说明:本文为读《从Paxos到Zookeeper 分布式一致性原理与实践》读书笔记
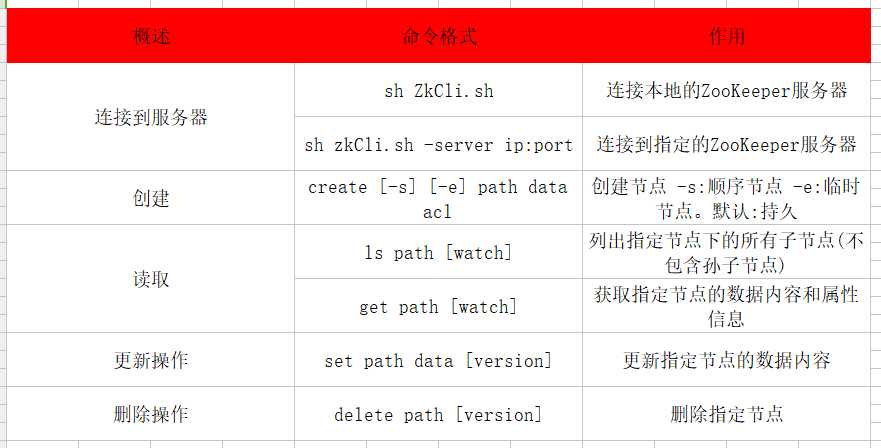
shell操作
Java客户端
原始API
pom文件:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.4.10</version>
</dependency>Java代码:
public class ZkClientUtil {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ZkDemo.class);
private static ZooKeeper zk;
// /zfpt 必须提前创建好
private static String zkPath = "master:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181/zfpt" ;
static CountDownLatch connectedSemaphore = new CountDownLatch( 1 );
static {
try {
zk = new ZooKeeper(zkPath, 1000 , new Watcher() {
// 监控所有被触发的事件
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
logger.info("已经触发了 {} 事件! ", event.getType());
connectedSemaphore.countDown();
}
});
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("系统异常");
}
}
public static ZooKeeper getZKConnection() {
try {
if (zk == null) {
connectedSemaphore.await();
}
return zk ;
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.printf("ZK初始化失败");
}
return null ;
}
}
/**
* 相应操作
*/
public class ZkDemoTest {
/**
* 同步创建 zk节点
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void create() throws Exception {
String response = getZKConnection().create("/aa3","test".getBytes(), ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
System.out.println(response) ;
}
/**
* 异步回调创建 zk节点
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void createASync() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1) ;
//StringCallback 异步回调 ctx:用于传递给回调方法的一个参数。通常是放一个上下文(Context)信息
getZKConnection().create("/aa2", "test".getBytes(), ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL, (rc, path, ctx, name) -> {
System.out.println("rc:" + rc + "&path:" + path + "&ctx:" + ctx + "&name:" + name );
countDownLatch.countDown();
},"1212121");
countDownLatch.await();
}
/**
* 同步删除
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void delete() throws Exception {
// version 表示此次删除针对于的版本号。 传-1 表示不忽略版本号
getZKConnection().delete("/aa1",-1);
}
/**
* 异步删除
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void deleteASync() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1) ;
getZKConnection().delete("/aa1",-1, (rc, path, ctx) -> {
System.out.println("rc:" + rc +"&path:" + path + "&ctx:" + ctx);
countDownLatch.countDown();
},"删除操作");
countDownLatch.await();
}
/**
* 同步获取数据,包括子节点列表的获取和当前节点数据的获取
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void getChildren() throws Exception {
Stat stat = new Stat() ;
// path:指定数据节点的节点路径, 即API调用的目的是获取该节点的子节点列表
// Watcher : 注册的Watcher。一旦在本次获取子节点之后,子节点列表发生变更的话,就会向该Watcher发送通知。Watcher仅会被触发一次。
// state: 获取指定数据节点(也就是path参数对应的节点)的状态信息(无节点名和数据内容),传入旧的state将会被来自服务端响应的新state对象替换。
List<String> list = ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().getChildren("/", event -> {
System.out.println("我是监听事件,监听子节点变化");
} ,stat);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(stat);
}
/**
* 异步获取子节点
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void getChildrenASync() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1) ;
ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().getChildren("/",event -> {
System.out.println("我是监听事件,监听子节点变化");
} , (rc, path, ctx, children) -> {
//异步回调
System.out.println("children:" + children);
countDownLatch.countDown();
},"context");
countDownLatch.await();
}
/**
* 同步获取数据
