标签:style blog http io os 使用 ar for 数据
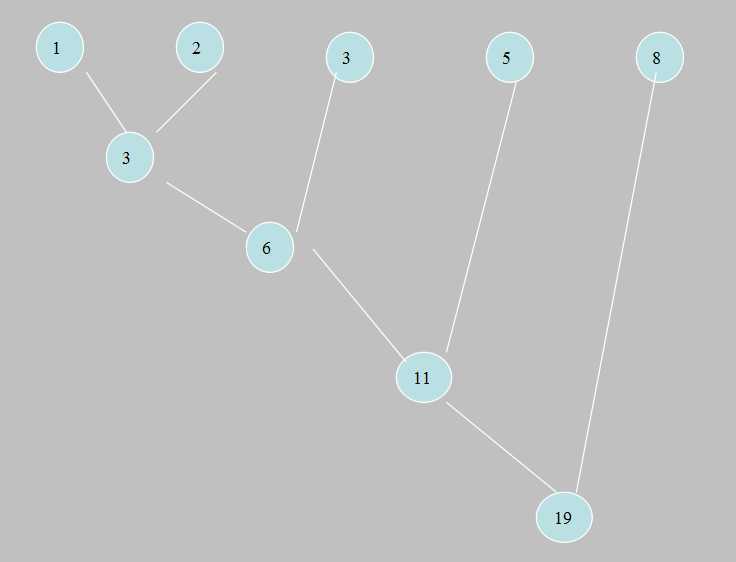
如上图中的2,用4位二进制(总共4层)来表示,同时总共出现2次。即共需要位数为2*4,实际上反应在哈佛曼树中,即为在每层都加上2,总共加了4次(4即为2的层数,从最底层一直到19,19不算),因此将除最顶层19除外,将树种所有的数总加起来,即为每个数总共需要的位数。
关于priority_queue<int,vecto<int>r,greater<int> >, 第一个参数为队列中的数据类型,第二个参数为容器类型,第三个参数为比较方法,常用的有greater,less等,也可以根据实际情况自己去写.当参数为greater<int>时,则可以保证每次插入后队头的数都是最小的数.
Huffman树的构造就不赘述了,使用优先队列每次选择队头的两个数并将其出列,相加后将结果放入队列中,直到队列为空为止
//这题考查哈弗曼编码,但其实没必要建树得出编码,只需要统计哈弗曼编码后的总码长即可
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class mycomparison
{
public:
bool operator() (const int& lhs, const int&rhs) const
{
return (lhs > rhs);//使得从小到大排序,队列头为最小元素,优选权队列默认队列头最大
}
};
int main(){
char s[500];
int count[200] = {0};//count[i]记录ASCII码为i的字符的个数
int i, sum, len;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, mycomparison> pq;
while(cin>>s){
if(!strcmp(s,"END")){
break;
}
len = strlen(s);
for(i = 0; i < len; i++){
count[s[i]]++;
}
sum = 0;
for(i = 0;i < 200; i++){
if(count[i]){
pq.push(count[i]);
count[i] = 0;
}
}
while(pq.size() > 1){
int a = pq.top(); pq.pop();
int b = pq.top(); pq.pop();
sum += a + b;//其实就是把越小的频率反复多加几次,越大的频率少加几次
pq.push(a + b);
}
if(!sum){
sum = len;//此时pq中只有一个元素
}
while(!pq.empty()){
pq.pop();
}
printf("%d %d %.1f\n",8*len,sum,double(double(8*len)/sum));//注意精度设置
}
return 0;
}
标签:style blog http io os 使用 ar for 数据
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/notlate/p/3973180.html