标签:put roo dsp sum 一个 log height png 背景
代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about this m-file fprintf(‘\n***********************************************************\n‘); fprintf(‘ <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 2.19 \n\n‘); banner(); %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ b = [1, 2, 0, 1]; a = [1, -0.5, 0.25]; n = [0:100]; h1 = impz(b, a, n); x = impseq(0, 0, 100); h2 = filter(b, a, x); figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 2.19 Impulse response‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,[1,1,1]) % 改变坐标外围背景颜色 subplot(2,1,1); stem(n, h1); title(‘impz function‘); xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘h1(n)‘) ; grid on subplot(2,1,2); stem(n, h2); title(‘filter function‘); xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘h2(n)‘); grid on; %% --------------------------------------------- %% stability %% --------------------------------------------- fprintf(‘\n1st impz : sum(abs(h)) = %f \n‘, sum(abs(h1))); fprintf(‘\n2nd filter: sum(abs(h)) = %f \n‘, sum(abs(h2))); figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 2.19 Zero-Pole‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,[1,1,1]) % 改变坐标外围背景颜色 pzmap(b, a); z = roots(a); magz = abs(z) %% -------------------------------------- %% another input %% -------------------------------------- n2 = [0:200]; x2 = (5 + 3*cos(0.2*pi*n2) + 4*sin(0.6*pi*n2)) .* stepseq(0, 0, 200); y2 = filter(b, a, x2); figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 2.19 Another input‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,[1,1,1]) % 改变坐标外围背景颜色 subplot(2,1,1); stem(n2, x2); title(‘input‘); xlabel(‘n2‘); ylabel(‘x2(n)‘) ; grid on subplot(2,1,2); stem(n2, y2); title(‘Output‘); xlabel(‘n2‘); ylabel(‘y2(n)‘); grid on;
运行结果:
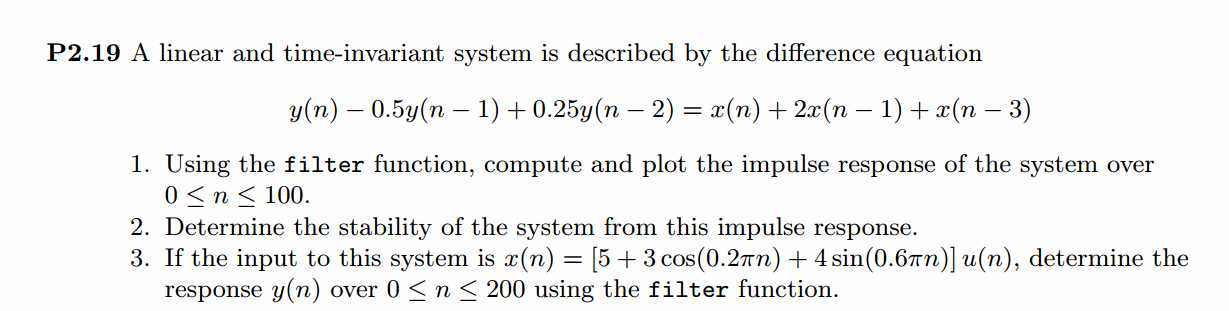
上图是分别用impz和filter函数得到的脉冲响应序列。
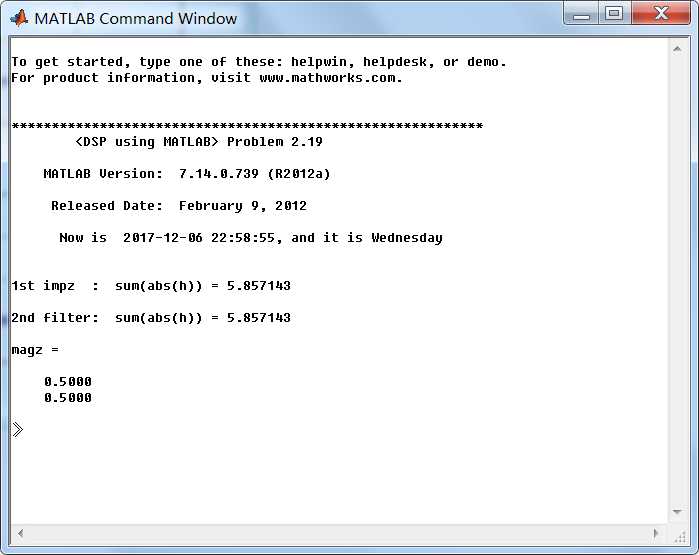
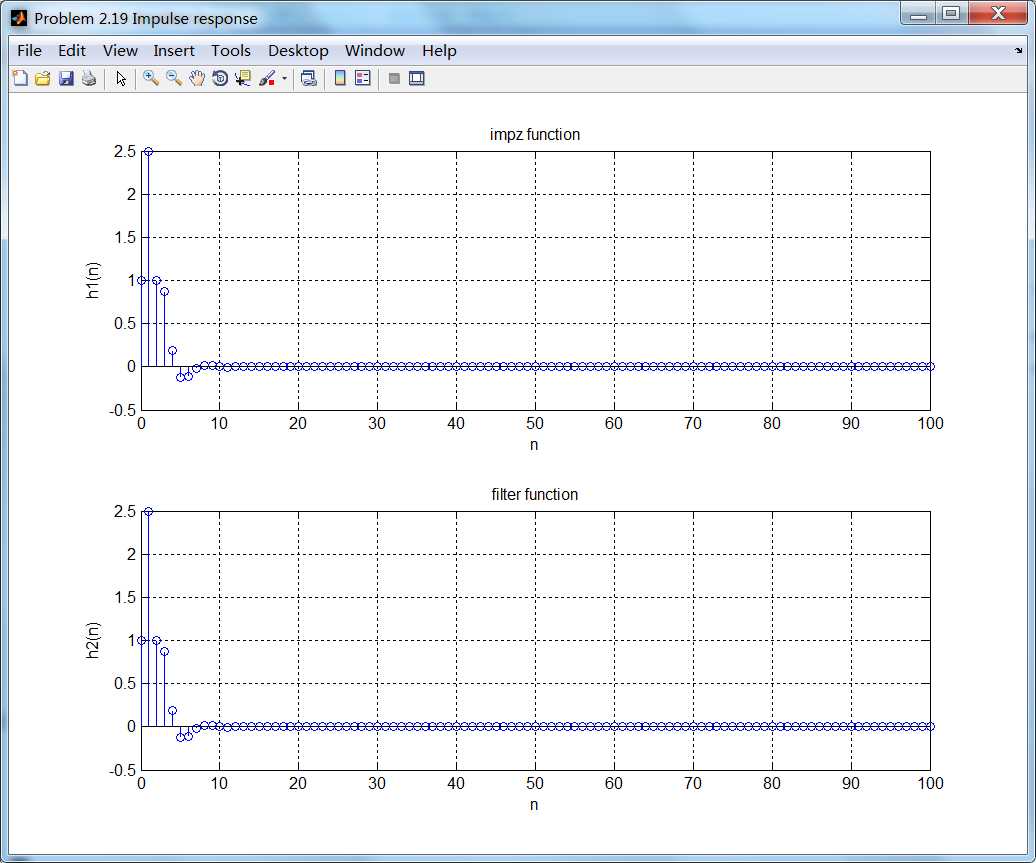
系统的脉冲响应序列是绝对可和的,另外系统的极点都位于单位圆内部(见下图),所以系统是稳定的。
给系统一个新的输入,计算新的输出,如下图:
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 2.19
标签:put roo dsp sum 一个 log height png 背景
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ky027wh-sx/p/8016420.html