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void getDataTest() throws Exception {
Stat stat = new Stat() ;
byte[] bytes = ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().getData("/aa1",event -> {
System.out.println("我是监听事件,监听数据状态发生变化");
},stat);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
@Test
public void getDataASync() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1) ;
ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().getData("/aa1",event -> {
System.out.println("我是监听事件,监听数据状态发生变化");
}, (rc, path, ctx, data, stat) -> {
System.out.println("获取到的内容是:"+new String(data));
countDownLatch.countDown();
},"121");
countDownLatch.await();
}
/**
* 同步更新数据
*/
@Test
public void setData() throws Exception{
byte[] oldValue = ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().getData("/aa1",false,null);
System.out.println("更新前值是:" + new String(oldValue));
Stat stat = ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().setData("/aa1","helloWorld".getBytes(),-1);
byte[] newValue = ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().getData("/aa1",false,null);
System.out.println("更新后值是:" + new String(newValue));
}
/**
* 异步更新数据
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void setDataASync() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1) ;
ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().setData("/aa1","helloChina".getBytes(),-1, (rc, path, ctx, name) -> {
System.out.println("更新成功");
countDownLatch.countDown();
},"1111");
countDownLatch.await();
byte[] newValue = ZkClientUtil.getZKConnection().getData("/aa1",false,null);
System.out.println("更新前值是:" + new String(newValue));
}
}使用ZkClient客户端
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.4.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.101tec/zkclient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.101tec</groupId>
<artifactId>zkclient</artifactId>
<version>0.10</version>
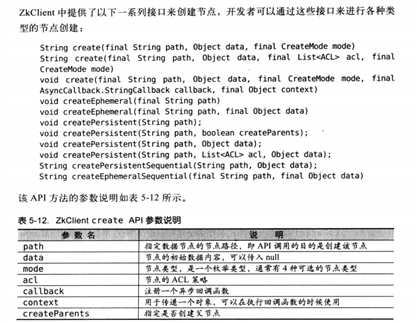
</dependency>创建节点:
public class ZKClientTest {
private static final String zkPath = "master:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181/zfpt";
private static ZkClient zkClient = null;
@Before
public void init() {
zkClient = new ZkClient(zkPath,10000,10000);
}
@Test
public void create() {
// 创建节点
String result = zkClient.create("/aa3","test", CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);
System.out.println(result);
// 递归创建
zkClient.createPersistent("/trade/open",true);
// 注意不要写成这种,API的问题,这种无法递归创建
// zkClient.createPersistent("/trade/open",true);
}
}相比原始API,ZkClient创建Znode的特性:
- 支持同步创建。
- 更丰富更简单的序列化方式,原始的只能传递byte[]数组。
- 更简便的API,
createPersistent和createEphemeral等。 - 支持递归创建。
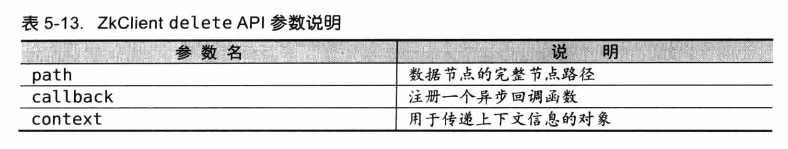
删除接口:

@Test
public void delete() {
// 递归删除
Boolean results = zkClient.deleteRecursive("/trade");
System.out.println("删除结果:" + results);
}特性:
- 递归删除。原始ZooKeeper只支持删除叶子节点。ZkClient支持层级遍历递归删除。
读取子节点:
/**
* 获取子节点
*/
@Test
public void getChildren() {
List<String> childrenList = zkClient.getChildren("/trade");
System.out.println(childrenList);
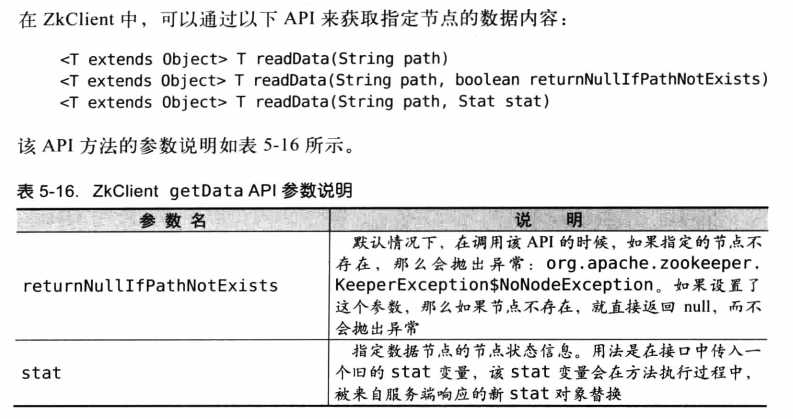
}获取节点数据:
@Test
public void readData() {
String data = zkClient.readData("/trade");
System.out.println(data);
}更新数据:
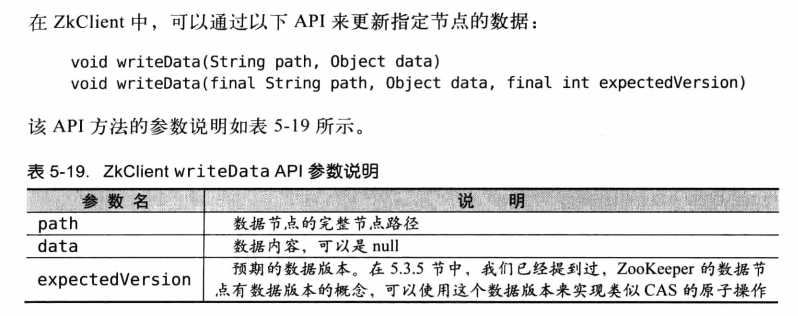
@Test
public void setData() {
String oldValue = zkClient.readData("/trade");
