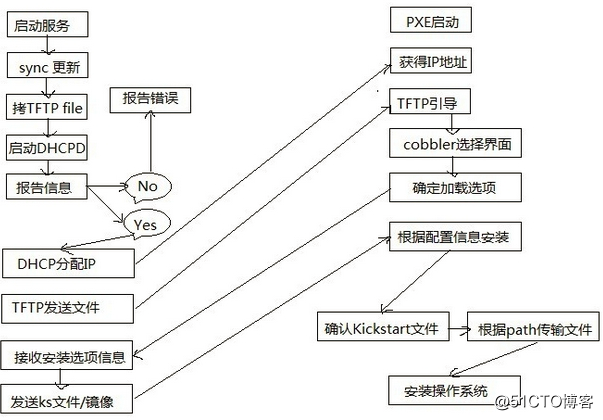
环境:
Cobbler服务器:CentOS6.9 ---> IP:192.168.137.38
客户端(需要部署Linux系统及IP):
CentOS6.8 ---> IP地址段:192.168.137.100-254 DNS:8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4
CentOS7.4 ---> IP地址段:192.168.137.100-254 DNS:8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4
准备镜像文件
CentOS-7.4-x86_64
CentOS-6.8-x86_64
Cobbler服务端安装部署:
以下配置可用通过脚本自动安装配置,笔者写了个脚本自动完成部署(github)地址:
https://github.com/Ljohn001/ljohn_ops/tree/master/cobbler
用着顺手记得给个Star,请赐予我力量吧,笔者的脚本功力还很弱,但脚本在CentOS68/69反复测了5-6遍才让它面世,这是一种苛求,亦是一种执着。
一:配置YUM源(epel)
Cobbler 集成服务需要epel,这里提供Aliyun的镜像
# cp -r /etc/yum.repos.d /etc/yum.repos.d.backup && rm -rf /etc/yum.repos.d/*
# wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/{Centos-6.repo,epel-6.repo}二:关闭服务端的防火墙及selinux
清除防火墙规则,并关闭(或者开放22 80 67 68 69 443 端口)
# iptables -F && /etc/inist.d/iptables stop # chkconfig iptables off 关闭selinux # setenforce 0 # sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/^SELINUX=.*/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
三:安装Cobbler集成服务
安装Cobbler 程序 # yum -y install cobbler cobbler-web tftp tftp-server xinetd dhcp httpd pykickstart mod_wsgi mod_ssl rsync 安装Cobbler 依赖程序 # yum -y install debmirror python-ctypes python-cheetah python-netaddr python-simplejson python-urlgrabber PyYAML syslinux cman fence-agents createrepo mkisofs yum-utils debian/ubuntu 系统需要 debmirror 软件包;想使用电源管理功能的话需要安装 cman 或fence-agents。
四:配置Cobbler及集成服务
#设置部署系统初始密码
# openssl passwd -1 -salt 'ljohn' '123456' # -salt 表示”加盐“ , ”ljohn“ 可以是任意字符 $1$ljohn$yBMDpKkntQ9jfV1ZAWKpU1
1、修改Coobler配置文件
# cp /etc/cobbler/settings{,.bak}
# sed -i 's@default_password_crypted: .*@default_password_crypted: "\$1\$ljohn\$yBMDpKkntQ9jfV1ZAWKpU1"@'/etc/cobbler/settings##注意$ 需要转义
# sed -i "s/server: 127.0.0.1/server: 192.168.137.38/g" /etc/cobbler/settings
# sed -i "s/next_server: 127.0.0.1/next_server: 192.168.137.38/g" /etc/cobbler/settings
# pxe安装 只允许一次,防止误操作( 在正式环境有用。实际测试来,这个功能可以屏蔽掉 )
# sed -i 's/pxe_just_once: 0/pxe_just_once: 1/g' /etc/cobbler/settings
# sed -i 's/manage_rsync: 0/manage_rsync: 1/g' /etc/cobbler/settings
# sed -i 's/manage_dhcp: 0/manage_dhcp: 1/g' /etc/cobbler/settings2、配置debmirror
# debian/ubuntu 系统需要 debmirror 的配置
# cp /etc/debmirror.conf{,.bak}
# sed -i -e 's/@dists=.*/#@dists=/' /etc/debmirror.conf
# sed -i -e 's/@arches=.*/#@arches=/' /etc/debmirror.conf3、修改httpd配置
# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf{,.bak}
# sed -i "s/#ServerName www.example.com:80/ServerName 192.168.137.38:80/" /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# sed -i 's/#LoadModule/LoadModule/g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/wsgi.conf4、修改tftp配置
# sed -i '/disable/c disable = no' /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
5、配置rsync
# sed -i -e 's/= yes/= no/g' /etc/xinetd.d/rsync
6、修改dhcp配置
# cp /etc/cobbler/dhcp.template{,.bak}
# sed -i 's/DHCPDARGS=.*/DHCPDARGS=eth0/' /etc/sysconfig/dhcpd
##将DHCP配置文件中的192.168.1部分修改为192.168.0,删除22,23行;并保存为原始文档。##
# sed -i.ori 's@192.168.1@192.168.137@g;22d;23d' /etc/cobbler/dhcp.template
#也可以通过vim /etc/cobbler/dhcp.template,查看dhcp配置文件仅编辑修改部分
............
