题目描述
某一天,少年邂逅了同病相连的IA。见面后,IA一把牵起少年的手,决定和他一起逃离部落,离开这个无法容身的是非之地。
要逃离部落,少年和IA就需要先选择一条耗时最少的路线,从而避免被部落的大人们抓到。部落可以大致分为N个区域,少年和IA在区域1,部落的出口设在区域N。此外部落还有M条连接两个区域道路。道路是无向的,没有一条道路的两端连接相同的区域,也没有两条道路所连接的两个区域完全相同。对于其中前(M?1)条道路,其通过时间是确定的,但最后一条道路,由于地理因素,通过其的时间会不断变化。
现在,少年和IA得知了在K个不同的时段里,通过第M条道路的时间,请您分别计算出在这K 个时段中逃离部落的最少时间,以帮助他们确定行动的时刻。
思路
对于每一条不确定的路径(a,b),我们可以不经过它,可以从a进去,也可以从b进去
那么我们就可以用头尾跑两遍Kruskal就可以知道到这两个点的最短距离
然后判断出解即可
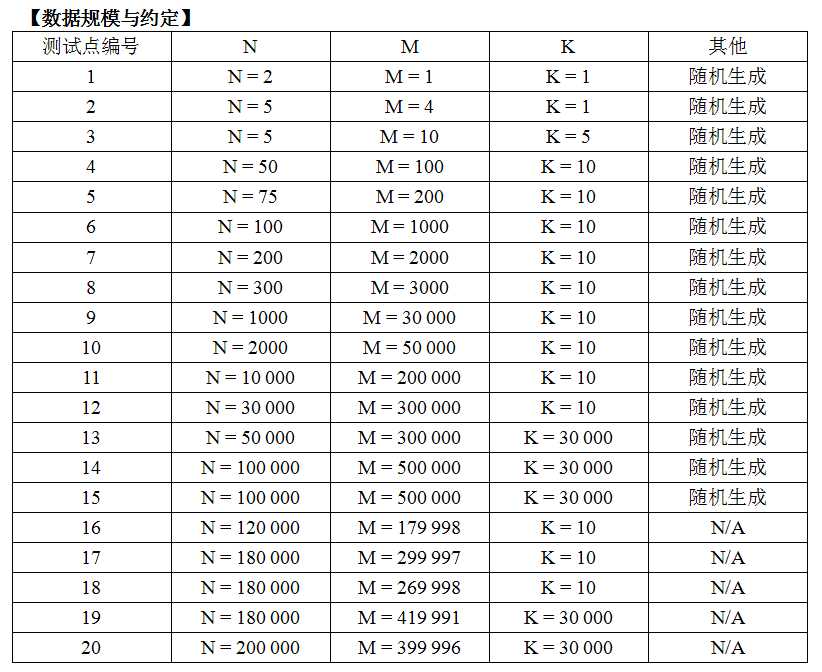
特意放出数据规模,我们可以看到有点的数据是构造出来卡spfa的,所以
Kruskal!!!!
#include <stdio.h> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <queue> using namespace std; #define N 200505 #define M 1000005 #define fill(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x)) #define LL long long #define min(x, y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y)) const LL INF = 1e+18; LL state[N], state1[N]; int ls[M], n, m, k, st, ed; bool exits[N]; struct edge { int to, w, next; }e[M]; int l = 0; struct cmp { int operator()(int a, int b) { return state[a] > state[b]; } }; struct cmp1 { int operator()(int a, int b) { return state1[a] > state1[b]; } }; int add(int x, int y, int w) { e[++l] = (edge){y, w, ls[x]}; ls[x] = l; } inline int read() { int x = 0, p = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘) {if (ch == ‘-‘) p = -1; ch = getchar();} while (ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘) {x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - ‘0‘; ch = getchar();} return x * p; } void write(LL x) { if (x < 10) { putchar(x + ‘0‘); return; } else { write(x / 10); write(x % 10); } } int spfa() { priority_queue<int, vector<int>, cmp > t; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) state[i] = INF; exits[1] = 1; t.push(1); state[1] = 0; while (!t.empty()) { int now = t.top(); t.pop(); for (int i = ls[now]; i; i = e[i].next) { if (state[e[i].to] > state[now] + e[i].w) { state[e[i].to] = state[now] + e[i].w; if (!exits[e[i].to]) { exits[e[i].to] = 1; t.push(e[i].to); } } } exits[now] = 0; } } int spfa1() { priority_queue<int, vector<int>, cmp1 > t; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) state1[i] = INF; exits[n] = 2; t.push(n); state1[n] = 0; while (!t.empty()) { int now = t.top(); t.pop(); for (int i = ls[now]; i; i = e[i].next) { if (state1[e[i].to] > state1[now] + e[i].w) { state1[e[i].to] = state1[now] + e[i].w; if (exits[e[i].to] != 2) { exits[e[i].to] = 2; t.push(e[i].to); } } } exits[now] = 0; } } int main() { freopen("monogatari.in", "r", stdin); freopen("monogatari.out", "w", stdout); n = read(); m = read(); k = read(); for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) { int x = read(), y = read(), w = read(); add(x, y, w); add(y, x, w); } st = read(); ed = read(); spfa(); spfa1(); for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) { int x = read(); LL mi = state[n]; mi = min(state[st] + state1[ed] + x, mi); mi = min(state[ed] + state1[st] + x, mi); if (mi < INF) { write(mi); putchar(‘\n‘); } else { printf("+Inf\n"); } } }