System.out.println("获取前:" + oldValue);
zkClient.writeData("/trade","I am trade");
String newValue = zkClient.readData("/trade");
System.out.println("更新后:" + newValue);
}监听器:
//监听子节点变化
zkClient.subscribeChildChanges("/trade",(parentPath,currenChilds)->{
System.out.println("子节点发生变化");
});
zkClient.subscribeDataChanges("/trade",new IZkDataListener() {
@Override
public void handleDataChange(String dataPath, Object data) throws Exception {
System.out.println("dataPath:" + dataPath +"发生变化,最新数据是:" + data);
}
@Override
public void handleDataDeleted(String dataPath) throws Exception {
System.out.printf("dataPath被删除");
}
});原生Watcher只支持一次注册,但是ZkClient的listener已经支持重复注册。
Curator
Curator在ZooKeeper原生API的基础上进行了包装,提供了一套易用性和可读性更强的Fluent风格的客户端API框架。
除此之外,Curator中还提供了ZooKeeper各种应用场景(Recipe 如共享锁服务、Master选举机制和分布式计数器等)的抽象封装。
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.curator/curator-recipes -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
</dependency>创建节点:
@Before
public void before() {
// 非Fluent风格
// CuratorFramework curatorFramework = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient(zkPath, new RetryOneTime(100));
// System.out.println(curatorFramework.getState());
// curatorFramework.start();
// System.out.println(curatorFramework.getState());
// Fluent风格
curatorFramework = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
.connectString("master:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181")
.retryPolicy(new RetryOneTime(1000)) //重试策略
.namespace("zfpt") // 命名空间
.build();
curatorFramework.start();
}
@Test
public void create() throws Exception {
// 创建一个持久化节点,初始化内容为空
curatorFramework.create().forPath("/dus");
// 创建一个持久化节点,初始化内容不为空
curatorFramework.create().forPath("/dus1","test".getBytes());
// 创建一个临时节点 初始化内容为空
curatorFramework.create().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/dus2");
// 创建一个临时节点,并递归创建不存在的父节点
// ZooKeeper中规定所有非叶子节点必须为持久节点。因此下面创建出来只有dus2会是临时节点。
curatorFramework.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/dj/dus2");
}删除节点:
//删除一个节点
client.delete().forPath(path);
// 删除一个节点,并递归删除其所有子节点
client.delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath(path)
// 删除一个节点,强制指定版本进行删除
client.delete().withVersion(version).forPath(path);
//删除一个节点,强制保证删除成功
client.delete().delete().guaranteed().forPath(path);guaranteed() 保证删除失败后,Curator会在后台持续进行删除操作。
读取数据:
// 读取一个节点的数据内容
client.getData().forPath(path);
// 读取一个节点的数据内容,同时获取到该节点的stat
client.getData().storingStatIn(stat).forPath(path);更新数据:
// 更新一个节点的数据内容
client.setData().forPath(path);
// 更新一个节点的数据内容,强制指定版本进行更新
client.setData().withVersion(version).forPath(path);异步接口:



也就是说如果没有传入自定义线程池,就由EventThread这个线程串行处理所有的事件通知,如果传入了,则由自定义线程池去处理。
@Test
public void BackgroundCallbackTest() throws Exception{
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
curatorFramework.getData().inBackground((client,event)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(event);
System.out.println(client);
}).forPath("/trade");
Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2,new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("curator-%d").build() );
curatorFramework.getData().inBackground((client,event)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(event);
System.out.println(client);
},executor).forPath("/trade");
countDownLatch.await();
}事件监听:
Curator引入了Cache来实现对ZooKeeper服务端事件的监听,Cache是Curator中对事件监听的包装,其对事件的监听其实可以近似看作是一个本地缓存视图和远程ZooKeeper视图的对比过程。同时Curator能够自动为开发人员处理反复注册监听,从而大大简化了原生API开发的繁琐过程。Cache分为两类监听类型:节点监听和子节点监听。
NodeCache:
NodeCache即可以用于监听指定ZooKeeper数据节点内容的变化,也能监听指定节点是否存在,如果原本节点不存在,那么Cache就会在节点被创建后出发NodeCacheListener。但是如果该数据节点被删除,那么Curator就无法再出发NodeCacheListener了。
@Test
public void NodeCacheTest() throws Exception{
// client : Curator 客户端实例 。 path: 监听节点的节点路径 。 dataIsCompressed:是否进行数据压缩
NodeCache nodeCache = new NodeCache(curatorFramework,"/trade",false);
// buildInitial:如果设置为true 则NodeCache在第一次启动的时候就会立刻从ZK上读取对应节点的数据内容 保存到Cache中。
nodeCache.start(false);
nodeCache.getListenable().addListener(()->{
System.out.println("Node data update , new data:" + new String(nodeCache.getCurrentData().getData()));
});
//******************** 监听一个不存在的节点 当节点被创建后,也会触发监听器 **********************//
// client : Curator 客户端实例 。 path: 监听节点的节点路径 。 dataIsCompressed:是否进行数据压缩
NodeCache nodeCache2 = new NodeCache(curatorFramework,"/trade1",false);
// buildInitial:如果设置为true 则NodeCache在第一次启动的时候就会立刻从ZK上读取对应节点的数据内容 保存到Cache中。
nodeCache2.start(false);
nodeCache2.getListenable().addListener(()->{
System.out.println("Node data update , new data:" + new String(nodeCache.getCurrentData().getData()));
});
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}PathChildrenCache:
用于监听指定ZooKeeper数据节点的子节点变化情况。当指定节点的子节点发生变化时,就会回调该方法。PathChildrenCacheEvent类中定义了所有的事件类型,主要包括新增子节点(CHILD_ADDED)、子节点数据变更(CHILD_UPDATED)和子节点删除(CHILD_REMOVED)三类。但是该数据节点的变化不会被此监听器监听到。无法监听孙子节点的变更。
@Test
public void PathChildrenCacheTest() throws Exception {
PathChildrenCache nodeCache = new PathChildrenCache(curatorFramework,"/trade",true);
// buildInitial:如果设置为true 则NodeCache在第一次启动的时候就会立刻从ZK上读取对应节点的数据内容 保存到Cache中。
nodeCache.start();
nodeCache.getListenable().addListener((client , event)->{
switch (event.getType()) {
case CHILD_ADDED :
System.out.println("新增子节点,数据内容是" + new String(event.getData().getData())); break;
case CHILD_UPDATED:
System.out.println("子节点被更新,数据内容是" + new String(event.getData().getData())); break;
case CHILD_REMOVED:
System.out.println("删除子节点,数据内容是" + new String(event.getData().getData())); break;
default: break;
}
});
curatorFramework.create().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/trade/PathChildrenCache","new".getBytes());
Thread.sleep(100L);
curatorFramework.setData().forPath("/trade/PathChildrenCache","update".getBytes());
Thread.sleep(100L);
curatorFramework.delete().withVersion(-1).forPath("/trade/PathChildrenCache");
}Master选举:
在分布式系统中,经常会碰到这样的场景:对于一个复杂的任务,仅需要从集群中选举出一台进行处理即可。诸如此类的分布式问题,我们统称为“Master选举”。借助于ZooKeeper,我们可以比较方便地实现Master选举的功能,其大体思路非常简单:
选择一个根节点,例如/master_select,多台机器同时向该节点创建一个子节点/master_select/lock,利用ZooKeeper的特性,最终只有一台机器能够创建成功,成功的那台机器就作为Master。
Curator也是基于这个思路,但是它将节点创建、事件监听和自动选举过程进行了封装,开发人员只需要调用简单的API即可实现Master选举。
@Test
public void leaderSelector() throws Exception {
AtomicInteger masterCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4,new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("master_selector-%d").build() );
for( int i = 0 ; i < 4; i++) {
executor.execute(()-> {
LeaderSelector leaderSelector = new LeaderSelector(curatorFramework, "/master_selector", new LeaderSelectorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void takeLeadership(CuratorFramework curatorFramework) throws Exception {