subnet 192.168.137.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
range dynamic-bootp 192.168.137.100 192.168.137.254;
default-lease-time 21600;
max-lease-time 43200;
next-server $next_server;
............7、配置cobbler启动服务,管理集成服务
设置开机启动:
# chkconfig httpd on # chkconfig xinetd on # chkconfig cobblerd on # chkconfig dhcpd on # /etc/init.d/httpd restart # /etc/init.d/xinetd restart # /etc/init.d/cobblerd restart cobbler SysV 服务脚本 cat >/etc/init.d/cobbler <<EOF #!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 345 80 90 # description:cobbler case $1 in start) /etc/init.d/httpd start /etc/init.d/xinetd start /etc/init.d/dhcpd start /etc/init.d/cobblerd start ;; stop) /etc/init.d/httpd stop /etc/init.d/xinetd stop /etc/init.d/dhcpd stop /etc/init.d/cobblerd stop ;; restart) /etc/init.d/httpd restart /etc/init.d/xinetd restart /etc/init.d/dhcpd restart /etc/init.d/cobblerd restart ;; status) /etc/init.d/httpd status /etc/init.d/xinetd status /etc/init.d/dhcpd status /etc/init.d/cobblerd status ;; sync) cobbler sync ;; *) echo "Input error,please in put 'start|stop|restart|status|sync'!" exit 2 ;; esac EOF # chmod +x /etc/init.d/cobbler # chkconfig cobbler on # /etc/init.d/cobbler restart Stopping httpd: [ OK ] Starting httpd: [ OK ] Stopping xinetd: [ OK ] Starting xinetd: [ OK ] Shutting down dhcpd: [ OK ] Starting dhcpd: [ OK ] Stopping cobbler daemon: [ OK ] Starting cobbler daemon: [ OK ] # cobbler get-loader #加载部分缺失的网络boot-loaders,否则会报错。 # cobbler sync #同步配置到dhcp pxe和数据目录 # cobbler check #检查是否有错误
# 注意:
#这里要提一下,根据错误提示自行度娘,连google都不需要,笔者就不啰嗦了。
所有配置基本完成,接下来我们来介绍一下cobbler命令,以及导入镜像
五:Cobbler命令管理
1、Cobbler命令
# cobbler usage ===== cobbler <distro|profile|system|repo|image|mgmtclass|package|file> ... [add|edit|copy|getks*|list|remove|rename|report] [options|--help] cobbler <aclsetup|buildiso|import|list|replicate|report|reposync|sync|validateks|version|signature|get-loaders|hardlink> [options|--help] Cobbler 命令介绍: cobbler get-loaders #加载部分缺失的网络boot-loaders cobbler check #检查cobbler配置 cobbler sync #同步配置到dhcp pxe和数据目录 cobbler list #列出所有的cobbler元素 cobbler import #导入安装的系统光盘镜像 cobbler report #列出各元素的详细信息 cobbler distro #查看导入的发行版系统信息 cobbler profile #查看配置信息 cobbler system #查看添加的系统信息 cobbler reposync #同步yum仓库到本地 cobbler signature update cobbler --help #获得cobbler的帮助 cobbler distro --help #获得cobbler子命令的帮助 获取帮助: #cobbler import --help Usage: cobbler [options] Options: -h, --help show this help message and exit --arch=ARCH OS architecture being imported --breed=BREED the breed being imported --os-version=OS_VERSION the version being imported --path=PATH local path or rsync location --name=NAME name, ex 'RHEL-5' --available-as=AVAILABLE_AS tree is here, don't mirror --kickstart=KICKSTART_FILE assign this kickstart file --rsync-flags=RSYNC_FLAGS pass additional flags to rsync
2、导入镜像(重点)
