标签:class strong position 在顶部 高度 flex ima 超出 区域
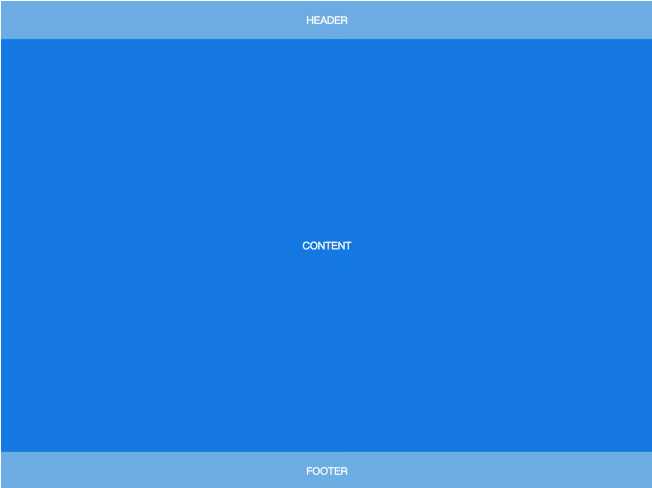
第一种:上中下布局(Sticky Footer)
1当页面内容高度小于可视区域高度时,footer 吸附在底部;
2当页面内容高度大于可视区域高度时,footer 被撑开排在 content 下方
<body> <header>HEADER</header> <article>CONTENT</article> <footer>FOOTER</footer> </body>
body {
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
article {
flex: auto;
}
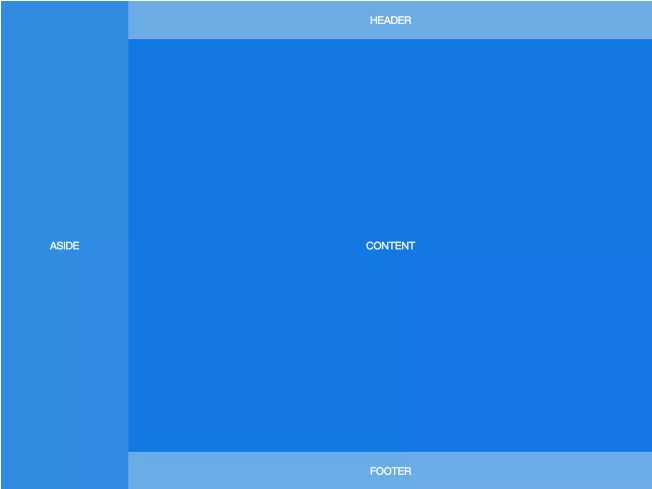
第二种:Fixed-Width Sidebar——在上-中-下布局的基础上,加了左侧定宽 sidebar。
<body>
<header>HEADER</header>
<div class="content">
<aside>ASIDE</aside>
<article>CONTENT</article>
</div>
<footer>FOOTER</footer>
</body>
body {
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.content {
flex: auto;
display: flex;
}
.content article {
flex: auto;
}
第三种:Sidebar——左边是定宽 sidebar,右边是上-中-下布局。
<body>
<aside>ASIDE</aside>
<div class="content">
<header>HEADER</header>
<article>CONTENT</article>
<footer>FOOTER</footer>
</div>
</body>
body {
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
}
aside {
flex: none;
}
.content {
flex: auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.content article {
flex: auto;
}
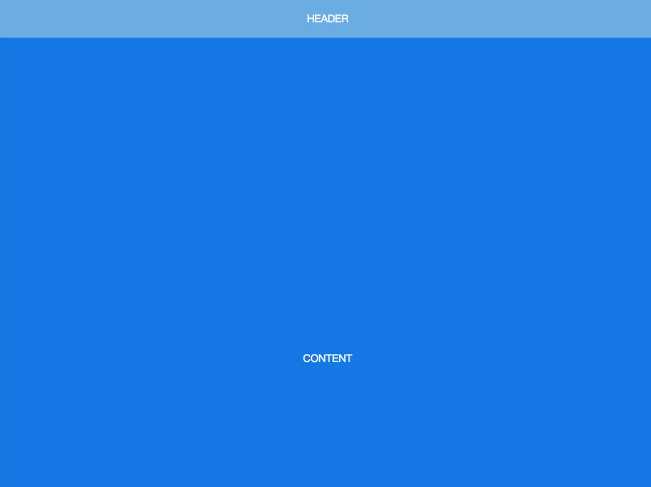
第四种:Sticky Header还是上-中-下布局,区别是 header 固定在顶部,不会随着页面滚动。
<body> <header>HEADER</header> <article>CONTENT</article> <footer>FOOTER</footer> </body>
body {
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
padding-top: 60px;
}
header {
height: 60px;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
padding: 0;
}
article {
flex: auto;
height: 1000px;
}
第五种:Sticky Sidebar左侧 sidebar 固定在左侧且与视窗同高,当内容超出视窗高度时,在 sidebar 内部出现滚动条。左右两侧滚动条互相独立。
<body>
<aside>
ASIDE
<p>item</p>
<p>item</p>
<!-- many items -->
<p>item</p>
</aside>
<div class="content">
<header>HEADER</header>
<article>CONTENT</article>
<footer>FOOTER</footer>
</div>
</body>
body {
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
}
aside {
flex: none;
width: 200px;
overflow-y: auto;
display: block;
}
.content {
flex: auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
overflow-y: auto;
}
.content article {
flex: auto;
}

标签:class strong position 在顶部 高度 flex ima 超出 区域
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liumengdie/p/7920467.html