标签:训练 流程 set sizeof dir 驱动 str .com 拷贝
该实验要求实现对虚拟设备(一段内存)的打开、关闭、读写的操作,并要通过编写测试程序来测试虚拟设备及其驱动运行是否正常。
源代码:
驱动程序的源代码 test_drv.c :
/* test_drv.c */
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#define TEST_DEVICE_NAME "test_dev"
#define BUFF_SZ 1024
/*全局变量*/
static struct cdev test_dev;
unsigned int major =0;
static char *data = NULL;
/*读函数*/
static ssize_t test_read(struct file *file, char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
int len;
if (count < 0 )
{
return -EINVAL;
}
len = strlen(data);
count = (len > count)?count:len;
if (copy_to_user(buf, data, count)) /* 将内核缓冲的数据拷贝到用户空间*/
{
return -EFAULT;
}
return count;
}
/*写函数*/
static ssize_t test_write(struct file *file, const char *buffer,size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
if(count < 0)
{
return -EINVAL;
}
memset(data, 0, BUFF_SZ);
count = (BUFF_SZ > count)?count:BUFF_SZ;
if (copy_from_user(data, buffer, count)) /* 将用户缓冲的数据复制到内核空间*/
{
return -EFAULT;
}
return count;
}
/*打开函数*/
static int test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("This is open operation\n");
/* 分配并初始化缓冲区*/
data = (char*)kmalloc(sizeof(char) * BUFF_SZ, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data)
{
return -ENOMEM;
}
memset(data, 0, BUFF_SZ);
return 0;
}
/*关闭函数*/
static int test_release(struct inode *inode,struct file *file)
{
printk("This is release operation\n");
if (data)
{
kfree(data); /* 释放缓冲区*/
data = NULL; /* 防止出现野指针 */
}
return 0;
}
/* 创建、初始化字符设备,并且注册到系统*/
static void test_setup_cdev(struct cdev *dev, int minor, struct file_operations *fops)
{
int err, devno = MKDEV(major, minor);
cdev_init(dev, fops);
dev->owner = THIS_MODULE;
dev->ops = fops;
err = cdev_add (dev, devno, 1);
if (err)
{
printk (KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding test %d", err, minor);
}
}
/* 虚拟设备的file_operations结构 */
static struct file_operations test_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = test_read,
.write = test_write,
.open = test_open,
.release = test_release,
};
/*模块注册入口*/
int init_module(void)
{
int result;
dev_t dev = MKDEV(major, 0);
if (major)
{/* 静态注册一个设备,设备号先前指定好,并设定设备名,用cat /proc/devices来查看 */
result = register_chrdev_region(dev, 1, TEST_DEVICE_NAME);
}
else
{
result = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 1, TEST_DEVICE_NAME);
}
if (result < 0)
{
printk(KERN_WARNING "Test device: unable to get major %d\n", major);
return result;
}
test_setup_cdev(&test_dev, 0, &test_fops);
printk("The major of the test device is %d\n", major);
return 0;
}
/*卸载模块*/
void cleanup_module(void)
{
cdev_del(&test_dev);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, 0), 1);
printk("Test device uninstalled\n");
}虚拟设备的驱动程序的 Makefile :
ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build /*内核代码编译路径*/
PWD := $(shell pwd)
modules:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
modules_install:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules_install
clean:
rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend .*.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions
.PHONY: modules modules_install clean
else
obj-m := test_drv.o /* 将生成的模块为test_drv.ko*/
endif加载和卸载模块:
通过下面两个脚本代码分别实现驱动模块的加载和卸载。
加载脚本 test_drv_load 如下所示:
#!/bin/sh
# 驱动模块名称
module="test_drv"
# 设备名称。在/proc/devices中出现
device="test_dev"
# 设备文件的属性
mode="664"
group="david"
# 删除已存在的设备节点
rm -f /dev/${device}
# 加载驱动模块
/sbin/insmod -f ./$module.ko $* || exit 1
# 查到创建设备的主设备号
major=`cat /proc/devices | awk "\\$2==\"$device\" {print \\$1}"`
# 创建设备文件节点
mknod /dev/${device} c $major 0
# 设置设备文件属性
chgrp $group /dev/${device}
chmod $mode /dev/${device}卸载脚本 test_drv_unload 如下所示:
#!/bin/sh
module="test_drv"
device="test_dev"
# 卸载驱动模块
/sbin/rmmod $module $* || exit 1
# 删除设备文件
rm -f /dev/${device}
exit 0编写测试代码:也就是用户空间的程序,该程序调用设备驱动来测试驱动的运行是否正常。测试代码如下所示:
test.c
/* test.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define TEST_DEVICE_FILENAME "/dev/test_dev" /* 设备文件名*/
#define BUFF_SZ 1024 /* 缓冲大小 */
int main()
{
int fd, nwrite, nread;
char buff[BUFF_SZ]; /*缓冲区*/
/* 打开设备文件 */
fd = open(TEST_DEVICE_FILENAME, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
do
{
printf("Input some words to kernel(enter ‘quit‘ to exit):");
memset(buff, 0, BUFF_SZ);
if (fgets(buff, BUFF_SZ, stdin) == NULL)
{
perror("fgets");
break;
}
buff[strlen(buff) - 1] = ‘\0‘;
if (write(fd, buff, strlen(buff)) < 0) /* 向设备写入数据 */
{
perror("write");
break;
}
if (read(fd, buff, BUFF_SZ) < 0) /* 从设备读取数据 */
{
perror("read");
break;
}
else
{
printf("The read string is from kernel:%s\n", buff);
}
} while(strncmp(buff, "quit", 4));
close(fd);
exit(0);
}首先在虚拟设备驱动源码目录下编译并加载驱动模块。
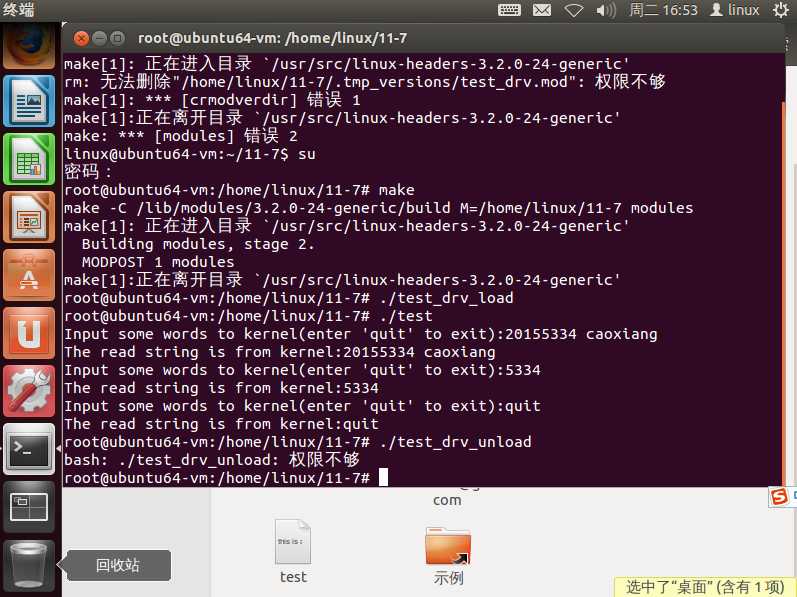
$ make clean;make
$ ./test_drv_load接下来,编译并运行测试程序
$ gcc –o test test.c
$ ./test测试程序运行效果如下:
Input some words to kernel(enter ‘quit‘ to exit):Hello, everybody!
The read string is from kernel:Hello, everybody! /* 从内核读取的数据 */
Input some words to kernel(enter ‘quit‘ to exit):This is a simple driver
The read string is from kernel: This is a simple driver
Input some words to kernel(enter ‘quit‘ to exit):quit
The read string is from kernel:quit最后,卸载驱动程序
$ ./test_drv_unload运行截图:
主要了解了嵌入式Linux设备驱动程序的开发。明白了设备驱动程序的概念及Linux对设备驱动的处理、字符设备驱动程序的编写、字符设备驱动程序的编写流程、重要的数据结构、设备驱动程序的主要组成以及proc文件系统。通过该实验,了解到编写驱动程序的完整流程。
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 75/75 | 1/1 | 5/0 | |
| 第二周 | 135/210 | 1/2 | 4/9 | |
| 第三周 | 234/444 | 1/3 | 6/15 | |
| 第四周 | 486/930 | 1/4 | 8/23 | |
| 第五周 | 753/1683 | 3/7 | 43/66 | |
| 第六周 | 503/2186 | 2/9 | 54/120 | |
| 第七周 | 823/3006 | 2/11 | 43/163 | |
| 第八周 | 756/3762 | 1/12 | 52/215 | |
| 第九周 | 1120/4882 | 3/15 | 63/278 | |
| 第十周 | 420/5302 | 0/15 | 32/310 | |
| 第十一周 | 531/5833 | 2/17 | 46/356 |
尝试一下记录「计划学习时间」和「实际学习时间」,到期末看看能不能改进自己的计划能力。这个工作学习中很重要,也很有用。
耗时估计的公式
:Y=X+X/N ,Y=X-X/N,训练次数多了,X、Y就接近了。
计划学习时间:XX小时
实际学习时间:XX小时
改进情况:
(有空多看看现代软件工程 课件
软件工程师能力自我评价表)
2017-2018-1 201553334 实验四 外设驱动程序设计
标签:训练 流程 set sizeof dir 驱动 str .com 拷贝
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bestixx/p/7922400.html