# Cobbler服务器先挂载CentOS7的系统镜像
# mount -r -t iso9660 /dev/cdrom /mnt
# 导入系统镜像
# cobbler import --path=/mnt --name=CentOS-7.4-x86_64 --arch=x86_64 # cobbler import --path=/mnt --name=CentOS-6.8-x86_64 --arch=x86_64 # --path 镜像路径 # --name 为安装源定义一个名字 # --arch 指定安装源是32位、64位、ia64, 目前支持的选项有: x86│x86_64│ia64 # 安装源的唯一标示就是根据name参数来定义,本例导入成功后,安装源的唯一标示就是:CentOS-7.4-x86_64,如果重复,系统会提示导入失败。 # cobbler distro list # 查看镜像列表 CentOS-7.4-x86_64 CentOS-7.4-x86_64
# 注意:
# 镜像存放目录,cobbler会将镜像中的所有安装文件拷贝到本地一份,放在/var/www/cobbler/ks_mirror下的CentOS-7.4-x86_64目录下。因此/var/www/cobbler目录必须具有足够容纳安装文件的空间,如果空间不够,可以对/var/www/cobbler目录进行移动,建软链接来修改文件存储位置。
例如:
# ln -s /home/cobbler /var/www
# cd /var/www/cobbler/ks_mirror/ && ls
CentOS-7.4-x86_64 CentOS-6.8-x86_64 config
# ls CentOS-7.4-x86_64/ CentOS_BuildTag GPL LiveOS RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 EFI images Packages RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-Testing-7 EULA isolinux repodata TRANS.TBL
到这里表示镜像已经导入成功了。
# 注意:
# 比较与光盘的文件大小是否一致
# du -sh /var/www/cobbler/ks_mirror/CentOS-7.4-x86_64/ # du -sh /mnt
六、 创建kickstarts文件(RHEL/CentOS)
这里要提一下,不同操作系统的kickstart 文件略有不同,笔者现在演示的RHEL/CentOS系列操作系统ks文件
1、 Cobbler的ks.cfg文件存放位置
# cd /var/lib/cobbler/kickstarts/ && ls#自带很多 default.ks install_profiles sample_autoyast.xml sample_esxi4.ks sample_old.seed esxi4-ks.cfg legacy.ks sample_end.ks(默认使用的ks文件) sample_esxi5.ks sample.seed esxi5-ks.cfg pxerescue.ks sample_esx4.ks sample.ks
2、编辑CentOS6.8和CentOS7.4 kickstart配置文件
这里贴出来我最小化安装两个版本ks文件,笔者喜欢最小化安装,你也可以根据自己需要,定制ks文件。
提供两种配置ks的方法:
方法1、 每安装好一台Centos机器,Centos安装程序都会创建一个kickstart配置文件,记录你的真实安装配置。如果你希望实现和某系统类似的安装,可以基于该系统的kickstart配置文件来生成你自己的kickstart配置文件。(生成的文件名字叫anaconda-ks.cfg位于/root/anaconda-ks.cfg)
方法2、Centos提供了一个图形化的kickstart配置工具。在任何一个安装好的Linux系统上运行该工具,就可以很容易地创建你自己的kickstart配置文件。kickstart配置工具命令为redhat-config-kickstart(RHEL3)或system-config-kickstart(RHEL5/6/7)
# yum install system-config-kickstart #安装
# yum groupinstall "X Window System" #安装X Window图形界面
# system-config-kickstart #运行kickstart配置
#笔者不喜欢使用Linux运行图形化界面,浪费资源,有兴趣的伙伴可以研究一下
接下来给两个实例(重点)
实例一(CentOS7.4 ks)