masterCount.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "成为Master, 当前Master数量:" + masterCount);
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "宕机,失去Master角色,剩下master数量:" + masterCount.decrementAndGet());
}
});
leaderSelector.autoRequeue();
leaderSelector.start();
});
}
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}分布式锁:
为了保证数据的一致性,临界资源加锁,保持有序访问。
/**
* 观察 Lock【n】 抢到锁 和 Lock【n】 释放锁 是不是成对出现。 如果不是,则说明有重复加锁的
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void InterProcessMutex() throws Exception {
InterProcessMutex lock = new InterProcessMutex(curatorFramework,"/trade/mylock") ;
for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) {
Thread currentThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 加锁
lock.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 抢到锁");
}catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 释放锁");
// 释放锁
lock.release();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
currentThread.setName("Lock【" + i + "】");
currentThread.start();
}
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}分布式计数器:
@Test
public void DistributedAtomicInteger() throws Exception {
DistributedAtomicInteger distributedAtomicInteger = new DistributedAtomicInteger(curatorFramework,"/trade/PathChildrenCache", new RetryNTimes(1000,3)) ;
System.out.println(distributedAtomicInteger.increment().postValue());
}分布式Barrier:
与CyClicBarrir同样的语义。
/**
* 没有定义成员数量。直接通过removeBarrier();释放屏障
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void barrier() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4,new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("barrier-%d").build() );
for( int i = 0 ; i < 4; i++) {
executor.execute(()-> {
CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
.connectString("master:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181")
.retryPolicy(new RetryOneTime(1000)) //重试策略
.namespace("zfpt") // 命名空间
.build();
client.start();
distributedBarrier = new DistributedBarrier(curatorFramework,"/trade/PathChildrenCache") ;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到达Barrier前");
try {
distributedBarrier.setBarrier();
distributedBarrier.waitOnBarrier();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "越过屏障");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
Thread.sleep(3000L);
distributedBarrier.removeBarrier();
}
/**
* 定义成员数量,到齐了就 越过屏障
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void barrier2() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4,new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("barrier-%d").build() );
for( int i = 0 ; i < 4; i++) {
executor.execute(()-> {
CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
.connectString("master:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181")
.retryPolicy(new RetryOneTime(1000)) //重试策略
.namespace("zfpt") // 命名空间
.build();
client.start();
DistributedDoubleBarrier distributedDoubleBarrier = new DistributedDoubleBarrier(client,"/trade/PathChildrenCache",4) ;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到达Barrier前");
distributedDoubleBarrier.enter();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "越过屏障");
Thread.sleep(1000L);
distributedDoubleBarrier.leave();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经离开");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}