#platform=x86, AMD64, or Intel EM64T #version=DEVEL # Install OS instead of upgrade install # Keyboard layouts # old format: keyboard us # new format: keyboard --vckeymap=us --xlayouts='us' # Root password rootpw --iscrypted $1$ljohn$yBMDpKkntQ9jfV1ZAWKpU1 # Use network installation url --url="http://192.168.137.38/cobbler/ks_mirror/CentOS-7.4-x86_64/" # System language lang en_US.UTF-8 # Firewall configuration firewall --disabled # System authorization information auth --useshadow --passalgo=sha512 # Use graphical install graphical # Run the Setup Agent on first boot firstboot --enable # SELinux configuration selinux --disabled # Do not configure the X Window System skipx # System services services --disabled="chronyd" ignoredisk --only-use=sda # Network information network --bootproto=dhcp --device=eth0 --onboot=on #network --bootproto=static --device=eth0 --gateway=192.168.137.1 --ip=192.168.137.40 --nameserver=8.8.8.8 --netmask=255.255.255.0 --activate # Reboot after installation reboot # System timezone timezone Asia/Shanghai # System bootloader configuration bootloader --location=mbr --boot-drive=sda # Clear the Master Boot Record zerombr # Partition clearing information clearpart --all --initlabel # Disk partitioning information part /boot --asprimary --fstype="xfs" --size=1024 part swap --fstype="swap" --size=2048 part / --fstype="xfs" --grow --size=1 %packages @^minimal @core %end
实例二(CentOS6.8 ks):
#platform=x86, AMD64, or Intel EM64T #version=DEVEL # Firewall configuration firewall --disabled # Install OS instead of upgrade install # Use network installation url --url="http://192.168.137.38/cobbler/ks_mirror/CentOS-6.8-x86_64/" #repo --name="CentOS" --baseurl=cdrom:sr0 --cost=100 # Root password rootpw --iscrypted $1$ljohn$yBMDpKkntQ9jfV1ZAWKpU1 # System authorization information auth --useshadow --passalgo=sha512 # Use graphical install graphical # System keyboard keyboard us # System language lang en_US.UTF-8 # SELinux configuration selinux --disabled # Do not configure the X Window System skipx # Installation logging level #logging --level=info # Reboot after installation reboot # System timezone timezone Asia/Shanghai # Network information network --bootproto=dhcp --device=eth0 --onboot=on #network --bootproto=dhcp --device=eth1 --onboot=on # System bootloader configuration bootloader --append="crashkernel=auto rhgb quiet" --location=mbr --driveorder="sda" # Clear the Master Boot Record zerombr # Partition clearing information clearpart --all --initlabel # Disk partitioning information part /boot --asprimary --fstype="ext4" --size=500 part swap --fstype="swap" --size=2048 part / --fstype="ext4" --grow --size=1 %packages --nobase @core %end
注意:
这两个实例安装包都使用了core的最小化版本安装,可以大大缩短系统部署时间,毕竟时间就是金钱。如果有需要的,可以在packages后面添加一些常用的工具,这里不再赘述。
3、关联镜像与kickstart 文件
# cobbler profile report --name CentOS-7.4-x86_64#查看镜像是否存在, # cobbler profile report --name CentOS-6.8-x86_64 # cobbler profile edit --name=CentOS-7.4-x86_64 --kopts='net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0'#这里还原centos7网卡名为“eth0” # cobbler profile edit --name=CentOS-7.4-x86_64 --distro=CentOS-7.4-x86_64 --kickstart=/var/lib/cobbler/kickstarts/CentOS-7.4-x86_64.cfg #关联ks文件与对应的CentOS7.4镜像 # cobbler profile edit --name=CentOS-6.8-x86_64 --distro=CentOS-6.8-x86_64 --kickstart=/var/lib/cobbler/kickstarts/CentOS-6.8-x86_64.cfg # service cobbler sync #与cobbler sync作用相同,同步配置,每次对cobbler更改都要执行同步
七、无人值守安装系统
安装启动前保证要安装的机器,所在的物理网络与现在Cobbler畅通,如果是虚拟机(VMware),要关闭其自身的DHCP服务
编辑--> 虚拟网络编辑器 --> 使用本地DHCP服务将IP地址分配给虚拟机(取消勾选),避免和Cobbler服务器的DHCP冲突。
虚拟机需要先创建一个虚拟机(按需配置,切记如果是CentOS7.x以上一定要给2G的内存,这都是坑...希望你没踩到)
1、检查cobbler各个组件
# cobbler sync # cobbler check # cobbler distro list # cobbler profile report --name CentOS-7.4-x86_64#查看你需要安装的镜像相关配置是否正确
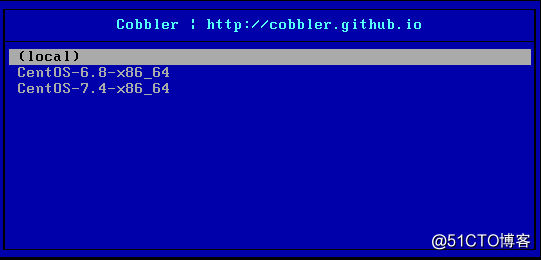
2、启动机器:
选择镜像安装即可

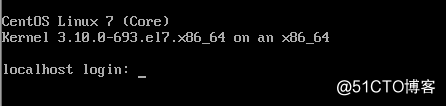
3、安装完成如图:

Cobbler-web 图形化配置
这里配置不做说明,
Linux系统重装测试
1,先确定当前linux系统中已经安装了koan软件。对于koan的安装可以放到ks文件中在安装系统的过程中完成安装操作。执行如下命令检查
# rpm -qa|grep koan koan-2.0.11-2.el6.noarch # yum install koan#安装koan
2,有了koan软件后可以执行如下操作,查看cobbler上的系统版本列表
#koan --server=192.168.137.38 --list=profiles - looking for Cobbler at http://192.168.137.38:80/cobbler_api CentOS-6.8-x86_64 CentOS-7.4-x86_64
这里我们选择CentOS-7.4-x86_64来重装。可以执行如下命令
# koan --server=192.168.137.38 --profile=CentOS-7.4-x86_64 --replace-self # reboot #直接重启即可自动重装
红色部分是手工输入的,从其他部分信息可以看到,koan帮我们做了很多本该人工操作的内容。
附录1:
Cobbler目录说明
1、Cobbler配置文件目录:/etc/cobbler
/etc/cobbler/settings #cobbler主配置文件 /etc/cobbler/dhcp.template #DHCP服务的配置模板 /etc/cobbler/tftpd.template #tftp服务的配置模板 /etc/cobbler/rsync.template #rsync服务的配置模板 /etc/cobbler/iso #iso模板配置文件 /etc/cobbler/pxe #pxe模板文件 /etc/cobbler/power #电源的配置文件 /etc/cobbler/users.conf #Web服务授权配置文件 /etc/cobbler/users.digest #用于web访问的用户名密码配置文件 /etc/cobbler/dnsmasq.template #DNS服务的配置模板 /etc/cobbler/modules.conf #Cobbler模块配置文件
2、Cobbler数据目录:/var/lib/cobbler
/var/lib/cobbler/config #配置文件 /var/lib/cobbler/triggers #Cobbler命令 /var/lib/cobbler/kickstarts #默认存放kickstart文件 /var/lib/cobbler/loaders #存放的各种引导程序
3、系统安装镜像目录:/var/www/cobbler
/var/www/cobbler/ks_mirror #导入的系统镜像列表 /var/www/cobbler/images #导入的系统镜像启动文件 /var/www/cobbler/repo_mirror #yum源存储目录
4、日志目录:/var/log/cobbler
/var/log/cobbler/install.log #客户端系统安装日志 /var/log/cobbler/cobbler.log #cobbler日志
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/ljohn/2045011